The Weekly Practice Quiz for OSSSC RI, ARI, and Amin is an essential tool for aspirants preparing for the Odisha Sub-ordinate Staff Selection Commission exams. These quizzes help candidates regularly assess their knowledge and understanding of the syllabus, covering topics like general awareness, mathematics, reasoning, and English. By consistently participating in these practice sessions, candidates can identify their strengths and weaknesses, improve their time management skills, and become familiar with the exam pattern. Regular practice through these quizzes enhances confidence and competence, paving the way for better performance in the actual examination.
Weekly Practice Quiz For OSSSC RI,ARI, Amin: July-02 PDF Download
Weekly Practice Quiz For For OSSSC RI,ARI, Amin: July-02
- What is Muruja?
A. A form of pottery
B. A type of embroidery
C. A contemporary art form similar to Rangoli
D. A style of mural painting
Answer: C. A contemporary art form similar to Rangoli - What materials are used to create Muruja?
A. Clay and charcoal
B. Powders of different hues such as white, green, black, yellow, and red
C. Oil paints and canvas
D. Fabric and thread
Answer: B. Powders of different hues such as white, green, black, yellow, and red - Which town in Odisha is famous for its applique work?
A. Cuttack
B. Bhubaneswar
C. Pipili
D. Konark
Answer: C. Pipili - What is the origin of Pipili’s applique work?
A. Mughal influence
B. British colonization
C. Lord Jagannath culture during the 12th century
D. Portuguese traders
Answer: C. Lord Jagannath culture during the 12th century - What are some common forms created using applique craft?
A. Pottery and ceramics
B. Sculptures and statues
C. Birds, animals, flowers, and leaves
D. Textiles and garments
Answer: C. Birds, animals, flowers, and leaves - For what occasions are large applique canopies used in Odisha?
A. Birthdays
B. Funerals
C. Marriage celebrations
D. Religious processions
Answer: C. Marriage celebrations - What is the significance of tiny mirrors in Odisha’s applique craft?
A. They reflect sunlight
B. They represent spiritual enlightenment
C. They enhance the aesthetic appeal
D. They ward off evil spirits
Answer: C. They enhance the aesthetic appeal - Which traditional colors are commonly used in Odisha’s applique craft?
A. Blue, green, purple, and orange
B. Red, black, yellow, and white
C. Pink, brown, gray, and teal
D. Gold, silver, bronze, and copper
Answer: B. Red, black, yellow, and white - Where is sand art a popular form of expression in Odisha?
A. Bhubaneswar
B. Cuttack
C. Puri Beach
D. Konark Sun Temple
Answer: C. Puri Beach - What is the primary medium used in sand art?
A. Clay
B. Sand
C. Paint
D. Stone
Answer: B. Sand - What are some common items made from bamboo and cane in Odisha?
A) Earthen pots
B) Baskets, mats, and lamp shades
C) Metal sculptures
D) Glassware
Answer: B) Baskets, mats, and lamp shades - How is bamboo and cane prepared before crafting items?
A) Soaked in water
B) Boiled in oil
C) Cut, split longitudinally, and heated over a low flame
D) Frozen
Answer: C) Cut, split longitudinally, and heated over a low flame - What process enhances the durability and flexibility of coir fiber?
A) Boiling in vinegar
B) Treating with saline water (retting) for 8-10 months
C) Exposure to direct sunlight
D) Mixing with synthetic fibers
Answer: B) Treating with saline water (retting) for 8-10 months - What kind of craft involves creating figures of animals, birds, and eco-friendly toys using yellow-colored fiber?
A) Pottery
B) Wood carving
C) Coir craft
D) Glassblowing
Answer: C) Coir craft - Which grass is known as “Golden Grass” and is found in many parts of Odisha after the rainy season?
A) Sabai Grass
B) Jute
C) Kaincha
D) Wheatgrass
Answer: C) Kaincha - Where is the Sabai Grass extensively grown in Odisha?
A) Mayurbhanj district
B) Sundergarh district
C) Balasore district
D) Puri district
Answer: A) Mayurbhanj district - Which village in Balasore district of Odisha is known for practicing Sabai Grass weaving?
A) Kendrapara
B) Jajang
C) Baliapal
D) Gop
Answer: C) Baliapal - What are some products made from Sabai Grass?
A) Metal sculptures
B) Pottery
C) Baskets, trays, hats, and bags
D) Glassware
Answer: C) Baskets, trays, hats, and bags - Which district in Odisha is famous for Grass Weaving Craft using Golden Grass?
A) Mayurbhanj
B) Kendrapara
C) Jajpur
D) Sundergarh
Answer: A) Mayurbhanj - What is a characteristic feature of products made from Golden Grass and Sabai Grass?
A) They are non-biodegradable
B) They are highly toxic
C) They are eco-friendly and biodegradable
D) They are very expensive
Answer: C) They are eco-friendly and biodegradable - What is the traditional craft work of Odisha primarily practiced by Santhals, Oraons, and Marijas tribes?
a) Lac Craft
b) Metal Craft
c) Horn Craft
d) Lacquer Craft
Answer: c) Horn Craft - Which items are commonly made from cow and buffalo horns in Odisha’s traditional craft?
a) Toys and vessels
b) Jewelry and lamp stands
c) Wall hangings and coasters
d) Pottery and paintings
Answer: b) Jewelry and lamp stands - What is the locally known name for lac comb in Odisha’s Lac Craft?
a) Lacquer
b) Lac Siredi
c) Horns comb
d) Buffalo comb
Answer: b) Lac Siredi - Which district of Odisha is famous for Lac Craft?
a) Cuttack
b) Gajapati
c) Koraput
d) Nabarangpur
Answer: d) Nabarangpur - What material is melted and mixed with lac to create lacquered bamboo craft?
a) Wax
b) Clay
c) Metal
d) Lac
Answer: d) Lac - Which tribal community practices Dhokra-Lost Wax Metal Casting in Odisha?
a) Santhals
b) Situlia
c) Oraons
d) Marijas
Answer: b) Situlia - How old is the Dhokra-Lost Wax Metal Casting craft in Odisha?
a) 100 years
b) 500 years
c) 4,000 years
d) 10,000 years
Answer: c) 4,000 years - Which district is NOT mentioned as a center for Dhokra-Lost Wax Metal Casting in Odisha?
a) Nayagarh
b) Dhenkanal
c) Rayagada
d) Khordha
Answer: d) Khordha - Which ancient artifact is cited as one of the earliest known lost-wax artifacts?
a) Horn comb
b) Dancing girl of Mohenjodaro
c) Lac Siredi
d) Bamboo craft
Answer: b) Dancing girl of Mohenjodaro - Which craft combines horn and silver filigree work to create beautiful ornaments?
a) Horn Craft
b) Lac Craft
c) Metal Craft
d) Lacquer Craft
Answer: a) Horn Craft - Who was the founder of the Mahameghavahana dynasty?
a) Mahameghavahana
b) Kharavela
c) Sri Gupta
d) Visakhavarman
Answer: a) Mahameghavahana - What is another name for the Mahameghavahana dynasty?
a) Gupta dynasty
b) Chedi dynasty
c) Nala dynasty
d) Muranda dynasty
Answer: b) Chedi dynasty - Which ruler of the Chedi dynasty is known for his conquests and promotion of Jainism?
a) Mahameghavahana
b) Kharavela
c) Sri Gupta
d) Visakhavarman
Answer: b) Kharavela - Where is most of the information about Kharavela found?
a) Lingaraj Temple
b) Konark Sun Temple
c) Hathigumpha inscription
d) Jagannath Temple
Answer: c) Hathigumpha inscription - Which dynasty ruled in the Kalinga region during the 4th and 5th centuries?
a) Matharas
b) Nalas
c) Parvatadvarkas
d) Meghas
Answer: a) Matharas - Who was the founder of the Mathara dynasty?
a) Visakhavarman
b) Umavarman
c) Shaktivarman
d) Vardhamanpura
Answer: a) Visakhavarman - Which dynasty established a kingdom in the Trikalinga region?
a) Matharas
b) Nalas
c) Parvatadvarkas
d) Meghas
Answer: b) Nalas - What was the capital of the Nala dynasty?
a) Vardhamanpura
b) Parvatadvarka
c) Pushkari
d) Parvatadvarka
Answer: c) Pushkari - In which region did the Parvatadvarkas dynasty appear?
a) Ganjam
b) Koraput
c) Jajpur
d) Kalahandi
Answer: d) Kalahandi - Who was the founder of the Parvatadvarkas dynasty?
a) Nandaraja
b) Tustikara
c) Parvatadvarka
d) Maharaja Narendra
Answer: c) Parvatadvarka - Which dynasty ruled over South Kosala in the middle of the 6th century AD?
a) Matharas
b) Nalas
c) Meghas
d) Sarbhapuriyas
Answer: c) Meghas - Which dynasty established its kingdom over South Kosala around the 5th century AD?
a) Matharas
b) Nalas
c) Meghas
d) Sarbhapuriyas
Answer: d) Sarbhapuriyas - What is another name for the Somavamshi dynasty?
a) Keshari dynasty
b) Gajapati dynasty
c) Bhoi dynasty
d) Chola dynasty
Answer: a) Keshari dynasty - Who is credited with building a new temple at Puri and installing the image of Purushottama (Jagannatha) there?
a) Janmejaya I
b) Yayati I
c) Janmejaya II
d) Abhinava-Yayati
Answer: b) Yayati I - What was the capital of the Somavamshi dynasty after the conquest of the Bhauma-Kara kingdom?
a) Yayatinagara
b) Binika
c) Jajpur
d) Chaudwar
Answer: c) Jajpur - What marks the beginning of the Somavamshi style of temple architecture in Odisha?
a) Construction of Lingaraj Temple
b) Installation of the image of Purushottama at Puri
c) The Utkaliya era
d) Conquest of Dakshina Kosala
Answer: b) Installation of the image of Purushottama at Puri - Which king is described as “lord of Kosala” in the Chaudwar inscription?
a) Yayati I
b) Janmejaya I
c) Janmejaya II
d) Abhinava-Yayati
Answer: b) Janmejaya I - What is the modern-day name for the capital of the Somavamshi dynasty, Abhinava-Yayatinagara?
a) Binika
b) Jajpur
c) Puri
d) Cuttack
Answer: b) Jajpur - Which epoch marked the reign of Yayati I and implied the start of the era for the Odia calendar?
a) Kalinga epoch
b) Utkaliya era
c) Keshari dynasty era
d) Madala Panji era
Answer: b) Utkaliya era - Who established the Gajapati Dynasty in 1435?
a) Kapilendra Deva
b) Bhanudeva IV
c) Hamira
d) Purushottama Deva
Answer: a) Kapilendra Deva - In which year did Kapilendra Deva die?
a) 1450
b) 1467
c) 1484
d) 1541
Answer: b) 1467 - Who succeeded Kapilendra Deva to the throne of the Gajapati Dynasty after a civil war?
a) Hamira
b) Govinda Vidyadhara
c) Chakrapratap
d) Purushottama Deva
Answer: d) Purushottama Deva - What was the cause of the founding of the Bhoi Dynasty?
a) A civil war
b) A foreign invasion
c) A natural disaster
d) A peaceful transition of power
Answer: a) A bloody coup - Who succeeded Govinda Vidyadhara in the Bhoi Dynasty?
a) Raghubhanja Chhotray
b) Chakrapratap
c) Mukunda Deva
d) Hamvira
Answer: b) Chakrapratap - What title did Mukunda Deva take after declaring himself ruler of Odisha?
a) Maharaja
b) Rajguru
c) Minister
d) King
Answer: a) Maharaja - Which event led to the downfall of the Bhoi Dynasty?
a) Mukunda Deva’s rebellion
b) The death of Chakrapratap
c) Raghubhanja Chhotray’s rebellion
d) Govinda Vidyadhara’s coup
Answer: c) Raghubhanja Chhotray’s rebellion - Who was installed as the governor of Rajamundry and Kondavidu by Kapilendra Deva?
a) Bhanudeva IV
b) Hamira
c) Govinda Vidyadhara
d) Chakrapratap
Answer: b) Hamira - What is another name for the Gajapati Dynasty?
a) Bhoi Dynasty
b) Suryavamsi dynasty
c) Kapilendra Dynasty
d) Eastern Ganga dynasty
Answer: b) Suryavamsi dynasty - When did the Bhoi Dynasty come to an end?
a) 1484
b) 1457
c) 1541
d) 1557
Answer: d) 1557 - During which period did the Bhauma-Kara Dynasty exist?
a) c. 500 CE to c. 736 CE
b) c. 736 CE to c. 940 CE
c) c. 940 CE to c. 1100 CE
d) c. 1100 CE to c. 1300 CE
Answer: b) c. 736 CE to c. 940 CE - What is the purpose of establishing the Biju Patnaik Aviation Centre (BPAC) at the Birasal airstrip in Dhenkanal district?A) To create a commercial airport for international flightsB) To establish a tourism hub in the districtC) To provide aviation training and pilot educationD) To host annual air shows and exhibitionsAnswer: C) To provide aviation training and pilot education
- In which district of Odisha is the Biju Patnaik Aviation Centre (BPAC) planned to be established?A) BhubaneswarB) CuttackC) PuriD) DhenkanalAnswer: D) Dhenkanal
- Which institute collaborated with Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) to strengthen disaster preparedness?A) Indian Institute of Technology, DelhiB) National Institute of Technology, RourkelaC) Regional Integrated Multi-Hazard Early Warning System (RIMES), BangkokD) University of HyderabadAnswer: C) Regional Integrated Multi-Hazard Early Warning System (RIMES), Bangkok
- Bhadraka inscription gives a description of which dynasty of Odisha?
[A] Muranda
[B] Gupta
[C] Nanda
[D] ChediCorrect Answer: A [Muranda]
Notes: The Bhadrak inscription refers to the Muranda dynasty, believed to be a foreign tribe that entered India with the Kushanas. - Taranath referred Odisha as?
[A] Odiya
[B] Odivisa
[C] Orissya
[D] None of the aboveCorrect Answer: B [Odivisa]
Notes: The Tibetan historian Taranath referred to Odisha as Odivisa in his works. - The Chandra Kala Natika was written by?
[A] Viswanath Kaviraj
[B] Ananta Dasa
[C] Jayadeva
[D] AchyutanandaCorrect Answer: A [Viswanath Kaviraj]
Notes: The Chandra Kala Natika was authored by the renowned Odishan poet Viswanath Kaviraj and depicts the conquest of Gauda (Bengal) by the last Ganga king Bhanudeva IV. - Which of the following was a famous poet, also a contemporary to Rajaraja II?
[A] Dandin
[B] Utbi
[C] Jayadeva
[D] TulsidasaCorrect Answer: C [Jayadeva]
Notes: Jayadeva, renowned for his work Gita Govind, was a court poet of the Bengal ruler Laxmansena and lived during the time of Rajaraja II. - Who was the first ruler to issue coins with Odia inscriptions?
[A] Mahameghavahana Aira Kharavela
[B] Samudragupta
[C] Ashoka
[D] Pulakesin IICorrect Answer: A [Mahameghavahana Aira Kharavela]
Notes: Mahameghavahana Aira Kharavela, a ruler of Kalinga in the 2nd century BCE, was the first to issue coins with Odia inscriptions. - What is the purpose of the collaboration between OSDMA, RIMES, and Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham?
A) To establish research facilities in natural sciences
B) To strengthen disaster preparedness through impact-based forecasting and early warning dissemination
C) To create a platform for international trade
D) To launch new educational programs in the state
Answer: B) To strengthen disaster preparedness through impact-based forecasting and early warning dissemination - Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) falls under which ministry?
A) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
B) Ministry of Rural Development
C) Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
D) Ministry of Home Affairs
Answer: D) Ministry of Home Affairs - What is the full form of OSDMA?
A) Odisha State Development Management Association
B) Odisha State Disaster Management Authority
C) Odisha State Disease Monitoring Association
D) Odisha State Domestic Market Association
Answer: B) Odisha State Disaster Management Authority - In which Indian state was the ‘Ama Bank’ initiative launched to extend banking services to all unbanked panchayats?
A) Karnataka
B) Odisha
C) Maharashtra
D) Tamil Nadu
Answer: B) Odisha - What is the primary objective of the ‘Ama Bank’ initiative launched in Odisha?
A) To promote foreign investments in the state
B) To encourage the use of digital payments in urban areas
C) To provide banking services to all unbanked panchayats in Odisha
D) To establish new bank branches in every city
Answer: C) To provide banking services to all unbanked panchayats in Odisha - How many CSP Plus outlets (Customer Service Points) were launched under the ‘Ama Bank’ initiative in Odisha?
A) 1,500
B) 1,800
C) 2,000
D) 2,500
Answer: C) 2,000 - Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary is located in which Indian state?
A) West Bengal’
B) Jharkhand
C) Odisha
D) Chhattisgarh
Answer: C) Odisha - Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in which district of Odisha?
A) Cuttack
B) Puri
C) Balasore
D) Bhadrak
Answer: C) Balasore - Which type of forest is predominantly found in Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary?
A) Evergreen forest
B) Mixed deciduous forest dominated by Sal trees
C) Coniferous forest
D) Mangrove forest
Answer: B) Mixed deciduous forest dominated by Sal trees - The sustainability grants extended to 11 research centers of excellence (CoEs) in Odisha are part of which program?
A) Odisha Higher Education Initiative for Equity and Excellence (OHEIEE)
B) Odisha Higher Education Programme for Excellence and Equity (OHEPEE)
C) Odisha Advanced Education Programme (OAEP)D) Odisha Education and Research Support Initiative (OERSI)
Answer: B) Odisha Higher Education Programme for Excellence and Equity (OHEPEE) - How much total sustainability grant was awarded to the 11 CoEs for the academic sessions of 2023-24 and 2024-25 under the Mukhyamantri Research and Innovation Fellowship programme?
A) Rs 45 lakh
B) Rs 50 lakh
C) Rs 61.5 lakh
D) Rs 75 lakh
Answer: C) Rs 61.5 lakh - Which research center at Sambalpur University received the highest grant, and how much was the grant?
A) Research on ‘biotechnology and bioinformatics’ received Rs 25 lakh
B) Research on ‘agricultural sciences’ received Rs 30 lakh
C) Research on ‘natural products and therapeutics’ received Rs 35 lakh
D) Research on ‘environmental sciences’ received Rs 40 lakh
Answer: C) Research on ‘natural products and therapeutics’ received Rs 35 lakh - Which phase of the Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) is mentioned in the context of the CoEs in Odisha?
A) Phase One
B) Phase Two
C) Phase Three
D) Phase Four
Answer: B) Phase Two - What types of support are being provided to the CoEs under the Mukhyamantri Research and Innovation Fellowship programme?
A) Research grants to fellows and maintenance of equipment
B) Research internships, publication of critical texts
C) Engagement of research associates
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above - Until what year has the Odisha government extended its command area development and water management scheme?
A) 2025
B) 2027
C) 2029
D) 2031
Answer: C) 2029 - What is the total outlay of the Odisha government’s command area development and water management scheme?
A) Rs 500 crore
B) Rs 763.47 crore
C) Rs 1,000 crore
D) Rs 900 crore
Answer: B) Rs 763.47 crore - How many kilometers of field channel network are planned for construction in the 80,000 hectares of command area?
A) 1,200 km
B) 3,600 km
C) 2,400 km
D) 3,000 km
Answer: C) 2,400 km - What is one of the main goals of the scheme related to water management?
A) To promote tourism in the state
B) To enhance production and productivity through on-farm water management and crop diversification
C) To establish new urban areas in the state
D) To promote industrialization
Answer: B) To enhance production and productivity through on-farm water management and crop diversification - How much funding does the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) contribute to the scheme?
A) Approximately Rs 108 crore
B) Approximately Rs 200 crore
C) Approximately Rs 150 crore
D) Approximately Rs 50 crore
Answer: A) Approximately Rs 108 crore - NTPC’s Kaniha power plant is located in which district of Odisha?
A) Khordha
B) Angul
C) Balasore
D) Puri
Answer: B) Angul - What is the installed capacity of NTPC’s Kaniha power plant?
A) 1500MW
B) 3000MW
C) 4500MW
D) 5000MW
Answer: B) 3000MW - The source of water for NTPC’s Kaniha power plant is from which reservoir?
A) Hirakud Reservoir
B) Chilika Lake
C) Samal Barrage Reservoir
D) Puri Lake
Answer: C) Samal Barrage Reservoir - The fire at NTPC’s Kaniha power plant originated from which part of the plant?
A) Cooling tower
B) Turbine generator
C) Coal transporting conveyor belt
D) Control room
Answer: C) Coal transporting conveyor belt - Which of the following states does the Talcher power plant supply power to?
A) Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Telangana, Bihar, and West Bengal
B) Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Gujarat, and Maharashtra
C) Odisha, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh
D) Odisha, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur, and Meghalaya
Answer: A) Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Telangana, Bihar, and West Bengal - Which rivers in southern Odisha are currently facing a lack of water according to data from the Central Water Commission?
A) Baitarani, Subarnarekha, Brahmani, and BudhabalangaB) Rushikulya, Bahuda, Vamsadhara, and NagavaliC) Mahanadi, Brahmani, Baitarani, and SubarnarekhaD) Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari, and KrishnaAnswer: B) Rushikulya, Bahuda, Vamsadhara, and Nagavali - What is one of the main causes attributed to the lack of water in the rivers of southern Odisha?
A) Excessive rainfall
B) Strong wind patterns
C) Reduced monsoon rainfall and changes in rainfall patterns
D) Rising sea levels
Answer: C) Reduced monsoon rainfall and changes in rainfall patterns - What did Nitin Bassi from the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) suggest to reduce the water deficit in the Mahanadi river basin?
A) Building more dams and reservoirs
B) Implementing water diversion projects
C) Adopting micro-irrigation systems and changing cropping patterns
D) Increasing the use of groundwater
Answer: C) Adopting micro-irrigation systems and changing cropping patterns - Which town in Odisha has a very poor Air Quality Index (AQI) value of 304, as reported by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)?
A) Bhubaneswar
B) Barbil
C) Cuttack
D) Rourkela
Answer: B) Barbil - What were the AQI values recorded in Keonjhar and Nayagarh in Odisha on the same day when Barbil had a very poor AQI?A) 100 and 150 respectively
B) 200 and 250 respectively
C) 228 and 275 respectively
D) 300 and 350 respectively
Answer: C) 228 and 275 respectively - What was the total population of Odisha according to the Census 2011?
A) 3.8 crore
B) 4.2 crore
C) 5.0 crore
D) 2.5 crore
Answer: B) 4.2 crore - What percentage of India’s population does Odisha’s population form according to the Census 2011?
A) 4.47%
B) 2.67%
C) 3.47%
D) 3.97%
Answer: C) 3.47% - What was the male population in Odisha according to the Census 2011?
A) 22,500,136
B) 21,112,136
C) 21,312,136
D) 21,212,136
Answer: D) 21,212,136 - What was the female population in Odisha according to the Census 2011?
A) 20,562,082
B) 20,962,082
C) 20,662,082
D) 20,762,082
Answer: D) 20,762,082 - What is the population density of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 270 per square km
B) 290 per square km
C) 230 per square km
D) 310 per square km
Answer: A) 270 per square km - What is the total area of Odisha?
A) 155,107 square km
B) 160,707 square km
C) 145,707 square km
D) 155,707 square km
Answer: D) 155,707 square km - Which district in Odisha has the highest literacy rate according to the Census 2011?
A) Cuttack
B) Puri
C) Khordha
D) Ganjam
Answer: C) Khordha - What is the literacy rate of Khordha District according to the Census 2011?
A) 84.88%
B) 86.88%
C) 82.88%
D) 88.88%
Answer: B) 86.88% - What is the national average population density of India per square km?
A) 392 per square km
B) 372 per square km
C) 382 per square km
D) 362 per square km
Answer: C) 382 per square km - What is the average sex ratio of Odisha as per the Census 2011?
A) 943
B) 979
C) 965
D) 982
Answer: B) 979 - How does Odisha’s average sex ratio compare to the national average according to Census 2011?
A) Below the national average
B) Equal to the national average
C) Above the national average
D) Fluctuates with the national average
Answer: C) Above the national average - What is the child sex ratio (age less than 6 years) in Odisha as per the Census 2011?
A) 918
B) 941
C) 960
D) 930
Answer: B) 941 - What percentage of Odisha’s population lived in urban regions according to the Census 2011?
A) 20.50%
B) 16.69%
C) 19.40%
D) 14.30%
Answer: B) 16.69% - What percentage of Odisha’s population lived in rural areas according to the Census 2011?
A) 78.20%
B) 73.50%
C) 83.31%
D) 80.45%
Answer: C) 83.31% - What was the total urban population of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 8,103,656
B) 7,203,656
C) 7,003,656
D) 7,503,656
Answer: C) 7,003,656 - What was the male population in urban regions of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 3,625,933
B) 3,745,933
C) 3,525,933
D) 3,605,933
Answer: A) 3,625,933 - What was the female population in urban regions of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 3,377,723
B) 3,177,723
C) 3,477,723
D) 3,577,723
Answer: A) 3,377,723 - What was the average sex ratio in urban regions of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 932 females per 1000 males
B) 949 females per 1000 males
C) 922 females per 1000 males
D) 913 females per 1000 males
Answer: A) 932 females per 1000 males - What was the average sex ratio in rural areas of Odisha as per Census 2011?
A) 978 females per 1000 males
B) 990 females per 1000 males
C) 978 females per 1000 males
D) 989 females per 1000 males
Answer: D) 989 females per 1000 males - As per the census conducted in 2011, what is the rank of Odisha in terms of the total population in India?
A) 7th
B) 10th
C) 9th
D) 11th
Answer: D) 11th - Which of the following districts of Odisha has the highest population as per the census 2011?
A) Khordha
B) Puri
C) Ganjam
D) Cuttack
Answer: C) Ganjam - Which of the following districts of Odisha has the lowest population as per the census 2011?
A) Malkangiri
B) Nayagarh
C) Jharsuguda
D) Nabarangpur
Answer: A) Malkangiri - As per the census 2011, what is the population growth rate of Odisha?
A) 13.97%
B) 15.45%
C) 16.69%
D) 12.21%
Answer: A) 13.97% - Which district is considered the most developed and richest district in Odisha?
A) Cuttack
B) Puri
C) Khordha
D) Ganjam
Answer: C) Khordha - Which district in Odisha is considered the second most developed after Khordha?
A) Puri
B) Cuttack
C) Bhadrak
D) Ganjam
Answer: B) Cuttack - Which district in Odisha has the lowest literacy rate in rural areas, as per the information provided?
A) Malkangiri
B) Gajapati
C) Nabarangpur
D) Kandhamal
Answer: C) Nabarangpur - Which district in Odisha has the lowest urban literacy rate?
A) Boudh
B) Malkangiri
C) Rayagada
D) Jajpur
Answer: B) Malkangiri - Which district is the largest in Odisha by area?
A) Mayurbhanj
B) Ganjam
C) Cuttack
D) Khordha
Answer: A) Mayurbhanj - Which is the most populous district in Odisha as per the 2011 census?
A) Khordha
B) Cuttack
C) Ganjam
D) Puri
Answer: C) Ganjam - Which is the smallest district in Odisha by area?
A) Nayagarh
B) Jagatsinghpur
C) Malkangiri
D) Boudh
Answer: B) Jagatsinghpur - Which of the following kings is known for the construction of the Sun Temple at Konark?
[A] Prithviraj Chauhan
[B] Ashoka
[C] Narasimha Deva I
[D] Raja Raja Chola
Correct Answer: [C] Narasimha Deva I
Notes: The Sun Temple at Konark was constructed in the 13th century by King Narasimha Deva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty. - Which famous Buddhist site in Odisha is known for its rock-cut caves?
[A] Dhauli
[B] Ratnagiri
[C] Lalitgiri
[D] Udayagiri and Khandagiri
Correct Answer: [D] Udayagiri and Khandagiri
Notes: The Udayagiri and Khandagiri caves are rock-cut caves associated with Jain and Buddhist traditions, located near Bhubaneswar. - Who was the last independent Hindu king of Odisha?
[A] Raja Raja Chola
[B] Prithviraj Chauhan
[C] Mukunda Deva
[D] Prataprudra Deva
Correct Answer: [C] Mukunda Deva
Notes: Mukunda Deva was the last independent Hindu king of Odisha who ruled until the state fell under the control of the Mughals in the late 16th century. - What is the significance of Dhauli in the history of Odisha?
[A] Site of a famous battle during the time of Ashoka
[B] The birthplace of a famous poet
[C] Location of a major temple
[D] An important port
Correct Answer: [A] Site of a famous battle during the time of Ashoka
Notes: Dhauli is known for the famous Kalinga War fought by Emperor Ashoka. It marked his transformation and the adoption of Buddhism. - The capital city of ancient Kalinga was:
[A] Bhubaneswar
[B] Cuttack
[C] Jeypore
[D] Puri
Correct Answer: [B] Cuttack
Notes: Cuttack was the capital city of ancient Kalinga and continued to serve as the capital of Odisha until the colonial period. - The Puri Rath Yatra is dedicated to which Hindu deity?
[A] Shiva
[B] Vishnu
[C] Jagannath
[D] Brahma
Correct Answer: [C] Jagannath
Notes: The Puri Rath Yatra is dedicated to Lord Jagannath, a form of Vishnu, and is one of the most significant religious festivals in India. - Quli Qutub Shah, who invaded Odisha, was the general of which ruler?
[A] Mahmud Shah
[B] Tajuddin Firoz
[C] Ahmad Shah
[D] Humayun Shah
Correct Answer: [A] Mahmud Shah
Notes: Quli Qutub Shah was the general of Sultan Mahmud Shah of the Bahamani kingdom. He invaded Odisha in 1522 AD but was defeated by Prataprudradeva. - Who was one of the Odia leaders that took part in the Great Revolt of 1857?
[A] Surendra Sai
[B] Chakhi Khuntia
[C] Ramakrushna Samanta Singhar
[D] All of the above
Correct Answer: [D] All of the above
Notes: Surendra Sai, Chakhi Khuntia, and Ramakrushna Samanta Singhar were some of the great patriots of Odisha who participated in the Great Revolt of 1857. - Which Odia leader led a strong armed resistance against British rule during the 19th century?
[A] Baji Rout
[B] Jagannath Das
[C] Surendra Sai
[D] Raja Anangabhima Deva
Correct Answer: [C] Surendra Sai
Notes: Surendra Sai was one of the most significant leaders in Odisha who led an armed resistance against British rule during the 19th century. - What was the role of Chakhi Khuntia in the Great Revolt of 1857?
[A] He was a poet
[B] He provided spiritual guidance to the rebels
[C] He acted as a guide and adviser to Rani Lakshmibai
[D] He led the revolt in Odisha
Correct Answer: [C] He acted as a guide and adviser to Rani Lakshmibai
Notes: Chakhi Khuntia was an important figure in the Great Revolt of 1857, known for his role as a guide and adviser to Rani Lakshmibai. - Laxman Nayak led the Quit India movement of Odisha in which district?
[A] Keonjhar
[B] Cuttack
[C] Koraput
[D] Ganjam
Correct Answer: [C] Koraput
Notes: Laxman Nayak led the Quit India movement in Koraput district by organizing an army of 200 men. He was later arrested and executed on 29th March 1943. - Who was the first woman to be elected to the Odisha Legislative Assembly?
[A] Sarala Devi
[B] Rama Devi
[C] Sarojini Devi
[D] Malati Devi
Correct Answer: [A] Sarala Devi
Notes: Sarala Devi was the first woman to be elected to the Odisha Legislative Assembly on 1st April 1936. She also became the first female speaker of the Odisha Legislative Assembly. - Who was felicitated as “Bhumi Putra” by the Indonesian government?
[A] Biju Pattanaik
[B] Gopabandhu Das
[C] Gopabandhu Choudhury
[D] Naveen Pattanaik
Correct Answer: [A] Biju Pattanaik
Notes: Biju Pattanaik, former chief minister of Odisha, was honored with the title of “Bhumi Putra” by the Indonesian government. - Which event inspired Laxman Nayak to lead the Quit India movement in Koraput?
[A] The Non-Cooperation Movement
[B] The Salt March
[C] The call of Mahatma Gandhi
[D] The Rowlatt Satyagraha
Correct Answer: [C] The call of Mahatma Gandhi
Notes: Laxman Nayak was inspired by the call of Mahatma Gandhi to lead the Quit India movement in Koraput. - What role did Sarala Devi play in Odisha’s political history?
[A] First woman to lead a political party
[B] First female Chief Minister of Odisha
[C] First female governor of Odisha
[D] First female speaker of the Odisha Legislative Assembly
Correct Answer: [D] First female speaker of the Odisha Legislative Assembly
Notes: Sarala Devi was the first female speaker of the Odisha Legislative Assembly and played a significant role in Odisha’s political history. - Badaghagara waterfall is located in which district of Odisha?
[A] Mayurbhanj
[B] Koraput
[C] Keonjhar
[D] Balangir
Correct Answer: [C] Keonjhar
Notes: Badaghagara waterfall lies in Keonjhar district of Odisha and is located at a distance of 3 km downstream of Sanaghagara waterfall. - Which river is the source of the Badaghagara waterfall?
[A] Budhabalanga River
[B] Machha Kandana
[C] Rushikulya River
[D] Subarnarekha River
Correct Answer: [B] Machha Kandana
Notes: Badaghagara waterfall is a source of a small river known as Machha Kandana. - What is the height of the Barehipani waterfall in Mayurbhanj district, Odisha?
[A] 200 m
[B] 300 m
[C] 400 m
[D] 500 m
Correct Answer: [C] 400 m
Notes: Barehipani waterfall is the highest waterfall in Odisha with a total height of 400 m. It is also the second-highest waterfall in India. - Where is Duduma waterfall located?
[A] Mayurbhanj district
[B] Keonjhar district
[C] On the border of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh
[D] In the core area of Simlipal National Park
Correct Answer: [C] On the border of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh
Notes: Duduma waterfall is located on the boundary of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha states, situated at a distance of 92 km from Koraput district (Odisha). - Which other waterfall is near Barehipani waterfall in Simlipal National Park?
[A] Duduma waterfall
[B] Badaghagara waterfall
[C] Joranda waterfall
[D] Chilika waterfall
Correct Answer: [C] Joranda waterfall
Notes: Joranda waterfall (150 m) is near Barehipani waterfall in Simlipal National Park and is in the core area of the park. - What date is Utkal Divas, also known as Odisha Foundation Day, celebrated annually?
[A] March 15th
[B] April 1st
[C] May 1st
[D] January 26th
Correct Answer: [B] April 1st
Notes: Utkal Divas, also known as Odisha Foundation Day, is celebrated annually on April 1st to commemorate the formation of Odisha as a state. - Under British rule, Odisha was part of which presidency?
[A] Madras Presidency
[B] Bombay Presidency
[C] Bengal Presidency
[D] Punjab Presidency
Correct Answer: [C] Bengal Presidency
Notes: Under British rule, Odisha was part of the Bengal Presidency, which also included present-day Bihar and West Bengal. - Who was the ancient king of Odisha known for establishing the state’s reputation as a center of art, architecture, and sculpture?
[A] Ashoka
[B] Prithviraj Chauhan
[C] Chandragupta Maurya
[D] Kharavela
Correct Answer: [D] Kharavela
Notes: King Kharavela’s reign is credited with establishing Odisha’s reputation as a center of art, architecture, and sculpture. - The Choudwar fortress site is located in which district of Odisha?
[A] Puri
[B] Bhubaneswar
[C] Cuttack
[D] Balasore
Correct Answer: [C] Cuttack
Notes: The Choudwar fortress site is located in Cuttack district on the left bank of river Birupa. - Which act is being violated by the Industrial Infrastructure Development Corporation (IDCO) due to its actions at the Choudwar fortress?
[A] Indian Forest Act, 1927
[B] Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
[C] Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, 1958
[D] Environmental Protection Act, 1986
Correct Answer: [C] Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, 1958
Notes: IDCO has been accused of violating the AMASR Act, 1958, by excavating and leveling the protected area of the Choudwar fortress. - Choudwar fortress is one of the five forts (Panchakatakas) built by which ruler?
[A] Ashoka
[B] Harsha Vardhana
[C] Chodagangadeva of the Ganga dynasty
[D] Raja Raja Chola
Correct Answer: [C] Chodagangadeva of the Ganga dynasty
Notes: The Choudwar fortress is one of the five forts (Panchakatakas) built by Chodagangadeva of the Ganga dynasty. - Which temple remains at the Choudwar fortress site?
[A] Lingaraja Temple
[B] Jagannath Temple
[C] Kedaresvara Temple
[D] Konark Sun Temple
Correct Answer: [C] Kedaresvara Temple
Notes: The only remains at the Choudwar fortress site are those of the Kedaresvara temple. - By which financial year are eight Indian states expected to have economies exceeding one trillion dollars each?
[A] 2030-31
[B] 2046-47
[C] 2040-41
[D] 2050-51
Correct Answer: [B] 2046-47
Notes: By the 2046-47 financial year, eight states are expected to have economies exceeding one trillion dollars each. - Which state is expected to achieve a one trillion dollar economy by 2046 according to the report?
[A] Karnataka
[B] Odisha
[C] Uttar Pradesh
[D] Andhra Pradesh
Correct Answer: [D] Andhra Pradesh
Notes: Andhra Pradesh is expected to achieve a one trillion dollar economy by 2046. - What was the estimated size of Odisha’s economy in 2023-24?
[A] USD 75.5 billion
[B] USD 103.2 billion
[C] USD 93.7 billion
[D] USD 80.4 billion
Correct Answer: [C] USD 93.7 billion
Notes: Odisha’s economy was estimated to be USD 93.7 billion in 2023-24, ranking 13th among sub-national economies. - Which important Ganga dynasty ruler ruled from 1077 to 1147 AD?
A) Rajaraja II
B) Anangabhimadeva III
C) Narasimhadeva I
D) Anantavarma Chodagangadeva
Answer: D) Anantavarma Chodagangadeva - What was the capital of the Ganga dynasty?
A) Ujjain
B) Kalinganagara
C) Pataliputra
D) Tosali
Answer: B) Kalinganagara - Who was the last Ganga king?
A) Anangabhimadeva III
B) Bhanudeva IV
C) Narasimhadeva I
D) Rajaraja II
Answer: B) Bhanudeva IV - Which temple was built by Narasimhadeva I?
A) Jagannath temple
B) Lingaraj temple
C) Mukteswara temple
D) Sun temple at Konark
Answer: D) Sun temple at Konark - During which ruler’s reign did poet Jayadeva flourish?
A) Anantavarma Chodagangadeva
B) Rajaraja II
C) Narasimhadeva I
D) Anangabhimadeva III
Answer: B) Rajaraja II - Who built the Jagannath temple in Puri?
A) Rajaraja II
B) Anangabhimadeva III
C) Anantavarman Vajrahasta V
D) Narasimhadeva I
Answer: B) Anangabhimadeva III - Which style of temple architecture flourished during the Ganga period?A) Dravidian style
B) Nagara style
C) Vesara style
D) Pallava style
Answer: B) Nagara style - Which temple in Bhubaneswar is an example of the Nagara style?
A) Lingaraj temple
B) Meenakshi temple
C) Brihadeeswarar temple
D) Somanath temple
Answer: A) Lingaraj temple - The Ganga dynasty provided patronage to which religious tradition primarily?
A) Buddhism
B) Jainism
C) Shaivism
D) Vaishnavism
Answer: D) Vaishnavism - Which famous literary work is attributed to Jayadeva?
A) Mahabharata
B) Meghaduta
C) Ramayana
D) Gita Govinda
Answer: D) Gita Govinda - What were the notable architectural features of temples built during the Ganga dynasty?
A) Minarets and domes
B) Shikharas, Amlaka, Mandap
C) Pagodas and stupas
D) Frescoes and arches
Answer: B) Shikharas, Amlaka, Mandap - What is another name for the Ganga dynasty?
A) Western Gangas
B) Eastern Gangas
C) Southern Gangas
D) Northern Gangas
Answer: B) Eastern Gangas - Which notable rulers were part of the Ganga dynasty?
A) Skandagupta and Kumaragupta I
B) Chandragupta II and Vikramaditya
C) Chodagangadeva, Rajaraja II, Anangabhimadeva III
D) Devapala and Bhaskaravarman
Answer: C) Chodagangadeva, Rajaraja II, Anangabhimadeva III - Which region did Anantavarma Chodagangadeva rule over during his reign?
A) From the Ganga to the Godavari
B) From the Yamuna to the Cauvery
C) From the Indus to the Brahmaputra
D) From the Narmada to the Krishna
Answer: A) From the Ganga to the Godavari - What were the main reasons for the golden era under the Ganga dynasty?
A) Military conquests and territorial expansion
B) Cultural and religious patronage, architectural achievements
C) Efficient administration and strong trade networks
D) Strong navy and maritime dominance
Answer: B) Cultural and religious patronage, architectural achievements - What were the provinces under the Ganga dynasty known as?A) Districts
B) Talukas
C) Visayas
D) Subdivisions
Answer: C) Visayas - Which of the following officials assisted the Ganga kings?
A) Mantri and Purohita
B) Yuvaraja and Sandhivigrahika
C) Senapati and Dauvarika
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above - What political divisions were provinces divided into during the Ganga dynasty?A) Districts
B) Panchali and Bhoga
C) Villages
D) Cities and towns
Answer: B) Panchali and Bhoga - Which of the following taxes was collected during the Ganga dynasty rule?
A) Bheta
B) Voda
C) Paridarsana
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above - Who founded the Gajapati dynasty?A) Anangabhimadeva III
B) Kapilendra Deva
C) Prataparudra Deva
D) Purushottam Deva
Answer: B) Kapilendra Deva - Which language’s literature saw a renaissance during the Gajapati period?
A) Hindi
B) Bengali
C) Odia
D) Sanskrit
Answer: C) Odia - Who was the most powerful Hindu king during the Gajapati dynasty?
A) Prataparudra Deva
B) Purushottam Deva
C) Kapilendra Deva
D) Kakharua Deva
Answer: C) Kapilendra Deva - Which Odia poet wrote Mahabharata in Odia during the Gajapati period?
A) Kalidasa
B) Sarala Dasa
C) Jayadeva
D) Banabhatta
Answer: B) Sarala Dasa - Who was the last ruler of the Gajapati dynasty?
A) Purushottam Deva
B) Kapilendra Deva
C) Prataparudra Deva
D) Kakharua Deva
Answer: D) Kakharua Deva - Who was the minister that killed the last ruler of the Gajapati dynasty?A) Krishnadevaraya
B) Sri Chaitanya
C) Govinda Vidyadhara
D) Sarala Dasa
Answer: C) Govinda Vidyadhara - Which Vaishnav saint came to Odisha during the reign of Prataparudra Deva?
A) Kabir
B) Tulsidas
C) Sri Chaitanya
D) Surdas
Answer: C) Sri Chaitanya - Which fort did Krishnadevaraya attack and capture in 1512 AD?
A) Simhachalam
B) Udayagiri fort
C) Lingaraj temple
D) Jagannath temple
Answer: B) Udayagiri fort - Who did Krishnadevaraya marry after concluding peace with Prataparudra Deva?
A) Anangabhimadeva’s daughter
B) Kapilendra Deva’s sister
C) Prataparudra Deva’s daughter, Jagamohini
D) None of the above
Answer: C) Prataparudra Deva’s daughter, Jagamohini - What was the result of the Peace Treaty between Krishnadevaraya and Prataparudra Deva?
A) Vijayanagara empire expanded into Odisha
B) Prataparudra Deva married Krishnadevaraya’s sister
C) River Krishna was the line of demarcation between the two empires
D) Odisha gained control over parts of the Vijayanagara empire
Answer: C) River Krishna was the line of demarcation between the two empires - What was the dynasty of the Gajapati rulers of Odisha known as?
A) Gupta dynasty
B) Maurya dynasty
C) Suryavamsi lineage
D) Eastern Gangas
Answer: C) Suryavamsi lineage - What was the time period of the Gajapati dynasty’s rule in Odisha?
A) 1200-1300 AD
B) 1434-1541 AD
C) 1000-1100 AD
D) 1600-1700 AD
Answer: B) 1434-1541 AD - Where are the painted rock shelters from the prehistoric era primarily located?
a) Western part of Karnataka
b) Western part of Odisha
c) Northern part of Tamil Nadu
d) Southern part of Rajasthan
Answer: b) Western part of Odisha - What is the predominant theme depicted in these prehistoric rock paintings?
a) Religious rituals
b) Modern city life
c) Hunting, dancing, fighting, and domestic activities
d) Agricultural practices
Answer: c) Hunting, dancing, fighting, and domestic activities - What colors were used in these paintings, extracted from various sources?
a) Blue, green, and yellow
b) Red, white, and brown
c) Black, purple, and orange
d) Pink, turquoise, and gold
Answer: b) Red, white, and brown - Which script do the characters in these rock paintings resemble a mix of?
a) Indus Valley Civilization script
b) Egyptian hieroglyphs
c) Mohenjodaro and Brahmi scripts
d) Greek alphabet
Answer: c) Mohenjodaro and Brahmi scripts - Where can examples of these prehistoric paintings be found, depicting a procession scene of a king riding an elephant among other motifs?
a) Lakshmi temple in Odisha
b) Jagannath temple in Odisha
c) Ajanta caves in Maharashtra
d) Ellora caves in Maharashtra
Answer: b) Jagannath temple in Odisha - What is the primary subject matter of Saura paintings?
A) Tribal deities
B) Agricultural activities
C) Animals and nature
D) Mythological figures
Answer: A) Tribal deities - Which of the following tribal communities is associated with Kondh paintings?
A) Saura
B) Juang
C) Kondh
D) Paudi Bhuyan
Answer: C) Kondh - What are Kondh wall paintings known as?
A) Idital
B) Tikangkuda
C) Manji Gunda
D) Jhanjira
Answer: C) Manji Gunda - Which community’s paintings primarily depict the Samlai deity and agricultural activities?
A) Saura
B) Kondh
C) Paudi Bhuyan
D) Juang
Answer: C) Paudi Bhuyan - What themes are commonly depicted in Juang paintings?
A) Tribal deities
B) Agricultural activities
C) Birds, animals, and flowers
D) Mythological figures
Answer: C) Birds, animals, and flowers - What is the primary theme of Pattachitra paintings of Odisha?
A) Buddhist mythology
B) Hindu mythology
C) Islamic folklore
D) Tribal legends
Answer: B) Hindu mythology - Which village in Odisha is renowned for being the original hub of Pattachitra painters?
A) Bhubaneswar
B) Konark
C) Raghurajpur
D) Sonepur
Answer: C) Raghurajpur - When is the origin of Pattachitra art traced back to?
A) 1st century AD
B) 5th century BC
C) 10th century AD
D) 15th century AD
Answer: B) 5th century BC - Which mythical creature is depicted in the Navagunjara theme of Pattachitra?
A) Dragon
B) Griffin
C) Chimera
D) Nine different creatures
Answer: D) Nine different creatures - In which regions of Odisha did Pattachitra painting flourish?
A) Konark and Bhubaneswar
B) Puri and Chikiti
C) Paralakhemundi and Sonepur
D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above - What are Ganjapa playing cards in relation to Pattachitra?
A) Square shaped painted cards
B) Circular shaped painted cards
C) Rectangular shaped painted cards
D) Triangular shaped painted cards
Answer: B) Circular shaped painted cards - Who primarily prepares the canvas and applies colors in Pattachitra painting?
A) Men
B) Children
C) Women
D) Artisans
Answer: C) Women - What is the primary material used to prepare the canvas for Pattachitra paintings?
A) Paper
B) Cloth
C) Wood
D) Canvas
Answer: B) Cloth - How do artists create preliminary drawings in Pattachitra painting?
A) Pencil sketches
B) Charcoal sketches
C) Brush strokes
D) Stone etching
Answer: C) Brush strokes - Which festival is associated with the creation of Pattachitra paintings depicting Pith flowers and figures of charming women?
A) Diwali
B) Holi
C) Durga Puja
D) Jhulana
Answer: D) Jhulana - What is the traditional name for the type of pattachitra painting described in the passage?
a) Tala Pattachitra
b) Madhubani
c) Warli
d) Kalamkari
Answer: a) Tala Pattachitra - How are the images in Tala Pattachitra drawn on palm leaf?
a) Painted with watercolors
b) Carved into the palm leaf
c) Traced using black or white ink to fill grooves
d) Embroidered onto the palm leaf
Answer: c) Traced using black or white ink to fill grooves - What unique feature distinguishes Tala Pattachitra paintings from other forms of pattachitra?
a) They are painted on cloth
b) They are drawn on tree bark
c) They have superimposing layers with some areas left open to show a second image
d) They are drawn on canvas
Answer: c) They have superimposing layers with some areas left open to show a second image - Where are some examples of palm leaf manuscripts preserved?
a) Kolkata
b) Delhi
c) Bhubaneswar
d) Mumbai
Answer: c) Bhubaneswar - What material is used to create rows of equal-sized panels for Tala Pattachitra paintings?
a) Canvas
b) Paper
c) Palm leaf
d) Silk
Answer: c) Palm leaf - What is the name of the folk art form described in the passage?
A) Pattachitra
B) Jhoti or Chita
C) Warli
D) Madhubani
Answer: B) Jhoti or Chita - In which month do women folk in Odisha typically engage in decorating mud walls and floors with murals?
A) January
B) Margasira
C) May
D) September
Answer: B) Margasira - What is the primary purpose of creating Jhoti or Chita paintings?
A) Religious worship
B) Harvest celebrations
C) Cultural festivals
D) Historical documentation
Answer: A) Religious worship - Which of the following motifs are commonly used in Jhoti or Chita paintings?
A) Mountains and rivers
B) Cars and airplanes
C) Lotus, flowers, and elephants
D) Computers and smartphones
Answer: C) Lotus, flowers, and elephants - Besides mud walls and floors, where else are Jhoti paintings sometimes printed?
A) Canvas
B) Wood
C) Sarees
D) Metal plates
Answers: C) Sarees - Which of the following is the largest river in Odisha?
A. Brahmani
B. Subarnarekha
C. Mahanadi
D. Vansadhara
Answer: C. Mahanadi - Chilika Lake, one of the world’s largest brackish water lagoons, is located on which coast of Odisha?
A. West Coast
B. South Coast
C. East Coast
D. North Coast
Answer: C. East Coast - What percentage of the state of Odisha is covered by a green cover?
A. 10%
B. 20%
C. 33%
D. 50%
Answer: C. 33% - Which craton is not found in Odisha?
A. North Odisha Craton
B. Western Odisha Craton
C. Eastern Odisha Craton
D. None of the above
Answer: C. Eastern Odisha Craton - Which of the following rivers does NOT flow through Odisha?
A. Baitarani
B. Vansadhara
C. Subarnarekha
D. Godavari
Answer: D. Godavari - The coasts of Odisha are predominantly made up of which type of sediments?
A. Igneous rocks
B. Deltaic sediments
C. Metamorphic rocks
D. None of the above
Answer: B. Deltaic sediments - Which one of these is a lake in Odisha?
A. Sambhar
B. Kanjia
C. Vembanad
D. Dal
Answer: B. Kanjia - In terms of geological age, what period do the sediments found in Odisha’s cratons belong to?
A. Jurassic
B. Paleozoic
C. Quaternary
D. Cretaceous
Answer: D. Cretaceous - Which of these physiographic divisions is not a part of Odisha?
A. Coastal plains
B. Central plateaus
C. Central hilly regions
D. Western desert
Answer: D. Western desert - What is the catchment area percentage of the Mahanadi river in Odisha?
A. 10%
B. 20%
C. 30%
D. 42%
Answer: D. 42% - What body of water bounds the fertile coastal plains of Odisha to the east?
A. Arabian Sea
B. Indian Ocean
C. Bay of Bengal
D. None of the above
Answer: C. Bay of Bengal - Which part of Odisha consists of rolling uplands?
A. Eastern and southern
B. Western and northwestern
C. Northern and eastern
D. Central and southern
Answer: B. Western and northwestern - The western and northern portions of Odisha are part of which plateau?
A. Malwa Plateau
B. Deccan Plateau
C. Chota Nagpur Plateau
D. Vindhya Plateau
Answer: C. Chota Nagpur Plateau - What percentage of Odisha is covered by forests?
A. 25%
B. 30%
C. 31.41%
D. 35%
Answer: C. 31.41% - Which national park in Odisha is known for its population of tigers, elephants, and other wildlife?
A. Nandankanan
B. Simlipal National Park
C. Bhitarkanika National Park
D. Satkosia National Park
Answer: B. Simlipal National Park - What type of wildlife is protected by the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary?
A. Tigers
B. Estuarine crocodiles
C. Elephants
D. Rhinoceroses
Answer: B. Estuarine crocodiles - Which coastal lake in Odisha is the largest in India?
A. Wular Lake
B. Vembanad Lake
C. Pulicat Lake
D. Chilka Lake
Answer: D. Chilka Lake - How many migratory and resident species of birds does the Chilka Lake Bird Sanctuary harbor?
A. Over 50 species
B. Over 100 species
C. Over 150 species
D. Over 200 species
Answer: C. Over 150 species - The valleys of which rivers empty into the Bay of Bengal?
A. Godavari and Krishna
B. Narmada and Tapi
C. Mahanadi, Brahmani, and Baitarani
D. Ganges and Brahmaputra
Answer: C. Mahanadi, Brahmani, and Baitarani - Which of the following is not a major physiographic feature of Odisha?A. Fertile coastal plains
B. Central hilly regions
C. Desert region
D. Mountainous highlands and plateau regions
Answer: C. Desert region - Which sanctuary in Odisha has been protecting estuarine crocodiles since 1975?
A. Satkosia
B. Balukhand-Konark
C. Bhitarkanika
D. Kuldiha
Answer: C. Bhitarkanika - What type of lake is Chilka Lake?A. Freshwater lake
B. Brackish water lake
C. Glacial lake
D. Volcanic crater lake
Answer: B. Brackish water lake - Which wildlife sanctuary is known for its protection of olive ridley sea turtles?
A. Satkosia
B. Bhitarkanika
C. Simlipal
D. Gahirmatha
Answer: D. Gahirmatha - Which region of Odisha is known for having the largest expanse of lush green forests with waterfalls?
A. Gajapati district
B. Balasore district
C. Cuttack district
D. Mayurbhanj district
Answer: D. Mayurbhanj district - Which of the following rivers does not have a major floodplain in Odisha?
A. Subarnarekha
B. Brahmani
C. Mahanadi
D. Godavari
Answer: D. Godavari - What is the height of Deomali, the highest mountain peak in Odisha?
A. 1400 m
B. 1550 m
C. 1672 m
D. 1800 m
Answer: C. 1672 m - In which district of Odisha is Deomali located?
A. Ganjam
B. Puri
C. Koraput
D. Khordha
Answer: C. Koraput - Deomali is part of which mountain subsystem in Odisha?
A. Gandhamardhan Hill
B. Chandragiri-Pottangi
C. Mahendragiri Hills
D. Nilgiri Hills
Answer: B. Chandragiri-Pottangi - Deomali is one of the tallest peaks of which mountain range?
A. Himalayas
B. Aravalli
C. Eastern Ghats
D. Western Ghats
Answer: C. Eastern Ghats - Which of the following is true about Deomali?
A. It is a volcanic peak.
B. It is the highest mountain peak in Odisha.
C. It is the second highest peak in India.
D. It is located in the coastal plains of Odisha.
Answer: B. It is the highest mountain peak in Odisha. - The central mountainous and highlands region of Odisha is known for its:
A. Coastal plains
B. Rich mineral deposits
C. Desert terrain
D. Dense urban areas
Answer: B. Rich mineral deposits - The history of Odisha begins in which era, based on the discovery of Acheulian tools?
A. Bronze Age
B. Iron Age
C. Lower Paleolithic era
D. Upper Paleolithic era
Answer: C. Lower Paleolithic era - which ancient texts can the early history of Odisha be traced back to?A. Vedas and Upanishads
B. Mahabharata and some Puranas
C. Ramayana and Manusmriti
D. Arthashastra and Kalidasa’s works
Answer: B. Mahabharata and some Puranas - Which East Indian region was Odisha known to due to maritime trade relations?
A. China
B. East Indies
C. Persia
D. Arabian Peninsula
Answer: B. East Indies - In which year did the armies of the Sultanate of Bengal conquer the region?
A. 1450 CE
B. 1505 CE
C. 1568 CE
D. 1650 CE
Answer: C. 1568 CE - Who led the armies of the Sultanate of Bengal during the conquest of the region?
A. Aurangzeb
B. Kalapahad
C. Sher Shah Suri
D. Shah Jahan
Answer: B. Kalapahad - By which year had Odisha completely passed to the Mughal Empire?A. 1593
B. 1650
C. 1700
D. 1751
Answer: A. 1593 - Which empire took control of Odisha after the Marathas?
A. Mughal Empire
B. Maurya Empire
C. British Empire
D. Gupta Empire
Answer: C. British Empire - In which year was the province of Odisha formed on the basis of populations of Odia-speaking people?A. 1920
B. 1936
C. 1947
D. 1956
Answer: B. 1936 - Which famous general led the conquest of Odisha under the Sultanate of Bengal?
A. Malik Kafur
B. Kalapahad
C. Babur
D. Tipu Sultan
Answer: B. Kalapahad - During which era did literature and poetry flourish in Odisha under the Marathas’ control?
A. 15th century
B. 16th century
C. 17th century
D. 18th century
Answer: D. 18th century - Which ancient kingdom did prince Kalinga found, according to some scriptures?
A. Utkala
B. Kalinga
C. Vanga
D. Pundra
Answer: B. Kalinga - What is the literal meaning of the name “Mahakantara” found in some Gupta-era inscriptions?
A. Great River
B. Great Plain
C. Great Forest
D. Great Mountain
Answer: C. Great Forest - Which ancient region might be associated with the modern-day Kalahandi and Jeypore region?
A. Tosali
B. Mahakantara
C. Utkala
D. Kongoda
Answer: B. Mahakantara - Which ethnic group might “Udra” (or Udra-desha) have originally referred to?
A. Vaisya
B. Brahmin
C. Sudra
D. Udra
Answer: D. Udra - Which name was used in Buddhist texts and might have referred to Odisha?
A. Mahakantara
B. Kongoda
C. Oddiyana
D. Kalinga
Answer: C. Oddiyana - Which ancient region is associated with the name “Kamala Mandala” in a 13th-century inscription?
A. Ganjam
B. Jajpur
C. Kalahandi
D. Koraput
Answer: C. Kalahandi - Which region is also known as Dakshina Kosala and may include parts of modern-day Chhattisgarh and Western Odisha?
A. Chedi
B. Utkala
C. Kongoda
D. South Kosala
Answer: D. South Kosala - What does “Trikalinga” refer to according to copper plate inscriptions found in Sonepur?
A. A region in the northern part of Odisha
B. A subdivision of Kalinga
C. Three different Kalinga states (Kalinga, South Kosala, and Kangoda)
D. A region in the southern part of Odisha
Answer: C. Three different Kalinga states (Kalinga, South Kosala, and Kangoda) - Which name was used in the Tabaqat-i-Nasiri and Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi to refer to Odisha?
A. Odivissa
B. Jajnagar
C. Tosali
D. Uranshin
Answer: B. Jajnagar - What was the capital of Tosala, possibly a subdivision of Kalinga in the Ashoka-era?
A. Bhubaneswar
B. Puri
C. Cuttack
D. Dhauli
Answer: D. Dhauli - What geological supercontinent did peninsular India, including Odisha, belong to 140 million years ago?
A. Laurasia
B. Pangaea
C. Gondwana
D. Rodinia
Answer: C. Gondwana - What type of rock from the Mayurbhanj granite pluton has been dated to 3.09 billion years ago (Ga)?
A. Basalt
B. Marble
C. Granite
D. Limestone
Answer: C. Granite - Where were charophytes from the Permian Period discovered in Odisha?
A. Ib river area
B. Mahanadi basin
C. Talcher region
D. Cuttack district
Answer: C. Talcher region - In which districts have Acheulian tools dating to Lower Paleolithic times been found in Odisha?
A. Balasore and Bhadrak
B. Khordha and Puri
C. Mayurbhanj, Keonjhar, Sundargarh, and Sambalpur
D. Ganjam and Rayagada
Answer: C. Mayurbhanj, Keonjhar, Sundargarh, and Sambalpur - Where are rock carvings and paintings dating to the Upper Paleolithic found in Odisha?
A. Garjan Dongar in Sundergarh district
B. Gudahandi hills in Kalahandi district
C. Ushakothi in Sambalpur district
D. Vimkramkhol in Jharsuguda district
Answer: B. Gudahandi hills in Kalahandi district - What kinds of Neolithic tools were found in Kuchai, near Baripada?
A. Arrowheads and spear points
B. Hoes, chisels, pounders, and pottery
C. Flint hand axes and scrapers
D. Bone needles and awls
Answer: B. Hoes, chisels, pounders, and pottery - Where have prehistoric paintings and inscriptions been found in Odisha?
A. Dhankanal and Nayagarh districts
B. Garjan Dongar in Sundergarh district
C. Rayagada and Koraput districts
D. Khordha and Nayagarh districts
Answer: B. Garjan Dongar in Sundergarh district - What script might the inscriptions at Ushakothi and Vimkramkhol possibly be?
A. Sanskrit
B. Devanagari
C. Proto-Brahmi
D. Tamil-Brahmi
Answer: C. Proto-Brahmi - In which district can cave paintings from the Neolithic era be found in Odisha?
A. Cuttack district
B. Khordha district
C. Koraput district
D. Nuapada district (Yogimath near Khariar)
Answer: D. Nuapada district (Yogimath near Khariar) - What kind of fossils are known to be found in the coal fields of Mahanadi and Ib river basins?
A. Dinosaur bones
B. Megaspores from the Upper Permian
C. Trilobites from the Ordovician
D. Ammonites from the Jurassic
Answer: B. Megaspores from the Upper Permian - In which city was Asia’s first dedicated command and control centre for space domain awareness inaugurated?
A) Mumbai
B) Delhi
C) Bengaluru
D) Hyderabad
Answer: C) Bengaluru - What type of facility was inaugurated in Bengaluru, making it the first of its kind in Asia?
A) Hospital
B) School
C) Command and control centre for space domain awareness
D) Research laboratory
Answer: C) Command and control centre for space domain awareness - Which company’s global headquarters houses the newly opened command and control centre for space domain awareness in Bengaluru?
A) SpaceX
B) NASA
C) Digantara
D) ISRO
Answer: C) Digantara - What is the specialization of Digantara, the company that inaugurated the command and control centre in Bengaluru?
A) Health awareness
B) Space situational awareness (SSA)
C) Agricultural technology
D) Financial services
Answer: B) Space situational awareness (SSA) - At which meeting did ISRO Chairman S. Somanath announce India’s commitment to achieving debris-free space missions by 2030?
A) 40th IADC meeting
B) 42nd IADC meeting
C) 44th IADC meeting
D) 46th IADC meeting
Answer: B) 42nd IADC meeting - What is India’s target year to achieve debris-free space missions, as announced by ISRO Chairman S. Somanath?
A) 2025
B) 2030
C) 2040
D) 2050
Answer: B) 2030 - Who made the announcement regarding India’s commitment to debris-free space missions at the 42nd IADC meeting?
A) Prime Minister Narendra Modi
B) ISRO Chairman S. Somanath
C) DRDO Chief G. Satheesh Reddy
D) Indian Space Minister Jitendra Singh
Answer: B) ISRO Chairman S. Somanath - Which country recently received the first batch of BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles from India?
A) Vietnam
B) Philippines
C) Indonesia
D) Malaysia
Answer: B) Philippines - What is significant about the delivery of BrahMos missiles to the Philippines?
A) It marks the first export of BrahMos missiles to any country.
B) It signifies India’s defense cooperation with Malaysia.
C) It represents the first-ever defense deal between India and Vietnam.
D) It indicates India’s military alliance with Indonesia.
Answer: A) It marks the first export of BrahMos missiles to any country. - How much was the deal worth between India and the Philippines for the BrahMos missiles?
A) $200 million
B) $300 million
C) $375 million
D) $500 million
Answer: C) $375 million - When was the deal for the BrahMos missiles between India and the Philippines signed?
A) January 2020
B) January 2021
C) January 2022
D) January 2023
Answer: C) January 2022 - What kind of missiles are BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles?
A) Ballistic missiles
B) Anti-aircraft missiles
C) Cruise missiles
D) Intercontinental ballistic missiles
Answer: C) Cruise missiles - Where was the Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM) test-fired by DRDO?
A) Bengaluru
B) Hyderabad
C) Chandipur, Odisha
D) New Delhi
Answer: C) Chandipur, Odisha - What key features of the Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM) were demonstrated during the test?
A) High-altitude flight and long-range accuracy
B) Precise navigation, low-altitude sea-skimming flight, and reliability of propulsion
C) Surface-to-air capability and anti-ship targeting
D) Submarine-launched deployment and stealth capability
Answer: B) Precise navigation, low-altitude sea-skimming flight, and reliability of propulsion - Who conducted the successful test flight of the Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM)?
A) Indian Navy
B) Indian Army
C) Indian Air Force
D) Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
Answer: D) Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) - Which location in Odisha served as the testing site for the Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM)?
A) Bhubaneswar
B) Cuttack
C) Chandipur
D) Puri
Answer: C) Chandipur - Which entity closely monitored the performance of the Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM) during the test?
A) Indian Navy
B) Various sensors
C) Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
D) Foreign military observers
Answer: B) Various sensors - Who shared plans for the next moon mission, Chandrayaan-4, in 2040?
A) Narendra Modi
B) S Somanath
C) Rakesh Sharma
D) K Sivan
Answer: B) S Somanath
Which organization is spearheading India’s lunar exploration efforts?
A) NASA
B) ISRO
C) ESA
D) CNSA
Answer: B) ISRO - What is the primary objective of the upcoming phase of the Chandrayaan project?
A) Exploring Mars
B) Advancing lunar exploration efforts
C) Studying asteroids
D) Investigating exoplanets
Answer: B) Advancing lunar exploration efforts - What milestone does Chandrayaan-4 aim to achieve for India by 2040?
A) Establishing a permanent lunar base
B) Landing an astronaut on the moon
C) Mapping the entire lunar surface
D) Extracting water from lunar soil
Answer: B) Landing an astronaut on the moon - When is the expected timeline for the Chandrayaan-4 mission?
A) 2030
B) 2040
C) 2050
D) 2060
Answer: B) 2040 - When did Arabica coffee reportedly develop according to genome sequencing?
A) 6,000 years ago
B) 60,000 years ago
C) 600,000 years ago
D) 6 million years ago
Answer: C) 600,000 years ago - Where did Arabica coffee develop, according to the report?
A) Colombia
B) Ethiopia
C) Brazil
D) Indonesia
Answer: B) Ethiopia - What were the two coffee species involved in the natural hybridization process?
A) Coffea robusta and Coffea arabica
B) Coffea arabica and Coffea liberica
C) Coffea canephora and Coffea eugenioides
D) Coffea arabica and Coffea excelsa
Answer: C) Coffea canephora and Coffea eugenioides - What is the aim of India’s ₹10,000 crore Artificial Intelligence Mission?
A) Boosting the coffee industry
B) Enhancing the country’s AI ecosystem
C) Promoting tourism
D) Supporting traditional farming methods
Answer: B) Enhancing the country’s AI ecosystem - Which company is India considering striking a deal with for sourcing GPUs?
A) Intel
B) AMD
C) Nvidia
D) Qualcomm
Answer: C) Nvidia - Who announced the launch of the new artificial intelligence (AI) assistant, Meta AI?
A) Google
B) Apple
C) Meta Platforms
D) Microsoft
Answer: C) Meta Platforms - What is the name of the latest AI model powering Meta AI?
A) Tiger 5
B) Llama 3
C) Elephant 2
D) Rhino 4
Answer: B) Llama 3 - What is the purpose of Meta AI?
A) Enhancing virtual reality experiences
B) Providing users with highly intelligent AI assistance
C) Developing self-driving cars
D) Improving mobile gaming performance
Answer: B) Providing users with highly intelligent AI assistance - Which social media and messaging platforms will integrate Meta AI?
A) Twitter and LinkedIn
B) Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp
C) Snapchat and TikTok
D) Pinterest and Reddit
Answer: B) Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp - What is the pricing strategy for Meta AI?
A) Premium subscription-based model
B) Pay-per-use model
C) Freemium model
D) Free-to-use model
Answer: D) Free-to-use model - What is the purpose of a fathometer?
A) Measuring earthquakes
B) Measuring rainfall
C) Measuring ocean depth
D) Measuring sound intensity
Answer: C) Measuring ocean depthExplanation: A fathometer is a depth finder that uses sound waves to determine the depth of water. - What is Epsom, England, associated with?
A) Snooker
B) Shooting
C) Polo
D) Horse racingAnswer: D) Horse racingExplanation: Epsom is a town in Surrey, England, known for Epsom Downs Racecourse, - where The Derby horse race is held.
Who was the fastest shorthand writer?
A) Dr. G. D. Bist
B) J.R.D. Tata
C) J.M. Tagore
D) Khudada Khan
Answer: A) Dr. G. D. BistExplanation: Dr. G. D. Bist, a Guinness Record Holder, achieved a speed of 250 w.p.m. in shorthand. - Which country does golf player Vijay Singh belong to?
A) USA
B) Fiji
C) India
D) UK
Answer: B) FijiExplanation: Vijay Singh, known as “The Big Fijian,” is an Indo-Fijian golfer born in Fiji. - “One People, One State, One leader” was the policy of
A) Stalin
B) Hitler
C) Lenin
D) Mussolini
Answer: B) HitlerExplanation: This policy was associated with Hitler’s regime in Germany. - What is the full form of IG in the police department?
Answer: IG stands for Inspector General of Police. - What does DRDL stand for?
A) Defence Research and Development Laboratory
B) Department of Research and Development Laboratory
C) Differential Research and Documentation Laboratory
D) None of the above
Answer: A) Defence Research and Development Laboratory - Why does exposure to sunlight help improve health?
A) The infrared light kills bacteria in the body
B) Resistance power increases
C) The pigment cells in the skin get stimulated and produce a healthy tan
D) The ultraviolet rays convert skin oil into Vitamin D
Answer: D) The ultraviolet rays convert skin oil into Vitamin D - Where is the headquarters of the registered voluntary association “Transparency International” located?
(a) Helsinki, Finland
(b) Geneva, Switzerland
(c) Berlin, Germany
(d) Paris, France
Ans: (c) Berlin, Germany - Who appoints the Secretary-General of the United Nations Organization?
(a) General Assembly
(b) Security Council
(c) Trusteeship Council
(d) World Bank
Ans: (a) General Assembly - Which countries does the International Criminal Court lack jurisdiction over?
(a) France, China, Pakistan, Afghanistan
(b) UK, France, China, Pakistan
(c) USA, UK, Russia, France
(d) USA, Russia, China, Israel
Ans: (d) USA, Russia, China, Israel - Seasonal variation in Earth’s weather condition is the effect of _____ of the Earth?
(a) Diastrophism
(b) Erosion
(c) Revolution
(d) Rotation
Ans: (c) Revolution - Which planet of the Solar system experiences Sunrise on the West?
(a) Jupiter
(b) Venus
(c) Mercury
(d) Mars
Ans: (b) Venus - What is the difference between a Nuclear reactor and an atomic bomb?
(a) No chain reaction takes place in the atomic bomb while it takes place in a nuclear reactor
(b) The chain reaction in a nuclear reactor is not controlled
(c) The chain reaction in a nuclear reactor is controlled
(d) No chain reaction takes place in a nuclear reactor while in the atomic bomb there is a chain reaction
Ans: (c) The chain reaction in a nuclear reactor is controlled - Which of the following is used for indigestion?
(a) Baking Soda
(b) Milk of Magnesia
(c) Quick lime (calcium oxide)
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d) All of the above - What is the process of drilling small-sized holes deep into the Earth’s surface for injecting water, sand, and chemicals in order to obtain shale gas and oil reserves known as?
(a) Fracking
(b) Chroning
(c) Dreecking
(d) Pulverising
Ans: (a) Fracking - In superconductivity, the conductivity of a material becomes_______
(a) Infinite
(b) Finite
(c) Zero
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Infinite - What is the general pitch of the voice of women?
(a) The same as that of men
(b) Much lower than that of men
(c) Higher than that of men
(d) Marginally lower than that of men
Ans: (c) Higher than that of men - What is responsible for the diffusion of light in the atmosphere?
(a) Water vapors
(b) Helium
(c) Dust particles
(d) Carbon Dioxide
Ans: (c) Dust particles - What source provides some heat to the atmosphere even after sunset?
(a) Albedo effect
(b) Latent heat
(c) Invisible solar radiation
(d) Terrestrial radiation
Ans: (d) Terrestrial radiation - The permanent hardness of water is primarily due to the presence of _______.
(a) Bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium
(b) Carbonates of sodium and magnesium
(c) Sulphates of magnesium and calcium
(d) Sulphates of sodium and potassium
Ans: (c) Sulphates of magnesium and calcium - Among the following planets, which one does not orbit the Sun from west to east?
(a) Venus
(b) Jupiter
(c) Mars
(d) Mercury
Ans: (a) Venus - Which planet(s) does not have a natural satellite?
(a) Mercury
(b) Venus
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Saturn
Ans: (c) Both (a) and (b) - Which continent is known as a hollow continent due to its low population in the central areas?
(a) Europe
(b) South America
(c) Australia
(d) Africa
Ans: (b) South America - The Murray-Darling system, one of the greatest rivers in the world, is located in which country?
(a) Germany
(b) Australia
(c) Russia
(d) Canada
Ans: (b) Australia - Polar Stratospheric Clouds are associated with which environmental phenomenon?
(a) Artificial Rain
(b) Acid Rain
(c) Greenhouse effect
(d) Ozone layer depletion
Ans: (d) Ozone layer depletion - Which type of Laser is commonly used in Laser Printers?
(a) Gas Laser
(b) Dye Laser
(c) Excimer Laser
(d) Semiconductor Laser
Ans: (d) Semiconductor Laser - The ozone layer prevents the entry of which types of rays into the atmosphere?
(a) UV-A only
(b) UV-B only
(c) UV-C only
(d) Both UV-B and UV-C
Ans: (d) Both UV-B and UV-C - What happens to the value of ‘g’ as we move from the equator to the poles?
(a) Remains the same
(b) Increases
(c) Decreases
(d) None of these
Ans: (c) Decreases - Which of the following is not considered a structural reform in India?
(a) Reduction of interest rates
(b) Land reforms
(c) Tax reforms
(d) Delicensing
Ans: (c) Tax reforms - During which astronomical event can Baily’s beads be observed?
a) Occultation of Jupiter
b) Partial solar eclipse
c) Lunar eclipse
d) Total solar eclipse
Answer: d) Total solar eclipse - In the Northern Hemisphere, on which day does the Summer Solstice occur?
a) 22nd December
b) 21st March
c) 23rd September
d) 21st June
Answer: d) 21st June - What does the Japanese word “tsunami” mean?
a) Gneiss
b) Jishin
c) Volcano
d) Tsunami
Answer: d) Tsunami - Which state in India is the largest producer of mica?
a) Madhya Pradesh
b) Rajasthan
c) Jharkhand
d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer: d) Andhra Pradesh - Individuals like small farmers and seasonal workers who regularly move in and out of poverty are categorized as _______?
a) Occasionally poor
b) Churning poor
c) Always poor
d) Usually poor
Answer: b) Churning poor - Which branch of Economics is also known as “Income and employment theory”?
a) International economics
b) Public finance
c) Microeconomics
d) Macroeconomics
Answer: d) Macroeconomics - ______ is a type of good for which demand increases as its price rises?
a) Giffen Good
b) Capital Good
c) Consumer Good
d) None
Answer: a) Giffen Good - What is the full form of GSTIN in relation to GST?
a) Goods and Services Tax Identification Note
b) Goods and Services Tax Identification Number
c) Goods and Services Tax Information Number
d) Goods and Services Taxation Income Number
Answer: b) Goods and Services Tax Identification Number - What is the full form of NPCI, an umbrella organization for all retail payments systems in India?
a) National Payments Corporation of India
b) Non-cash Payments Corporation of India
c) Non-cash Payments Cooperative Inc
d) Net Payments Company Inc.
Answer: a) National Payments Corporation of India - The period of the 12th Five Year Plan was?
a) 2012-2017
b) 2007-2012
c) 2002-2007
d) 1997-2002
Answer: a) 2012-2017 - Which of the following entities is NOT classified as a Constitutional body?
A) Finance Commission
B) NITI Aayog
C) National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
D) Election Commission
Answer: B) NITI Aayog - From which country’s constitutional framework was the concept of judicial review and the principle of an independent judiciary adopted in the Indian Constitution?
A) Australia
B) Germany
C) Japan
D) America
Answer: D) America - Which article of the Indian Constitution pertains to the establishment of a Finance Commission?
A) Article 300
B) Article 290
C) Article 320
D) Article 280
Answer: D) Article 280 - In which year was the 44th Constitutional Amendment Act enacted?
A) 1978
B) 1975
C) 1976
D) 1972
Answer: A) 1978 - What constitutes the Parliament of India?
A) President, House of the People, and Council of States
B) House of the People
C) House of the People and Council of States
D) Council of States
Answer: A) President, House of the People, and Council of States - Which subject matter falls under the exclusive legislative jurisdiction of the Union Legislature?
A) Public health
B) Police
C) Railways
D) Local self-government
Answer: C) Railways - In which location was the Khilafat Committee established by the Ali brothers?
A) Bombay in 1919
B) Madras in 1920
C) Kolkata in 1919
D) Bombay in 1914
Answer: A) Bombay in 1919 - Which planet is known as the “Red Planet”?
A) Mars
B) Jupiter
C) Venus
D) Saturn
Ans: A) Mars - Who composed the Indian national anthem, “Jana Gana Mana”?
A) Rabindranath Tagore
B) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
C) Sarojini Naidu
D) Mahatma Gandhi
Ans: A) Rabindranath Tagore - Which Indian state is the largest producer of coffee?
A) Karnataka
B) Kerala
C) Tamil Nadu
D) Andhra Pradesh
Ans: A) Karnataka - Who is known as the “Father of Modern Physics”?
A) Albert Einstein
B) Isaac Newton
C) Galileo Galilei
D) Nikola Tesla
Ans: A) Albert Einstein - The “Bharat Ratna” award is given in which field?
A) Literature, Science, and Arts
B) Sports
C) Social Work
D) Journalism
Ans: A) Literature, Science, and Arts - Which country is known as the “Land of the Rising Sun”?
A) Japan
B) China
C) South Korea
D) Vietnam
Ans: A) Japan - The “Nobel Prize” was established by which country’s inventor and industrialist?
A) Alfred Nobel (Sweden)
B) Thomas Edison (USA)
C) Nikola Tesla (Croatia)
D) Alexander Graham Bell (Scotland)
Ans: A) Alfred Nobel (Sweden) - Which Indian state is known as the “Spice Garden of India”?
A) Kerala
B) Karnataka
C) Tamil Nadu
D) Andhra Pradesh
Ans: A) Kerala - Who was the founder of the Maurya Empire in ancient India?
A) Chandragupta Maurya
B) Ashoka the Great
C) Bindusara
D) Bimbisara
Ans: A) Chandragupta Maurya - The “World Health Day” is observed on which date?
A) April 7th
B) June 5th
C) October 2nd
D) December 10th
Ans: A) April 7th - Who wrote the epic Indian Sanskrit poem “Ramayana”?
A) Valmiki
B) Ved Vyasa
C) Tulsidas
D) Kalidasa
Ans: A) Valmiki - Which metal is used in the filament of an electric bulb?
A) Tungsten
B) Copper
C) Aluminum
D) Silver
Ans: A) Tungsten - Who is the author of the book “The God of Small Things”?
A) Arundhati Roy
B) Salman Rushdie
C) Amitav Ghosh
D) Jhumpa Lahiri
Ans: A) Arundhati Roy - Question: What is the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 3 cm and height of 10 cm?
Options:
A) 282.74 cm³
B) 282.45 cm³
C) 282.50 cm³
D) 283.33 cm³
Solution:
Volume of a cylinder = πr²h
= π * 3² * 10
= π * 9 * 10
= 282.74 cm³ (approx)
Answer: A) 282.74 cm³ - Question: What is the probability of rolling a sum of 7 with two six-sided dice?
Options:
A) 1/6
B) 1/9
C) 1/12
D) 1/36
Solution:
Possible ways to roll a 7: (1,6), (2,5), (3,4), (4,3), (5,2), (6,1).
There are 6 outcomes out of 36 total outcomes.
Probability = 6 / 36 = 1 / 6
Answer: A) 1/6 - Question: A can complete a work in 10 days, and B can complete the same work in 15 days. How many days will it take if they work together?
Options:
A) 6 days
B) 5 days
C) 7 days
D) 8 days
Solution:
Work done by A in one day = 1/10
Work done by B in one day = 1/15
Together, their work per day = 1/10 + 1/15
= 3/30 + 2/30 = 5/30 = 1/6
So, together they will take 6 days to complete the work.
Answer: A) 6 days - Question: If 3 parts of a mixture contains 2 parts of salt, how much salt would be there in a mixture of 15 parts?
Options:
A) 5 parts
B) 6 parts
C) 7 parts
D) 10 parts
Solution:
Ratio of salt to mixture = 2/3
Therefore, salt in 15 parts = (2/3) * 15 = 10 parts
Answer: D) 10 parts - Question: A boat can travel at 12 km/h in still water. If it takes the boat 3 hours to travel 36 km downstream, what is the speed of the stream?
Options:
A) 3 km/h
B) 4 km/h
C) 5 km/h
D) 6 km/h
Solution:
Speed downstream = Distance / Time
= 36 km / 3 hours = 12 km/h
Boat speed in still water = 12 km/h
Therefore, stream speed = (downstream speed) – (still water speed)
= 12 km/h – 12 km/h
= 0 km/h
Answer: A) 3 km/h - Question: What is the simple interest on a principal amount of $800 at an interest rate of 4% per year for 3 years?
Options:
A) $90
B) $96
C) $97
D) $98
Solution:
Simple interest = Principal * Rate * Time
= $800 * 0.04 * 3
= $96
Answer: B) $96 - Question: A car travels a distance of 120 km in 2 hours. What is the speed of the car in km/h?
Options:
A) 50 km/h
B) 60 km/h
C) 70 km/h
D) 80 km/h
Solution:
Speed = Distance / Time
= 120 km / 2 hours
= 60 km/h
Answer: B) 60 km/h - Question: A train 150 meters long is running at a speed of 60 km/h. How long will it take to pass a 180-meter-long platform?
Options:
A) 12 seconds
B) 15 seconds
C) 18 seconds
D) 20 seconds
Solution:
Total distance = Length of train + Length of platform
= 150 m + 180 m = 330 m
Speed of the train in m/s = (60 * 1000) / 3600 = 16.67 m/s
Time = Distance / Speed
= 330 m / 16.67 m/s
= 19.8 seconds
Answer: C) 18 seconds - Question: In 5 years, John’s age will be twice his age 3 years ago. How old is he now?
Options:
A) 8 years
B) 10 years
C) 12 years
D) 15 years
Answer: B) 11 years
Solution:
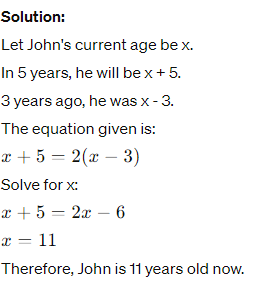
- Question: A 20-liter mixture contains milk and water in the ratio of 3:2. How much water must be added to the mixture to make the ratio 1:1?
Options:
A) 5 liters
B) 8 liters
C) 4 liters
D) 6 liters
Answer: C) 4 liters 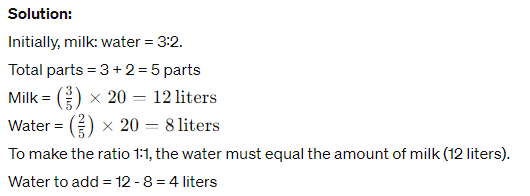
- Question: What is the total surface area of a cube with side length 5 cm?
Options:
A) 150 sq. cm
B) 125 sq. cm
C) 100 sq. cm
D) 75 sq. cm
Solution:
Total surface area of a cube = 6 * side²
= 6 * 5²
= 6 * 25
= 150 sq. cm
Answer: A) 150 sq. cm - Question: How many ways can the letters of the word “CAT” be arranged?
Options:
A) 6 ways
B) 4 ways
C) 3 ways
D) 2 ways
Solution:
The word “CAT” has 3 distinct letters.
Therefore, the number of permutations is 3! = 3 * 2 * 1 = 6 ways.
Answer: A) 6 ways - Question: The LCM of two numbers is 84, and their HCF is 6. If one number is 42, what is the other number?
Options:
A) 12
B) 14
C) 28
D) 21
Solution:
Let the other number be x.
We know the relation: LCM * HCF = a * b.
Therefore, 84 * 6 = 42 * x.
Simplify:
x=(84*6)/42=12
Answer: C) 12 - Question: Pipe A can fill a tank in 12 hours, and pipe B can fill it in 8 hours. How long will it take to fill the tank if both pipes are used together?
Options:
A) 4.8 hours
B) 5 hours
C) 6 hours
D) 6.4 hours
Solution:
Rate of pipe A = 1/12
Rate of pipe B = 1/8
Combined rate =
1/12+1/8=(2+3)/24=5/24
Time taken to fill the tank = 5/24=4.8 hours
Answer: A) 4.8 hours - Question: If a product originally costs $120 and it is on sale for a 25% discount, what is the sale price?
Options:
A) $100
B) $90
C) $100.50
D) $94
Solution:
Discount = 25% of $120
= 0.25 * $120
= $30
Sale price = $120 – $30
= $90
Answer: B) $90 - Question: Solve the equation: 3x−4=8.
Options:
A) x = 4
B) x = 5
C) x = 3
D) x = 2
Answer: A) x = 4
Solution:
3x−4=8
Add 4 to both sides:
3x=12
Divide by 3:
x=4 - Question: If the sum of two numbers is 45 and their difference is 15, what is the larger number?
Options:
A) 30
B) 20
C) 15
D) 25
Solution:
Let the numbers be x and y
then x+y=45 and x-y=15
Add the equations:
2x=60
Solve for x=30
Therefore, the larger number is 30.
Answer: A) 30 - Question: The average of five numbers is 20. If one number is removed, the average becomes 23. What was the number removed?
Options:
A) 5
B) 7
C) 15
D) 25
Solution:
Average of 5 numbers = 20
Sum of 5 numbers =
20×5=100
New average after removing one number = 23
Sum of 4 numbers = 23×4=92
Therefore, the number removed = 100−92=8.
Answer: D) 8 - Question: A shopkeeper buys 20 items for $10 each and sells them for $15 each. What is the total profit?
Options:
A) $75
B) $100
C) $50
D) $25
Solution:
Cost price = 20 items * $10 each = $200
Selling price = 20 items * $15 each = $300
Profit = Selling price – Cost price = $300 – $200 = $100
Answer: B) $100 - Question: Find the missing number in the sequence: 2, 3, 6, 4, 5, 20, ?, 3, 18.Options:
A) 5
B) 6
C) 3
D) 9
Answer: B) 6
Solution: The pattern in the series involves multiplication of consecutive numbers. - Question: Find the missing number in the sequence: 1, 3, 9, 15, 25, ?, 49.Options:
A) 29
B) 35
C) 33
D) 31
Answer: B) 35
Solution: The sequence consists of squares and (squares – 1) alternatively. - Question: Find the missing number in the sequence: 5, 7, 11, ?, 17, 19.Options:
A) 15
B) 14
C) 13
D) 12
Answer: C) 13
Solution: The sequence consists of consecutive prime numbers: 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19. Therefore, the missing number in the sequence is 13. - Question: Find the missing number in the sequence: 4, 8, 12, 20, ?, 40.Options:
A) 24
B) 28
C) 32
D) 36
Answer: C) 32
Solution: The sequence follows the pattern of multiplying the first number by an increasing multiplier - Question: Find the missing number in the sequence: 5, 10, 20, ?, 80, 160.Options:
A) 40
B) 25
C) 30
D) 50
Answer: A) 40
Solution: The sequence doubles each term:
5×2=10,
10×2=20, and so on. Therefore,
20×2=40. So, the missing number is 40. - A fruit seller had some apples. He sells 40% of the apples and still has 420 apples. What is the total number of apples he had originally?Options:
A) 700 apples
B) 720 apples
C) 600 apples
D) 650 apples
Answer: A) 700 apples - A person multiplied a number by 3/5 instead of 5/3. What is the percentage error in the calculation?Options:
A) 48%
B) 56%
C) 64%
D) 72%
Answer: C) 64% - Simplify: 5^2-3^2=?
- Simplify: 3^4/3^2=?
- Solve the Quadratic Equation: x^2-3x+2=0