The Weekly Practice Quiz for OSSSC RI, ARI, and Amin is an essential tool for aspirants preparing for the Odisha Sub-ordinate Staff Selection Commission exams. These quizzes help candidates regularly assess their knowledge and understanding of the syllabus, covering topics like general awareness, mathematics, reasoning, and English. By consistently participating in these practice sessions, candidates can identify their strengths and weaknesses, improve their time management skills, and become familiar with the exam pattern. Regular practice through these quizzes enhances confidence and competence, paving the way for better performance in the actual examination.
Weekly Practice Quiz For For OSSSC RI,ARI, Amin: September-4
Weekly Practice Quiz For For OSSSC RI,ARI, Amin: Sepetember-4
- If the price of a book is increased by 20%, by what percentage should the sales price be decreased to bring it back to the original price?(a) 16%
(b) 20%
(c) 25%
(d) 10%Ans: (a) 16%
Solution: Let the original price be 100. Increased price = 100 + 20% of 100 = 100 + 20 = 120. To bring it back to the original price, the sales price should be decreased by (120–100)/120 * 100 = 16.67%. - If 15% of a number is 45, what is 30% of that number?
(a) 90
(b) 60
(c) 30
(d) 15
Ans: (a) 90
Solution: Let the number be “x.” 15% of x = 45. x = (45 * 100)/15 = 300. 30% of x = (30/100) * 300 = 90. - A TV was originally priced at $800. It is now being sold at a discount of 20%. What is the discounted price?
(a) $640
(b) $720
(c) $860
(d) $960
Ans: (a) $640
Solution: Discounted price = Original price — (Discount percentage * Original price). Discounted price = $800 — (20% * $800) = $800 — $160 = $640. - The average of five numbers is 32. If one of the numbers is 45, what is the average of the remaining numbers?
(a) 30
(b) 34
(c) 35
(d) 36
Ans: (c) 35 Solution: Sum of the five numbers = 32 * 5 = 160. Sum of the remaining four numbers = 160–45 = 115. Average of the remaining numbers = 115 / 4 = 28.75. - The average age of a family of four is 28 years. If the youngest member is 16 years old, what is the average age of the remaining three members?
(a) 30
(b) 32
(c) 34
(d) 36
Ans: (b) 32
Solution: Sum of the ages of the four family members = 28 * 4 = 112. Sum of the ages of the remaining three members = 112–16 = 96. Average age of the remaining members = 96 / 3 = 32. - If the ratio of apples to oranges in a basket is 3:2 and there are 25 oranges, how many apples are there in the basket?
(a) 15
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 40
Ans: (c) 30
Solution: Since the ratio of apples to oranges is 3:2, for every 3 apples, there are 2 oranges. If there are 25 oranges, then there must be (3/2) * 25 = 37.5 apples. Rounding to the nearest whole number, there are 30 apples. - If the ratio of boys to girls in a classroom is 4:5, and there are 36 boys, how many girls are there in the classroom?
(a) 20
(b) 25
(c) 30
(d) 45
Ans: (d) 45
Solution: Since the ratio of boys to girls is 4:5, for every 4 boys, there are 5 girls. If there are 36 boys, then there must be (5/4) * 36 = 45 girls. - The ratio of the lengths of two rectangles is 3:4. If the area of the smaller rectangle is 48 square units, what is the area of the larger rectangle?
(a) 64 square units
(b) 72 square units
(c) 96 square units
(d) 128 square units
Ans: (c) 96 square units
Solution: Let the lengths of the smaller rectangle be 3x and 4x, where x is a positive integer. The area of the smaller rectangle = (3x) * (4x) = 12x² = 48. Solving for x, we get x² = 4, so x = 2. The lengths of the smaller rectangle are 6 units and 8 units. The area of the larger rectangle = (4x) * (3x) = 12x² = 12 * 4 = 48 square units. - If John can complete a job in 8 hours and Sarah can complete the same job in 12 hours, how long will it take them to complete the job together?
(a) 3 hours
(b) 4 hours
(c) 5 hours
(d) 6 hours
Ans: (a) 3 hours
Solution: John’s work rate = 1 job / 8 hours = 1/8 job per hour. Sarah’s work rate = 1 job / 12 hours = 1/12 job per hour. Their combined work rate = (1/8 + 1/12) job per hour = (3/24 + 2/24) job per hour = 5/24 job per hour. Time taken to complete the job together = 24/5 hours = 4.8 hours. - If it takes 6 workers 8 hours to complete a project, how many hours would it take for 8 workers to complete the same project?
(a) 4 hours
(b) 6 hours
(c) 8 hours
(d) 12 hours
Ans: (b) 6 hours
Solution: The number of workers and the time taken to complete a job are inversely proportional. Using the formula: (Number of workers) * (Time taken) = Constant. (6 workers) * (8 hours) = (8 workers) * (x hours). Solving for x, we get x = 6 hours. - If a machine can produce 100 units of a product in 5 hours, how many units can it produce in 10 hours?
(a) 100 units
(b) 150 units
(c) 200 units
(d) 250 units
Ans: (c) 200 units
Solution: The number of units produced and the time taken are directly proportional. Using the formula: (Number of units) = (Rate of production) * (Time). Thus, (Number of units) = (100 units / 5 hours) * (10 hours) = 200 units. - A shopkeeper purchased a shirt for $40 and sold it for $60. What is the profit percentage?
(a) 20%
(b) 33.33%
(c) 50%
(d) 66.67%
Ans: (c) 50%
Solution: Profit = Selling Price — Cost Price. Thus, Profit = $60 — $40 = $20. Profit Percentage = (Profit / Cost Price) * 100% = (20 / 40) * 100% = 50%. - If a bookshop sells a book at a loss of 10%, and the cost price of the book is $50, what is the selling price of the book?
(a) $45
(b) $50
(c) $55
(d) $60
Ans: (a) $45
Solution: Loss = Cost Price — Selling Price. Thus, 10% of Cost Price = $50. Selling Price = Cost Price — Loss = $50 — (0.10 * $50) = $50 — $5 = $45. - A trader sold a shirt for $180 and incurred a loss of 10%. What was the cost price of the shirt?
(a) $162
(b) $190
(c) $200
(d) $198
Ans: (a) $162
Solution: Loss = 10% of Cost Price. Thus, 10% of Cost Price = $180. Cost Price = $180 / (10/100) = $180 / 0.10 = $1800 / 10 = $180. - What is the perimeter (in meters) of an equilateral triangle whose height is 3.46 meters? Take 3=1.733=1.73.
Options:
(a) 12
(b) 9
(c) 6
(d) 10.4
Ans: (a) 12
Solution: The height of an equilateral triangle is given by 32×side23×side. Given that the height is 3.46 meters, we have: 1.732×side=3.4621.73×side=3.46 Solving for the side, side=2×2=4side=2×2=4. Therefore, the perimeter =3×side=3×4=12=3×side=3×4=12 meters. - The perimeters of two similar triangles ABC and PQR are 156 cm and 46.8 cm respectively. If BC=19.5 cm and QR=x cm, then the value of x is:
(a) 3.76 cm
(b) 5.85 cm
(c) 4.29 cm
(d) 6.75 cm
Ans: (b) 5.85 cm
- In two types of brass, the ratio of copper to zinc are 7: 4 and 2: 9 respectively if the two types of brass be melted and mixed in the ratio 6: 5, a new type of brass is obtained. Find the ratio of copper to zinc in this new type of brass.
(a) 52: 51
(b) 13: 35
(c) 52: 69
(d) 35: 13
Ans.(c)
Sol.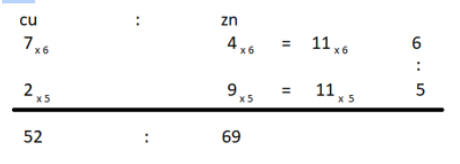
- A shopkeeper mixes 140 kg of P type of rice with 35 kg of Q type of rice. He then sold one-fifth of this mixture. In the remaining mixture, he again mixes P and Q type of rice in the ratio 2:3. Now the ratio of quantity of P type of rice to that of Q type of rice in the final mixture is 3:1. How much quantity of Q type of rice was added in the mixture?
(a) 8 kg
(b) 12 kg
(c) 10 kg
(d) 16 kg
Ans: (b) 12 kg
Solution: The problem involves multiple steps of mixing and ratio calculations. By carefully following the steps and applying the ratio rules, we find that 12 kg of Q type of rice was added. - If the difference between the present ages of Ram and Kush is 22 years and 4 years hence the age of Ram will be double the age of Kush, what is the average of their present ages?
(a) 39.1 years
(b) 33.4 years
(c) 35.2 years
(d) 37.5 years
Ans: (d) 37.5 years
Solution: Let the present age of Kush be ( x ) years. Then, Ram’s age is ( x + 22 ) years. According to the problem, ( x + 22 + 4 = 2(x + 4) ). Solving this equation gives ( x = 26 ). Therefore, Ram’s age is 48 years, and the average age is ( \frac{26 + 48}{2} = 37.5 ) years.
20. The sum of three numbers in an arithmetic progression (A.P) is -6 and their product is - Taking the positive value of the common difference as ‘d’, find the smallest of the three numbers.
(a) -6
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) More than one of the above
E) None of the above
Ans: (a) -6
Solution: Let the three numbers be ( m-d ), ( m ), and ( m+d ). Given ( 3m = -6 ) and ( m(m-(d)(m+(d) = 24 ). Solving these equations, we find ( m = -2 ) and ( d = 4 ). Thus, the numbers are -6, -2, and 2. The smallest number is -6. - Find the sum of all numbers divisible by 6 between 100 and 400.
(a) 12,550
(b) 12,450
(c) 11,450
(d) More than one of the above
E) None of the above
Ans: (b) 12,450
Solution: The sequence of numbers divisible by 6 between 100 and 400 is an arithmetic progression with the first term ( a = 102 ) and the last term ( l = 396 ). The common difference ( d = 6 ). Using the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series, we find the sum to be 12,450. - A and B invest in a business in the ratio 3:2. If 5% of the total profit goes to charity and A’s share is Rs. 855, what is the total profit?
(a) Rs. 500
(b) Rs. 1000
(c) Rs. 1500
(d) Rs. 2000
Ans: (c) Rs. 1500
Solution: Let the total profit be ( P ). After giving 5% to charity, 95% of the profit is shared between A and B in the ratio 3:2. Therefore, ( 0.95P \times \frac{3}{5} = 855 ). Solving this equation gives ( P = 1500 ). - A bag contains 50 P, 25 P, and 10 P coins in the ratio 5:9:4, amounting to Rs. 206. Find the number of coins of each type respectively.
(a) 360, 160, 200
(b) 160, 360, 200
(c) 200, 360, 160
(d) 200, 160, 300
Ans: (c) 200, 360, 160
Solution: Let the number of 50 P, 25 P, and 10 P coins be ( 5x ), ( 9x ), and ( 4x ) respectively. The total value is ( 50 \times 5x + 25 \times 9x + 10 \times 4x = 20600 ) paise. Solving for ( x ), we find ( x = 40 ). Therefore, the number of coins is 200, 360, and 160. - Two numbers are respectively 20% and 50% more than a third number. What is the ratio of the two numbers?
(a) 2:5
(b) 3:5
(c) 4:5
(d) 5:4
Ans: (c) 4:5
Solution: Let the third number be ( x ). The first number is ( 1.2x ) and the second number is ( 1.5x ). The ratio is ( \frac{1.2x}{1.5x} = \frac{4}{5} ). - A problem is given to three students whose chances of solving it are ( \frac{1}{2} ), ( \frac{1}{3} ), and ( \frac{1}{4} ) respectively. What is the probability that the problem will be solved?
(a) ( \frac{1}{4} )
(b) ( \frac{1}{2} )
(c) ( \frac{3}{4} )
(d) ( \frac{7}{12} )
Ans: (d) ( \frac{7}{12} )
Solution: The probability that the problem will not be solved by any student is ( \left(1 – \frac{1}{2}\right) \left(1 – \frac{1}{3}\right) \left(1 – \frac{1}{4}\right) = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{2}{3} \times \frac{3}{4} = \frac{1}{4} ). Therefore, the probability that the problem will be solved is ( 1 – \frac{1}{4} = \frac{3}{4} ). - Find the odd man out: 2, 5, 10, 17, 26, 37, 50, 64
(a) 50
(b) 37
(c) 26
(d) 64
Ans: (a) 50
Solution: The sequence follows the pattern ( n^2 + 1 ). The correct sequence should be 2, 5, 10, 17, 26, 37, 50, 65. Therefore, 50 is the odd one out. - A man buys a watch for Rs. 1950 and sells it for Rs. 2250. Calculate his profit percentage.
(a) 10%
(b) 15%
(c) 20%
(d) 25%
Ans: (b) 15%
Solution: Profit = Selling Price – Cost Price = 2250 – 1950 = 300. Profit percentage = ( {300}\{1950} *100 = 15.38% ). - If the cost price of 15 articles is equal to the selling price of 12 articles, find the profit percentage.
(a) 20%
(b) 25%
(c) 30%
(d) 40%
Ans: (b) 25%
Solution: Let the cost price of one article be ( x ). Therefore, the cost price of 15 articles is ( 15x ) and the selling price of 12 articles is ( 15x ). Hence, the selling price of one article is ( \frac{15x}{12} = 1.25x ). Profit percentage = ( \frac{1.25x – x}{x} \times 100 = 25% ). - A TV was originally priced at $800. It is now being sold at a discount of 20%. What is the discounted price?
(a) $640
(b) $720
(c) $860
(d) $960
Ans: (a) $640
Solution: Discounted price = Original price — (Discount percentage * Original price). Discounted price = $800 — (20% * $800) = $800 — $160 = $640. - The average of five numbers is 32. If one of the numbers is 45, what is the average of the remaining numbers?
(a) 30
(b) 34
(c) 35
(d) 36
Ans: (c) 35 Solution: Sum of the five numbers = 32 * 5 = 160. Sum of the remaining four numbers = 160–45 = 115. Average of the remaining numbers = 115 / 4 = 28.75. - What is the main purpose of RBI’s regulatory sandbox?
(a) To regulate financial institutions
(b) To test new financial innovations in a controlled environment
(c) To increase interest rates
(d) To provide loans to small businesses
Ans: (b) To test new financial innovations in a controlled environment - How many firms were selected for the test phase of the fifth cohort?
(a) Three
(b) Five
(c) Seven
(d) Ten
Ans: (b) Five - When was the fifth cohort of the regulatory sandbox announced?
(a) January of the previous year
(b) October of the previous year
(c) March of the current year
(d) July of the current year
Ans: (b) October of the previous year - How many applications were received for the fifth cohort?
(a) 15
(b) 18
(c) 22
(d) 30
Ans: (c) 22 - What is the theme of the fifth cohort?
(a) Digital Payments
(b) Financial Inclusion
(c) Fintech Solutions
(d) Theme-neutral
Ans: (d) Theme-neutral - By how much did digital payments in India increase year-over-year by March 31, 2024?
(a) 10.5%
(b) 12.6%
(c) 14.7%
(d) 15.3%
Ans: (b) 12.6% - What was the RBI-DPI as of March 31, 2024?
(a) 395.57
(b) 418.77
(c) 445.5
(d) 460.2
Ans: (c) 445.5 - What was the RBI-DPI in September 2023?
(a) 395.57
(b) 418.77
(c) 445.5
(d) 460.2
Ans: (b) 418.77 - What was the RBI-DPI in March 2023?
(a) 395.57
(b) 418.77
(c) 445.5
(d) 460.2
Ans: (a) 395.57 - By how many points did the All-India CPI for Agricultural Labourers increase in June 2024?
(a) 5 points
(b) 8 points
(c) 11 points
(d) 15 points
Answer: (c) 11 points - By how many points did the All-India CPI for Rural Labourers increase in June 2024?
(a) 5 points
(b) 8 points
(c) 11 points
(d) 15 points
Answer: (c) 11 points - What was the CPI-AL value in June 2024?
(a) 1270
(b) 1280
(c) 1290
(d) 1300
Answer: (b) 1280 - What does CPI-AL stand for?
(a) Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labourers
(b) Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Land
(c) Consumer Price Index for All Labourers
(d) Consumer Price Index for Allied Labourers
Answer: (a) Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labourers - What does CPI-RL stand for?
(a) Consumer Price Index for Rural Labourers
(b) Consumer Price Index for Rural Land
(c) Consumer Price Index for Real Labourers
(d) Consumer Price Index for Rural Locations
Answer: (a) Consumer Price Index for Rural Labourers - What is the estimated net tax receipt for the Budget 2024-25?
(a) ₹22.83 lakh crore
(b) ₹23.83 lakh crore
(c) ₹24.83 lakh crore
(d) ₹25.83 lakh crore
Ans: (d) ₹25.83 lakh crore - What is the projected fiscal deficit for 2024-25?
(a) 3.9% of GDP
(b) 4.0% of GDP
(c) 4.5% of GDP
(d) 4.9% of GDP
Ans: (d) 4.9% of GDP - How many industrial parks are planned under the “Viksit Bharat” theme?
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 14
Ans: (c) 12 - How many youth are expected to benefit from internship programs in top companies?
(a) 50 lakh
(b) 75 lakh
(c) 1 crore
(d) 1.5 crore
Ans: (c) 1 crore - What is the theme of Budget 2024-2025?
(a) Atmanirbhar Bharat
(b) Viksit Bharat
(c) Digital India
(d) Make in India
Ans: (b) Viksit Bharat - Which group is not a focus of the Budget 2024-2025?
(a) Women
(b) Poor
(c) Youth
(d) Senior Citizens
Ans: (d) Senior Citizens - What percentage of total expenditure is allocated for interest payments?
(a) 16%
(b) 19%
(c) 21%
(d) 25%
Ans: (b) 19% - What is the allocation for the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways?
(a) 2,00,000 crore
(b) 2,25,000 crore
(c) 2,50,000 crore
(d) 2,65,808 crore
Ans: (d) 2,65,808 crore - How much is allocated to Defence in the Budget 2024-25?
(a) 5.22 lakh crore
(b) 6.22 lakh crore
(c) 7.22 lakh crore
(d) 8.22 lakh crore
Ans: (b) 6.22 lakh crore - What is the budget allocation for Energy?
(a) 1,21,851 crore
(b) 1,31,851 crore
(c) 1,41,851 crore
(d) 1,51,851 crore
Ans: (d) 1,51,851 crore - What was India’s market capitalisation to GDP ratio rank globally?
(a) Second
(b) Third
(c) Fourth
(d) Fifth
Answer: (d) Fifth - What was the fuel inflation management measure taken in August 2023?
(a) LPG cylinder prices reduced by ₹200
(b) Petrol prices reduced by ₹2 per litre
(c) Diesel prices reduced by ₹2 per litre
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above - Which program aims to develop the world’s largest, universal, high-quality preschool network?
(a) Vidyanjali Initiative
(b) Poshan Bhi Padhai Bhi
(c) Ayushman Bharat
(d) National Education Policy
Answer: (b) Poshan Bhi Padhai Bhi - What is the GDP growth forecast for India for FY25 according to the Asian Development Bank (ADB)?
(a) 6%
(b) 6.5%
(c) 7%
(d) 7.5%
Answer: (c) 7% - On which date did the Asian Development Bank maintain its GDP growth forecast for India?
(a) July 10, 2024
(b) July 17, 2024
(c) July 19, 2024
(d) July 25, 2024
Answer: (b) July 17, 2024 - Which institution revised India’s GDP growth forecast upward to 7% for FY25?
(a) World Bank
(b) IMF
(c) ADB
(d) FICCI
Answer: (b) IMF - What is SEBEX 2?
(a) A new type of nuclear weapon
(b) A powerful non-nuclear explosive
(c) An AI-based defense system
(d) A medical device for brain stimulation
Ans: (b) - What explosive formulation does SEBEX 2 utilize?
(a) RDX
(b) TNT
(c) HMX
(d) PETN
Ans: (c) - How does SEBEX 2’s lethality compare to standard TNT?
(a) 0.75 times more deadly
(b) 1.01 times more deadly
(c) 1.5 times less deadly
(d) Equally deadly
Ans: (b) - Which company manufactures SEBEX 2?
(a) Bharat Dynamics Limited
(b) Economic Explosives Limited
(c) Larsen & Toubro
(d) Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Ans: (b) - Under which initiative was SEBEX 2 developed?
(a) Digital India
(b) Make in India
(c) Skill India
(d) Startup India
Ans: (b) - What does “AI washing” refer to?
(a) Using AI for cleaning purposes
(b) Exaggerating AI capabilities in products
(c) Developing AI in the healthcare sector
(d) Cleaning data using AI
Ans: (b) - Why do companies engage in AI washing?
(a) To improve product quality
(b) To capitalize on interest in AI
(c) To reduce manufacturing costs
(d) To enhance environmental friendliness
Ans: (b) - Which term is AI washing derived from?
(a) Brainwashing
(b) Greenwashing
(c) Whitewashing
(d) Blackwashing
Ans: (b) - What is the primary purpose of the deep brain stimulation (DBS) device fitted in Oran Knowlson?
(a) To enhance cognitive abilities
(b) To control epileptic seizures
(c) To improve memory retention
(d) To treat depression
Ans: (b) - How is the DBS device recharged post-surgery?
(a) By connecting to a USB port
(b) Through solar power
(c) Using a wireless headphone
(d) Via magnetic induction
Ans: (c) - Who is the New Shepard spacecraft named after?
(a) Neil Armstrong
(b) Yuri Gagarin
(c) Alan Shepard
(d) John Glenn
Ans: (c) Alan Shepard - What is the primary purpose of the New Shepard spacecraft?
(a) Military missions
(b) Space tourism
(c) Satellite deployment
(d) International Space Station resupply missions
Ans: (b) Space tourism - What significant feature does the New Shepard spacecraft’s design include?
(a) Single-use booster
(b) Fully reusable rocket system
(c) Solar-powered engine
(d) Nuclear propulsion system
Ans: (b) Fully reusable rocket system - How long does the New Shepard spacecraft’s flight last?
(a) 5 minutes
(b) 11 minutes
(c) 30 minutes
(d) 1 hour
Ans: (b) 11 minutes - During its flight, what do passengers experience aboard the New Shepard spacecraft?
(a) Extreme heat
(b) Severe turbulence
(c) Several minutes of weightlessness
(d) Zero gravity throughout the entire flight
Ans: (c) Several minutes of weightlessness - Which organization developed LOFAR?
(a) NASA
(b) ESA
(c) ASTRON
(d) ISRO
Ans: (c) ASTRON - LOFAR observes the universe at what range of radio frequencies?
(a) 30 to 50 MHz
(b) 90 to 200 MHz
(c) 300 to 400 MHz
(d) 500 to 600 MHz
Ans: (b) 90 to 200 MHz - Where is the main core of LOFAR located?
(a) France
(b) Germany
(c) United Kingdom
(d) Netherlands
Ans: (d) Netherlands - What technology does Li-Fi use to transmit data?
(a) Radio waves
(b) Sound waves
(c) Light waves
(d) Microwaves
Ans: (c) Light waves - What is the primary advantage of Li-Fi over Wi-Fi?
(a) Lower cost
(b) Higher data security
(c) Longer range
(d) Higher transmission power
Ans: (b) Higher data security - What is the primary objective of the CURIE mission?
(a) Investigate the origins of radio waves from the Sun.
(b) Explore the surface of Mars.
(c) Study the effects of cosmic rays on satellites.
(d) Monitor Earth’s weather patterns.
Ans: (a) - Which technique does CURIE use to achieve its objective?
(a) Optical telescopy
(b) Low-frequency radio interferometry
(c) X-ray imaging
(d) Infrared spectroscopy
Ans: (b) - What frequency range does CURIE measure radio waves in?
(a) 1 to 50 megahertz
(b) 20 to 100 megahertz
(c) 0.1 to 19 megahertz
(d) 10 to 1000 megahertz
Ans: (c) - Why is CURIE significant for future space-based radio astronomy?
(a) It is the first mission to use optical telescopy in space.
(b) It paves the way for future space-based radio astronomy.
(c) It will send astronauts to the Sun.
(d) It monitors Earth’s weather patterns.
Ans: (b) - Which organization sponsors the CURIE mission?
(a) European Space Agency (ESA)
(b) Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
(c) NASA’s Heliophysics Flight Opportunities for Research and Technology (H-FORT) Program
(d) Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
Ans: (c) - What is the role of the PM-STIAC?
(a) To oversee the construction of new universities in India.
(b) To support the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India.
(c) To regulate the telecom industry in India.
(d) To manage India’s space missions.
Ans: (b) - Which of the following is one of the ‘9 National Missions’ under PM-STIAC?
(a) Solar Power Initiative
(b) Natural Language Translation
(c) International Trade Mission
(d) Space Tourism Development
Ans: (b) - Which initiative of the Office of the PSA focuses on research in urban areas?
(a) Brahmaputra River System
(b) Energy Security
(c) City Research Clusters
(d) Jal Jeevan Mission
Ans: (c) - What recent discovery was made by NGRI scientists?
(a) A new type of mineral found in the Himalayas.
(b) Evidence of an ancient connection between the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica.
(c) A previously unknown underground river in India.
(d) New seismic activity patterns in the Indian Ocean.
Ans: (b) - Where is the National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI) located?
(a) New Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) Hyderabad, Telangana
(d) Bangalore
Ans: (c) - What was the main cause of the recent deaths in Kerala from Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)?
(a) Contaminated water
(b) Airborne particles
(c) Infected soil
(d) Unpasteurized milk
Ans. (a) Contaminated water - What type of safari was recently opened at Bannerghatta Biological Park?
(a) Leopard Safari
(b) Tiger Safari
(c) Elephant Safari
(d) Bear Safari
Ans. (a) Leopard Safari - Which organization updated the conservation status of the Iberian Lynx?
(a) International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
(b) World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
(c) Conservation International
(d) Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS)
Ans. (a) International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) - What species is associated with the discovery of the world’s oldest termite mounds?
(a) Southern Harvester Termite (Microhodotermes viator)
(b) African Wood Termite (Macrotermes bellicosus)
(c) Asian Subterranean Termite (Coptotermes formosanus)
(d) Drywood Termite (Cryptotermes cynocephalus)
Ans. (a) Southern Harvester Termite (Microhodotermes viator) - Which new snake eel species was discovered in Odisha’s estuarine ecosystems?
(a) Ophichthus gomesii
(b) Myrichthys tigrinus
(c) Muraenesox cinereus
(d) Uropterygius vitta
Ans. (a) Ophichthus gomesii - Which new flower fly species is associated with Kerala’s biodiversity?
(a) Mesembrius quadrivittatus
(b) Mesembrius aethiopicus
(c) Mesembrius keraliensis
(d) Mesembrius westensis
Ans. (a) Mesembrius quadrivittatus - What is the main reason for the reclassification of the Ibiza wall lizard?
(a) Habitat destruction
(b) Climate change
(c) Invasive species
(d) Overhunting
Ans. (c) Invasive species - Which recent study has highlighted the impact of rising temperatures on ice sheets?
(a) West Antarctica Vulnerability Study
(b) Antarctic Ice Core Study
(c) Polar Ice Melt Report
(d) Arctic Temperature Trends Analysis
Ans. (a) West Antarctica Vulnerability Study - What was the focus of the recent research from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) in Odisha?
(a) New species of snake eel
(b) New bird species
(c) New mammal species
(d) New plant species
Ans. (a) New species of snake eel - Which recent conservation effort involved the Iberian Lynx?
(a) Status upgrade from Endangered to Vulnerable
(b) Reintroduction into the wild
(c) New habitat creation
(d) Anti-poaching measures
Ans. (a) Status upgrade from Endangered to Vulnerable - What notable feature did the discovered termite mounds in Namaqualand have?
(a) Oldest known mounds
(b) Largest size
(c) Most intricate structure
(d) Highest density
Ans. (a) Oldest known mounds - What is the primary impact of Wolbachia bacteria on the reproductive system of wasps?
(a) Male sterility
(b) Female-only offspring
(c) Increased reproductive rate
(d) Gender reversal
Ans. (b) Female-only offspring - Which recent discovery highlights the importance of biodiversity in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands?
(a) New plant species
(b) New mammal species
(c) New bird species
(d) New amphibian species
Ans. (a) New plant species - What significant event took place at the Bannerghatta Biological Park in June 2024?
(a) Opening of South India’s first leopard safari
(b) Launch of a new tiger conservation program
(c) Establishment of a new elephant sanctuary
(d) Inauguration of a bird watching center
Ans. (a) Opening of South India’s first leopard safari - Which study provided insights into the changing conservation status of the Iberian Lynx?
(a) IUCN Red List Update
(b) Wildlife Population Monitoring Report
(c) Conservation Status Review
(d) Species Survival Assessment
Ans. (a) IUCN Red List Update - What is the typical period for assessing climate?(a) 10 years(b) 20 years(c) 35 years(d) 50 yearsAns: (c) 35 years
- What type of climate does most of India experience?(a) Polar(b) Tropical(c) Temperate(d) DesertAns: (b) Tropical
- What climate characterizes the northern regions of India?(a) Dry tropical(b) Wet tropical(c) Humid tropical(d) TemperateAns: (c) Humid tropical
- What defines weather?(a) Long-term patterns of variation(b) Instantaneous state of the atmosphere(c) Overall sum of weather conditions(d) Climate over an extended durationAns: (b) Instantaneous state of the atmosphere
- What defines climate?(a) Instantaneous state of the atmosphere(b) Long-term average patterns of variation(c) Short-term weather conditions(d) Weather on a specific dayAns: (b) Long-term average patterns of variation
- Which part of India lies within the sub-tropical and temperate zones?(a) Northern section(b) Southern section(c) Western section(d) Eastern sectionAns: (a) Northern section
- What is the maximum summer temperature recorded in Western Rajasthan?(a) 45°C(b) 50°C(c) 55°C(d) 60°CAns: (c) 55°C
- What is the lowest winter temperature recorded around Drass?(a) -20°C(b) -40°C(c) -50°C(d) -60°CAns: (d) -60°C
- Which region of India experiences minimal variation between day and night temperatures?(a) Western Rajasthan(b) Andaman and Nicobar Islands(c) Northern Himalayas(d) Thar DesertAns: (b) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Which area in India receives annual precipitation surpassing 1150 cm?(a) Rajasthan(b) Ladakh(c) Meghalaya(d) Western GhatsAns: (c) Meghalaya
- When does most of India receive rainfall?(a) January to March(b) April to June(c) June to September(d) October to DecemberAns: (c) June to September
- What factors protect India from the cold and dry winds of Central Asia?(a) Western Ghats(b) Eastern Ghats(c) Northern Mountain Ranges(d) Deccan PlateauAns: (c) Northern Mountain Ranges
- Which ocean current significantly impacts weather conditions in India?(a) Gulf Stream(b) El-Nino(c) Kuroshio Current(d) Benguela CurrentAns: (b) El-Nino
- What phenomenon causes a weakening of monsoon circulation in the Indian Ocean?(a) La-Nina(b) El-Nino(c) Southern Oscillation(d) Tropical CyclonesAns: (b) El-Nino
- Which theory explains the monsoon as an extensive land breeze and sea breeze?(a) Dynamic Concept(b) Jet Stream Theory(c) Thermal Concept(d) Indian Ocean DipoleAns: (c) Thermal Concept
- The Sun Temple at Konark was built by which Ganga ruler?
(a) Anangabhimadeva III
(b) Narasimhadeva I
(c) Rajaraja II
(d) Anantavarma Chodagangadeva
Ans: (b) Narasimhadeva I - Which Gajapati ruler concluded a peace treaty with Krishnadevaraya?
(a) Purushottam Deva
(b) Kapilendra Deva
(c) Prataparudra Deva
(d) Kakharua Deva
Ans: (c) Prataparudra Deva - Who was the last ruler of the Ganga dynasty?
(a) Rajaraja II
(b) Bhanudeva IV
(c) Anangabhimadeva III
(d) Narasimhadeva I
Ans: (b) Bhanudeva IV - Which poet flourished during the reign of Rajaraja II of the Ganga dynasty?
(a) Sarala Dasa
(b) Jayadeva
(c) Kapilendra Deva
(d) Anantavarma Chodagangadeva
Ans: (b) Jayadeva - What was the capital of the Ganga dynasty?
(a) Puri
(b) Kataka
(c) Kalinganagara
(d) Khurda
Ans: (c) Kalinganagara - Which Gajapati ruler was defeated by Krishnadevaraya?
(a) Kapilendra Deva
(b) Purushottam Deva
(c) Prataparudra Deva
(d) Kakharua Deva
Ans: (c) Prataparudra Deva - Who was the founder of the Bhoi dynasty?
(a) Kapilendra Deva
(b) Mukundadeva
(c) Govinda Vidyadhara
(d) Sulaiman Khan Karrani
Ans: (c) Govinda Vidyadhara - Which dynasty succeeded the Gajapati dynasty in Odisha?
(a) Bhoi
(b) Karrani
(c) Maratha
(d) Mughal
Ans: (a) Bhoi - The Nagara style of temples built during the Ganga period includes which of the following temples?
(a) Jagannath temple
(b) Mukteswara temple
(c) Konark Sun temple
(d) Mangalagiri temple
Ans: (b) Mukteswara temple - Who was the first Maratha Subahdar in Odisha?
(a) Sheo Bhatt Sathe
(b) Chimma Sau
(c) Bhawani Pandit
(d) Sadashiv Rao
Ans: (a) Sheo Bhatt Sathe - The Bhoi dynasty faced its first major external threat from which ruler?
(a) Sulaiman Khan Karrani
(b) Krishnadevaraya
(c) Daud Khan Karrani
(d) Quli Qutb Shah
Ans: (a) Sulaiman Khan Karrani - Who was the Hindu general of Sulaiman Karrani responsible for large-scale destruction of temples?
(a) Govinda Vidyadhara
(b) Kalapahar
(c) Kakharua Deva
(d) Mukundadeva
Ans: (b) Kalapahar - Who appointed Qutlu Khan Lohani as the governor of Odisha?
(a) Daud Khan Karrani
(b) Mansingh
(c) Sulaiman Khan Karrani
(d) Murshid Quli Khan
Ans: (c) Sulaiman Khan Karrani - What was the primary role of Amatyas in the administration under the Gajapatis?
(a) Military commanders
(b) Revenue officers
(c) Chief ministers
(d) Governors of provinces
Ans: (c) Chief ministers - Which ruler transferred the capital from Gaur to Tandah?
(a) Daud Khan Karrani
(b) Qutlu Khan Lohani
(c) Sulaiman Khan Karrani
(d) Mansingh
Ans: (c) Sulaiman Khan Karrani - Who declared himself independent and assumed the title of ‘Qutlu Shah’?
(a) Nasir Khan
(b) Murshid Quli Khan
(c) Qutlu Khan Lohani
(d) Daud Khan Karrani
Ans: (c) Qutlu Khan Lohani - During which Mughal emperor’s reign was Odisha divided into five sarkars?
(a) Akbar
(b) Jahangir
(c) Shah Jahan
(d) Aurangzeb
Ans: (a) Akbar - Who built the Qadam Rasul at Balasore?
(a) Taqi Khan
(b) Murshid Quli Khan II
(c) Suja-ud-din Muhammad Khan
(d) Muhammad Baqar Khan
Ans: (a) Taqi Khan - Who was the last representative of the Marathas in Odisha?
(a) Rajaram Pandit
(b) Sadashiv Rao
(c) Sheo Bhatt Sathe
(d) Shambhaji Ganesh
Ans: (b) Sadashiv Rao - Which Mughal emperor appointed Muhammad Baqar Khan as the Governor of Odisha?
(a) Akbar
(b) Jahangir
(c) Shah Jahan
(d) Aurangzeb
Ans: (c) Shah Jahan - Under whose reign was the Jagannath temple attacked in Puri?
(a) Taqi Khan
(b) Suja-ud-din Muhammad Khan
(c) Murshid Quli Khan I
(d) Alivardi Khan
Ans: (a) Taqi Khan - What marked the beginning of Maratha administration in Odisha?
(a) Peace Treaty of 1751
(b) Battle of Buxar
(c) Defeat of Nasir Khan
(d) Appointment of Sadashiv Rao
Ans: (a) Peace Treaty of 1751 - Which dynasty ruled Odisha immediately before the Gajapatis?
(a) Karrani
(b) Ganga
(c) Bhoi
(d) Mughal
Ans: (b) Ganga - Who was the most powerful ruler of the Gajapati dynasty?
(a) Purushottam Deva
(b) Kapilendra Deva
(c) Prataparudra Deva
(d) Kakharua Deva
Ans: (b) Kapilendra Deva - Which poet wrote the Mahabharata in Odia language during the Gajapati period?
(a) Jayadeva
(b) Sarala Dasa
(c) Kapilendra Deva
(d) Narasimhadeva I
Ans: (b) Sarala Dasa - The invasion by which ruler led to the construction of the Mangalagiri temple on the bank of the Krishna river?
(a) Krishnadevaraya
(b) Quli Qutb Shah
(c) Prataparudra Deva
(d) Purushottam Deva
Ans: (c) Prataparudra Deva - Who succeeded Sulaiman Khan Karrani in the Karrani dynasty?
(a) Qutlu Khan Lohani
(b) Daud Khan Karrani
(c) Nasir Khan
(d) Kalapahar
Ans: (b) Daud Khan Karrani - Who was the Mughal general who defeated Daud Khan Karrani in the battle of Tukaroi?
(a) Mansingh
(b) Bairam Khan
(c) Raja Todar Mal
(d) Mirza Hakim
Ans: (a) Mansingh - Who was the ruler of Odisha when the Mughal rule started?
(a) Mukundadeva
(b) Govinda Vidyadhara
(c) Narasimhadeva I
(d) Prataparudra Deva
Ans: (a) Mukundadeva - Which Mughal governor of Odisha faced resistance from King Balabhadra Deva?
(a) Raja Mansingh
(b) Qutlu Khan Lohani
(c) Muhammad Baqar Khan
(d) Zaman Teharani
Ans: (a) Raja Mansingh - Under whose rule was Odisha divided into 5 Sarkars?
(a) Akbar
(b) Jahangir
(c) Shah Jahan
(d) Aurangzeb
Ans: (a) Akbar - Which circular directed the abolition of Odia as the court language of Sambalpur in 1895?
(a) Risley Circular
(b) Andrew Fraser Circular
(c) Curzon Circular
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Andrew Fraser Circular - Who founded the Utkal Sammilani in 1903 to ventilate the grievances of the Odia-speaking people?
(a) Madan Mohan Mishra
(b) Brajamohan Patnaik
(c) Mahant Bihari Das
(d) Madhusudan Das
Answer: (d) Madhusudan Das - Which organization played a significant role in restoring the nationalism of Odisha?
(a) Ganjam Jatiya Samity
(b) Utkal Sammilani
(c) Indian National Congress
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Utkal Sammilani - In which year was the Ganjam National Conference held, expressing the desire for a united Odisha?
(a) 1895
(b) 1903
(c) 1907
(d) 1911
Answer: (c) 1907 - Who criticized the creation of Bihar and Odisha in the House of Lords in February 1912?
(a) Madan Mohan Mishra
(b) Brajamohan Patnaik
(c) Lord Curzon
(d) Mahant Bihari Das
Answer: (c) Lord Curzon - When was the province of Bihar and Odisha inaugurated?
(a) 1901
(b) 1911
(c) 1912
(d) 1920
Answer: (c) 1912 - Which publication strongly denounced Telugu ascendancy over Ganjam and pleaded for the fulfillment of the Odia demand for ‘Odian Odisha’?
(a) Utkal Sammilani
(b) Asha
(c) Utkala Dipika
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Asha - What was the population growth rate of rural areas in Odisha as per Census 2011?
(a) 7.50%
(b) 11.8%
(c) 14.05%
(d) 23.32%
Answer: (b) 11.8% - Which district in Odisha had the highest population growth rate according to Census 2011?
(a) Jagatsinghpur
(b) Balangir
(c) Cuttack
(d) Puri
Answer: (b) Balangir (23.32%) - What was the population growth rate of Jagatsinghpur district in Odisha as per Census 2011?
(a) 7.50%
(b) 11.8%
(c) 14.05%
(d) 23.32%
Answer: (a) 7.50% - What is the total population density of Odisha as per Census 2011?
(a) 270 persons per sq km
(b) 800 persons per sq km
(c) 91 persons per sq km
(d) 979 persons per sq km
Answer: (a) 270 persons per sq km - Which district in Odisha has the highest population density?
(a) Khordha
(b) Kandhamal
(c) Rayagada
(d) Nayagarh
Answer: (a) Khordha - What is the sex ratio of Odisha as per Census 2011?
(a) 979 females per 1000 males
(b) 1051 females per 1000 males
(c) 915 females per 1000 males
(d) 987 females per 1000 males
Answer: (a) 979 females per 1000 males - Which district in Odisha has the highest sex ratio?
(a) Rayagada
(b) Khordha
(c) Nayagarh
(d) Kandhamal
Answer: (a) Rayagada - Which dynasty was the first to establish a strong empire in Odisha during the Medieval era?
(a) Gajapati Dynasty
(b) Bhoi Dynasty
(c) Ganga or Eastern Ganga Dynasty
(d) Karrani Dynasty
Answer: (c) Ganga or Eastern Ganga Dynasty - Which renowned temples were built by the Ganga rulers during their reign in Odisha?
(a) Sun Temple and Lingaraja Temple
(b) Meenakshi Temple and Brihadeeswarar Temple
(c) Konark Temple and Jagannath Temple
(d) Kailasanathar Temple and Hoysaleswara Temple
Answer: (c) Konark Temple and Jagannath Temple - Who established the Gajapati dynasty in Odisha?
(a) Emperor Kapilendra Deva
(b) Marathas
(c) Mughals
(d) Karrani Dynasty
Answer: (a) Emperor Kapilendra Deva - Which dynasty was the first Muslim empire in Odisha?
(a) Karrani Dynasty
(b) Gajapati Dynasty
(c) Bhoi Dynasty
(d) Marathas
Answer: (a) Karrani Dynasty - Who took over Odisha after the Karrani Dynasty, making it a part of their empire?
(a) Marathas
(b) British
(c) Mughals
(d) Naib Nazims of Bengal
Answer: (d) Naib Nazims of Bengal - Who was the founder of the Ganga dynasty?
(a) Anantavarman Vajrahasta V
(b) Chodagangadeva
(c) Konkani Varma
(d) Narasimhadeva I
Answer: (c) Konkani Varma - Which type of forest in Odisha is permanently marked for the production of timber or other forest produce, allowing grazing and cultivation?
(a) Reserved Forest
(b) Protected Forest
(c) Unclassed Forest
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Reserved Forest - What percentage of Odisha’s total forest area is constituted by Reserved Forests according to the India State of Forest Report, 2017?
(a) 58.90%
(b) 40.75%
(c) 0.35%
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) 58.90% - Which type of forest in Odisha allows grazing and cultivation with minor restrictions?
(a) Reserved Forest
(b) Protected Forest
(c) Unclassed Forest
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Protected Forest - What is the percentage of Odisha’s total forest area constituted by Unclassed Forests according to the India State of Forest Report, 2017?
(a) 58.90%
(b) 40.75%
(c) 0.35%
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) 0.35% - What is the literal meaning of the name “Mahakantara” found in some Gupta-era inscriptions?
(a) Great River
(b) Great Plain
(c) Great Forest
(d) Great Mountain
Answer: (c) Great Forest - Which ancient region might be associated with the modern-day Kalahandi and Jeypore region?
(a) Tosali
(b) Mahakantara
(c) Utkala
(d) Kongoda
Answer: (b) Mahakantara - Which ancient region is associated with the name “Kamala Mandala” in a 13th-century inscription?
(a) Ganjam
(b) Jajpur
(c) Kalahandi
(d) Koraput
Answer: (c) Kalahandi - Which region is also known as Dakshina Kosala and may include parts of modern-day Chhattisgarh and Western Odisha?
(a) Chedi
(b) Utkala
(c) Kongoda
(d) South Kosala
Answer: (d) South Kosala - What does “Trikalinga” refer to according to copper plate inscriptions found in Sonepur?
(a) A region in the northern part of Odisha
(b) A subdivision of Kalinga
(c) Three different Kalinga states (Kalinga, South Kosala, and Kangod(a)
(d) A region in the southern part of Odisha
Answer: (c) Three different Kalinga states (Kalinga, South Kosala, and Kangod(a) - What kind of fossils are known to be found in the coal fields of Mahanadi and Ib river basins?
(a) Dinosaur bones
(b) Megaspores from the Upper Permian
(c) Trilobites from the Ordovician
(d) Ammonites from the Jurassic
Answer: (b) Megaspores from the Upper Permian - What is the primary objective of the 16th Finance Commission of India?
(a) To recommend measures for tax reforms
(b) To distribute tax revenues between the central government and the states
(c) To audit state finances
(d) To oversee state election processes
Answer: (b) - Under which Article of the Indian Constitution is the Finance Commission established?
(a) Article 280
(b) Article 290
(c) Article 270
(d) Article 300
Answer: (a) - Who is the current chairperson of the 16th Finance Commission?
(a) Dr. Manohar B. Bairagi
(b) Shri Arvind Panagariya
(c) Dr. Rajiv Kumar
(d) Mr. Ramesh Chand
Answer: (b) - What year is the 16th Finance Commission expected to be constituted?
(a) 2023
(b) 2025
(c) 2024
(d) 2026
Answer: (c) - What does ‘enemy property’ refer to in India?
(a) Property owned by foreign nationals
(b) Properties left by people who migrated to Pakistan or China
(c) Properties owned by criminals
(d) Properties seized during national emergencies
Answer: (b) - Which act established the framework for managing enemy properties in India?
(a) Enemy Property Act, 1968
(b) Enemy Property (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2017
(c) National Property Act, 1984
(d) Alien Property Act, 1952
Answer: (a) - How many enemy properties are estimated to exist in India?
(a) 5,000
(b) 10,000
(c) 13,252
(d) 20,000
Answer: (c) - When was the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights adopted by the UN General Assembly?
(a) 1948
(b) 1966
(c) 1976
(d) 1984
Answer: (b) - What is the significance of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights?
(a) It is part of the International Bill of Human Rights
(b) It provides guidelines for economic sanctions
(c) It regulates international trade
(d) It focuses on military cooperation
Answer: (a) - How many countries are parties to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights as of 2024?
(a) 150
(b) 160
(c) 174
(d) 180
Answer: (c) - What is the new name of the Durbar Hall in Rashtrapati Bhavan?
a) Ashok Mandap
b) Ganatantra Mandap
c) Durbar Mandap
d) Rashtrapati Mandap
Answer: b) Ganatantra Mandap - What historical figure is associated with the new name ‘Ashok Mandap’?
a) Emperor Akbar
b) Emperor Ashok
c) Emperor Chandragupta
d) Emperor Harsha
Answer: b) Emperor Ashok - Why was the term ‘Durbar’ replaced with ‘Ganatantra Mandap’?
a) To honor British colonial history
b) To emphasize the concept of a republic
c) To align with Islamic history
d) To preserve colonial influence
Answer: b) To emphasize the concept of a republic - What does the term ‘Ashok’ in ‘Ashok Mandap’ symbolize?
a) Conflict and warfare
b) Peace and unity
c) Colonial rule
d) Economic development
Answer: b) Peace and unity - What is the total financial outlay of the Prime Minister’s package to boost employment and skilling in the Union Budget 2024-25?
a) Rs. 1 lakh crore
b) Rs. 2 lakh crore
c) Rs. 3 lakh crore
d) Rs. 4 lakh crore
Answer: b) Rs. 2 lakh crore - Which organization will execute three of the five employment-linked schemes in the budget?
a) Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
b) Employee Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO)
c) National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC)
d) Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
Answer: b) Employee Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) - What does Scheme A in the employment-linked incentive schemes provide for first-time employees?
a) One-time wage support
b) Training vouchers
c) A one-month wage (up to Rs. 15,000) in three installments
d) A scholarship for further education
Answer: c) A one-month wage (up to Rs. 15,000) in three installments - What is the objective of Scheme D: Centrally Sponsored Skilling Scheme?
a) To create jobs in urban areas
b) To skill 20 lakh youth over five years
c) To provide loans to small businesses
d) To build infrastructure projects
Answer: b) To skill 20 lakh youth over five years - How many youth will benefit from the internship opportunities under Scheme E?
a) 50 lakh
b) 75 lakh
c) 1 crore
d) 1.5 crore
Answer: c) 1 crore - What infrastructure development is proposed to support women’s workforce participation?
a) New public transportation systems
b) Establishment of working women hostels and crèches
c) Expansion of higher education institutions
d) Increase in healthcare facilities
Answer: b) Establishment of working women hostels and crèches - By what percentage has the capital expenditure increased in the Union Budget 2024-25?
a) 5%
b) 7%
c) 9%
d) 11%
Answer: d) 11% - Which two countries signed the first-ever ‘Cultural Property Agreement’?
a) India and China
b) India and Japan
c) India and the USA
d) India and the UK
Answer: c) India and the USA - What does the Cultural Property Agreement aim to prevent?
a) Cultural exchange programs
b) Illegal trafficking of antiquities
c) Exchange of artworks
d) Travel restrictions for cultural workers
Answer: b) Illegal trafficking of antiquities - What type of materials does the import restriction under the agreement cover?
a) Only modern artworks
b) Archaeological and ethnological materials
c) Books and manuscripts only
d) Audio-visual materials
Answer: b) Archaeological and ethnological materials - What is the significance of the Designate List in the Cultural Property Agreement?
a) It lists materials eligible for export from the USA
b) It outlines materials eligible for cultural exchange
c) It includes objects to be returned to India if seized
d) It defines new import regulations for the USA
Answer: c) It includes objects to be returned to India if seized - What historical time frame does the import restriction cover for archaeological material?
a) 1000 BCE to 1500 CE
b) 500 CE to 1900 CE
c) 1.7 million years ago to 1770 CE
d) 1200 BCE to 1600 CE
Answer: c) 1.7 million years ago to 1770 CE - What is the role of US Customs in relation to the Cultural Property Agreement?
a) To facilitate cultural exchanges
b) To conduct archaeological excavations
c) To aid in the quick seizure of Indian antiquities and their repatriation
d) To promote tourism for cultural sites
Answer: c) To aid in the quick seizure of Indian antiquities and their repatriation - Which sector is specifically targeted by Scheme B in the employment-linked incentives?
a) Technology
b) Healthcare
c) Manufacturing
d) Agriculture
Answer: c) Manufacturing - What type of support is provided to employers under Scheme C?
a) Tax rebates
b) Reimbursement of Rs. 3,000 per month for EPFO contributions
c) Training programs for employees
d) Equipment subsidies
Answer: b) Reimbursement of Rs. 3,000 per month for EPFO contributions - How many Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) are planned to be upgraded under Scheme D?
a) 500
b) 800
c) 1,000
d) 1,200
Answer: c) 1,000 - What is the new name for the KALIA Scheme under the Mohan Majhi government?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Shree Anna Yojana
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
Ans: (a) CM-Kisan Yojana - Which scheme has been rebranded as Shree Anna Yojana?
(a) Millet Mission
(b) Mo School Abhiyaan
(c) Biju Setu Yojana
(d) Ama Odisha, Nabin Odisha
Ans: (a) Millet Mission - What is the new name for the Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyaan
Ans: (b) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana - Ama Odisha, Nabin Odisha has been renamed to?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Shree Anna Yojana
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyaan
Ans: (c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha - What is the new name for the Mo School Abhiyaan?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyaan
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
Ans: (b) Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyaan - Which initiative aims to attract domestic investment of over Rs. 2.5 lakh crore and FDI of over 2 billion USD by 2029?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Shree Anna Yojana
(c) Utkarsha Utkal
(d) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
Ans: (c) Utkarsha Utkal - How much has been allocated to the CM-Kisan Yojana in the Odisha Budget 2024?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (a) Rs. 1935 crore - What is the budget allocation for the Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (b) Rs. 5450 crore - How much has been allocated to the Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha initiative?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 1000 crore - What is the budget allocation for the Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyan?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (d) Rs. 332 crore - What is the main aim of the Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha initiative?
(a) Provide urban amenities in rural areas
(b) Support farmers financially
(c) Improve healthcare facilities
(d) Enhance education quality
Ans: (a) Provide urban amenities in rural areas - How much budget is allocated for the cashless treatment under the Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 500 crore
Ans: (d) Rs. 500 crore - What is the new name for the Biju Setu Yojana?
(a) Setu Bandhan Yojana
(b) Gramanchal Paribahan
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
Ans: (a) Setu Bandhan Yojana - What is the budget allocation for the Setu Bandhan Yojana?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1990 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 1990 crore - What is the new name for the LAccMI Scheme?
(a) Setu Bandhan Yojana
(b) Gramanchal Paribahan
(c) Viksit Gaon, Viksit Odisha
(d) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
Ans: (b) Gramanchal Paribahan - How much budget is allocated to the Gramanchal Paribahan scheme?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1990 crore
(d) Rs. 1085 crore
Ans: (d) Rs. 1085 crore - What is the budget allocation for the Utkarsha Utkal initiative?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 120 crore
Ans: (d) Rs. 120 crore - What is the primary goal of the Utkarsha Utkal initiative?
(a) Improve healthcare
(b) Enhance education
(c) Attract investments
(d) Support farmers
Ans: (c) Attract investments - How much budget is allocated for the PROSPER-Odisha Scheme?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 808 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 120 crore
Ans: (b) Rs. 808 crore - What is the goal of the PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana?
(a) Provide free electricity up to 300 units per month
(b) Enhance education facilities
(c) Support farmers financially
(d) Improve healthcare services
Ans: (a) Provide free electricity up to 300 units per month - Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana will be implemented in convergence with which scheme?
(a) Ayushman Bharat PM-Jay Yojana
(b) PM-Kisan Yojana
(c) Shree Anna Yojana
(d) Panchasakha Sikshya Setu Abhiyaan
Ans: (a) Ayushman Bharat PM-Jay Yojana - What is the budget allocation for cashless treatment under Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 500 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 500 crore - The new name for Biju Setu Yojana is:
(a) Setu Bandhan Yojana
(b) Setu Nirman Yojana
(c) Setu Vikas Yojana
(d) Setu Swasthya Yojana
Ans: (a) Setu Bandhan Yojana - How much has been allocated to Setu Bandhan Yojana?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1990 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 1990 crore - What is the budget allocation for Gramanchal Paribahan?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1085 crore
(d) Rs. 332 crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 1085 crore - The investment summit Make in Odisha Conclave is now known as:
(a) Utkarsha Bharat
(b) Utkarsha Odisha
(c) Utkarsha Utkal
(d) Utkal Vikas
Ans: (c) Utkarsha Utkal - The goal of the Utkarsha Utkal summit is to attract how much domestic investment by 2029?
(a) Rs. 1.5 lakh crore
(b) Rs. 2 lakh crore
(c) Rs. 2.5 lakh crore
(d) Rs. 3 lakh crore
Ans: (c) Rs. 2.5 lakh crore - What is the target for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) under Utkarsha Utkal by 2029?
(a) 1 billion USD
(b) 1.5 billion USD
(c) 2 billion USD
(d) 2.5 billion USD
Ans: (c) 2 billion USD - The PROSPER-Odisha Scheme aims to support how many entrepreneurs annually?
(a) 500
(b) 800
(c) 1000
(d) 1500
Ans: (c) 1000 - Which scheme has been implemented to promote rural entrepreneurship and startups?
(a) CM-Kisan Yojana
(b) Viksit Gaon Viksit Odisha
(c) Gopabandhu Jana Arogya Yojana
(d) PROSPER-Odisha
Ans: (d) PROSPER-Odisha - How much has been allocated to the Ama Odisha Nabin Odisha Scheme?
(a) Rs. 1935 crore
(b) Rs. 5450 crore
(c) Rs. 1000 crore
(d) Rs. 1500 crore
Ans: (d) Rs. 1500 crore - In the following question, select the odd letter/letters from the given alternatives.
(a) KQW
(b) RXD
(c) BHN
(d) AGL
Ans.(d)
Sol. +6 series except (AGL) - From the given alternatives, according to dictionary, which word will come at the LAST position?
1.Toast
2.Torpedo
3.Tongue
4.Trickle
5. Trick
(a) Trick
(b) Trickle
(c) Tongue
(d) Torpedo
Ans.(b) Trickle
Sol. Trickle(1,2,3,5,4) - In the following question, select the missing number from the given series.
13, 17, 19, 23, 29, ?
(a) 33
(b) 31
(c) 35
(d) 37
Ans.(b)
Sol. Sequence of prime numbers - A series is given with one term missing. Select the correct alternative from the given ones that will complete the series.
UY, SV, QS, OP, ?
(a) NM
(b) ML
(c) MM
(d) KL
Ans.(c)
Sol. –2, –3 series - L, M, N, O and P are sitting in a line facing east. L and M are sitting together. N is sitting at north end and O is sitting at south end. P is the neighbour of M and N. Who is third from north end?(a) L(b) O(c) M(d) P
Ans.(c)
Sol.

- Arrange the following words in a meaningful order :
- Tree
- Seed
- Flower
- Fruit
- Plant
(a) 2, 5, 1, 3, 4 (b) 1, 4, 2, 3, 5
(c) 4, 2, 3, 5, 1 (d) 2, 1, 3, 4, 5
S6. Ans. (a);
Sol.
Correct meaningful order is :-
- Seed
- Plant
- Tree
- Flower
- Fruit
- Three of the following four words are alike in a certain way and one is different. Pick the odd one.(a) Brono(b) Olomouc(c) Pilsen(d)Graz
S7. Ans.(d)
Sol. All are cities of Czech Republic except (d).
- Three of the following four letters clusters are alike in a certain way and one is different. Pick the odd one out.(a) EGIK(b) QSUW(c) YACF(d)BDFH
Ans.(c)
Sol. +2 series is followed except (c).
- Three of the following four words are alike in a certain way and one is different. Pick the odd one out.(a) Krona(b) Rupiah(c) Yen(d)Ringgit
Ans.(a)
Sol. All are Asian currencies except (a).
- Three of the following options are alike in a certain way and one is different. Find odd one out.(a) 14 : 45(b) 17 : 54(c) 23 : 69(d) 11 : 36
Ans.(c)
Sol. (first no.) x 3 + 3 = second number
All follows above logic except (c)
- Three of the following options are alike in a certain way and one is different. Find odd one out.(a) Rajasthan(b) Gujarat(c) Jammu & Kashmir(d) Delhi
Ans.(d)
Sol. All state touches the boundary of Pakistan except (d)
- Find the odd one out(a) Chrome(b) Mozilla(c) Opera mini(d) internet
Ans. (d)
Sol. Except (d), all others are browser.
- Heed : Neglect as Articulate:(a) Unclear(b) enunciate(c) eloquent(d) coherent
Ans. (a)
Sol. Words with their antonyms.
- Find the odd one out.49, 64, 81, 125, 144, 169(a) 64(b) 125(c) 169
(d) 49
Ans. (b)
Sol. Except 125, all other numbers are perfect Squares.
- Directions (15-19): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:Seven persons of different parties have voting in different days of a week which starts from Monday and ends on Sunday. At least three persons have voting after J who is from BJP. Three persons have voting between J and K who has voting just after the person who is from BSP. L has voting just before the person who is from AAP and just after the person who is from Congress. M has voting after the person who is from AAP but not on Saturday. N has voting before the person who is from SP and after the person who is from TDP. Person who is from NCP has voting before O and after P. Who among the following is from TDP?(a) J(b) K
(c) L
(d) None of these
Solutions (15-19):
Sol.
Days Persons Party Monday P TDP Tuesday J BJP Wednesday N NCP Thursday O Congress Friday L BSP Saturday K AAP Sunday M SP 15. Ans. (d)
- Which of the following party belongs to O?(a) BSP(b) Congress(c) SP(d) TDP
Ans. (b)
- In which of the following day the person who is from SP has voting?(a) Tuesday(b) Wednesday(c) Thursday(d) None of these
Ans. (d)
- How many days gap between the voting of O and P?(a) One(b) Two(c) Three(d) Four
Ans. (b)
- Four of the following five are alike in certain way and hence form a group, find the one which does not belong to that group?(a) M-SP(b) J-NCP(c) N-Congress(d) O-BSP
Ans. (a)
- If GOODNESS is coded as HNPCODTR. How can GREATNESS be written in that code?(a) HQFZSMFRT(b) HQFZUFRTM(c) HQFZUODTR(d) HQFZUMFRT
Ans. (a)
Sol.9×3–3=24
3×3–3=6
- Select the odd word/letters/number/number pair from the given alternatives.(a) Border Security Force(b) Central Reserve Police Force(c) IndoTibetan Border Police Force(d) Indian Air Force
Ans.(d)
Sol. Except Indian Air Force other three are central Armed police force.
- Select the odd word/letters/number/number pair from the given alternatives.(a) JQ(b) HS(c) BX(d) GT
Ans.(c)
Sol. Except BX other three are pair of corresponding opposite word.
- Select the odd word/letters/number/number pair from the given alternatives.(a) 8179(b) 7147(c) 8135(d) 9113
Ans.(d)
Sol. The middle term is sum of first and last term.
8179= 8+9=17
- A series is given with one term missing. Choose the correct alternative from the given ones that will complete the series.Hindi, ?, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil(a) English(b) Bengali(c) French
(d) German
Ans.(b)
Sol. Series of Indian regional language.
- Find the odd pair of letters from the given alternatives.
(a) Dollar
(b)Rupees
(c)Pound
(d)Gram
Ans: (d)Gram
Sol: All except Gram are names of currencies, while Gram is a unit of weight. - 81, 64, 100, 125, 121, ?
(a)162
(b)216
(c)282
(d)222
Ans : (b)
Sol: The pattern followed is :
92 = 81
43 = 64
102 =100
53 = 125
112 = 121
The next term will be 63 = 216. - 64: 512 : 49 : ?
(a) 312
(b) 372
(c) 343
(d) 332
Ans − (c)
Sol: Here relationship is 82 : 83 : 72: 73 - Find the odd one out from the given options.
(a) Arctic
(b) Atlantic
(c) Indian
(d) Greenland
Ans: Option (d)
Sol: a, b and c are oceans. - Choose the odd word from the given words.
(a)Leg
(b)Hand
(c) Brain
(d)Ear
Ans: Option (c) Brain
Sol: Except Brain, All are external body organs - A series is given with one term missing term. Choose the correct alternative
A, D, G, J, M, ?
(a)P
(b)M
(c)N
(d)W
Ans: (a)
Sol: Pattern follows,
A+3=D
D+3=G
G+3=J
J+3=M
M+3=P - Giddha is a folk dance associated with which region?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Kerala
(c) Punjab
(d) Karnataka
Answer: (c) Punjab - Ghoomar is traditionally performed by women from which Indian state?
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) West Bengal
Answer: (b) Rajasthan - Garba, a dance performed in a circle with batons, originates from which state?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Gujarat
(c) Punjab
(d) Bihar
Answer: (b) Gujarat - Dandiya Ras, known for its vigorous movements and use of batons, is a traditional dance of which state?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Kerala
Answer: (a) Gujarat - Lavani, a popular dance form known for its powerful rhythms and traditional attire, is from which state?
(a) Odisha
(b) Gujarat
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Karnataka
Answer: (c) Maharashtra - Nautanki, a traditional folk theatre form, is prevalent in which states?
(a) Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh
(b) Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar
(c) Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka
(d) Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh
Answer: (b) Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar - Bhavai, a traditional dance-drama, is performed in which Indian state?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) West Bengal
(d) Rajasthan
Answer: (a) Gujarat - Tamasha is a traditional folk theatre from which Indian state?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Karnataka
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer: (b) Maharashtra - Jatra, a popular form of folk theatre, is associated with which regions?
(a) Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu
(b) West Bengal, Odisha, Bihar
(c) Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab
(d) Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana
Answer: (b) West Bengal, Odisha, Bihar - Yakshagana, known for its elaborate costumes and expressive dance, is from which Indian state?
(a) Kerala
(b) Karnataka
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Tamil Nadu
Answer: (b) Karnataka - Which of the following is not a work by Kalidasa?
(a) Abhijnanashakuntala
(b) Vikramorvashi
(c) Malavikagnimitra
(d) Mudrarakṣhasa
Ans: (d) Mudrarakṣhasa - Who wrote “Raghuvamsha”?
(a) Vishakhadatta
(b) Kalidasa
(c) Bhasa
(d) Bharavi
Ans: (b) Kalidasa - What is the meaning of “Mudrarakṣhasa”?
(a) The Little Clay Cart
(b) The Ring of the Demon
(c) The Tale of the Ten Princes
(d) The Adventures of Shakuntala
Ans: (b) The Ring of the Demon - Who among the following is both a king and a poet?
(a) Kalidasa
(b) Bhasa
(c) Shudraka
(d) Harisena
Ans: (c) Shudraka - Which play is attributed to Shudraka?
(a) Mrichchhakatika
(b) Vikramorvashi
(c) Malavikagnimitra
(d) Meghaduta
Ans: (a) Mrichchhakatika - Who wrote the poems praising the bravery of Samudra Gupta?
(a) Kalidasa
(b) Harisena
(c) Dandin
(d) Bharavi
Ans: (b) Harisena - Which of the following works was written by Bhasa?
(a) Kavyadarshana
(b) Rāvaṇavadha
(c) Nitishatak
(d) None of the above
Ans: (d) None of the above - “Kiratarjuniya” is associated with which writer?
(a) Magha
(b) Bhatrihari
(c) Bharavi
(d) Ishwar Krishna
Ans: (c) Bharavi - Who is the author of “Dasakumarcharita”?
(a) Bhatti
(b) Dandin
(c) Vyasa
(d) Vatsyayana
Ans: (b) Dandin - Which work is attributed to Vatsyayana?
(a) Sankyakarika
(b) Vakyapadiya
(c) Nyaya Sutra Bhashya
(d) Sisupala
Ans: (c) Nyaya Sutra Bhashya - Odissi is a classical Indian dance form originating from which state?
(a) Kerala
(b) Karnataka
(c) Odisha
(d) Tamil Nadu
Ans. (c) Odisha - Odissi is considered a dance of which theme?
(a) War
(b) Harvest
(c) Love
(d) Devotion
Ans. (c) Love - The dance style called Odhra Magadha is associated with which classical dance form?
(a) Bharatanatyam
(b) Kathakali
(c) Kuchipudi
(d) Odissi
Ans. (d) Odissi - Which ancient text mentions Odhra Magadha as a southeastern style of classical dance?
(a) Vedas
(b) Ramayana
(c) Natya Shastra
(d) Mahabharata
Ans. (c) Natya Shastra - In which century can archaeological evidence of Odissi be found in the caves of Khandagiri and Udayagiri?
(a) 1st century
(b) 2nd century
(c) 3rd century
(d) 4th century
Ans. (b) 2nd century - Which stances form the basis of Odissi dance movements?
(a) Chowk and Tribhanga
(b) Mudra and Hasta
(c) Tandava and Lasya
(d) Nritta and Abhinaya
Ans. (a) Chowk and Tribhanga - The Chowk stance in Odissi is described as which of the following?
(a) Feminine and delicate
(b) Masculine and balanced
(c) Elegant and flowing
(d) Rigid and symmetrical
Ans. (b) Masculine and balanced - What kind of position is the Tribhanga in Odissi?
(a) A balanced stance with squared shoulders
(b) A feminine posture with three bends
(c) A neutral standing position
(d) A rigid and straight posture
Ans. (b) A feminine posture with three bends - Which texts are significant for the stylization of Odissi dance?
(a) Vedas and Upanishads
(b) Natya Shastra and Abhinaya Darpana
(c) Ramayana and Mahabharata
(d) Sangam literature
Ans. (b) Natya Shastra and Abhinaya Darpana - Odissi dance is often depicted in sculptures from which periods?
(a) 1st to 3rd century
(b) 2nd to 10th century
(c) 3rd to 5th century
(d) 4th to 6th century
Ans. (b) 2nd to 10th century - Why are the Western Ghats called Ghats?
(a) Because they have numerous temples
(b) Because they are a series of mountain passes
(c) Because they are located near the coast
(d) Because they are older than the Himalayas
Ans. (b) Because they are a series of mountain passes - Why are the Western Ghats important?
(a) They have a high population density
(b) They contain large deposits of minerals
(c) They perform important hydrological and watershed functions
(d) They are a famous tourist destination
Ans. (c) They perform important hydrological and watershed functions - How many states are covered by the Western Ghats?
(a) Four
(b) Five
(c) Six
(d) Seven
Ans. (c) Six - What is another name given to the Western Ghats?
(a) Sahyadri
(b) Vindhyas
(c) Aravalli
(d) Shivalik
Ans. (a) Sahyadri - Are the Western Ghats a continuous or discontinuous range of mountains?
(a) Continuous
(b) Discontinuous
(c) Both continuous and discontinuous
(d) None of the above
Ans. (a) Continuous - What is the speciality of Western Ghats?
(a) High altitude
(b) High biodiversity and endemism
(c) Numerous rivers
(d) Unique soil type
Ans. (b) High biodiversity and endemism - What kind of forests are found in the Western Ghats?
(a) Mangrove forests
(b) Temperate forests
(c) Evergreen and deciduous forests
(d) Coniferous forests
Ans. (c) Evergreen and deciduous forests - How were the Western Ghats formed?
(a) Volcanic activity
(b) Erosion of the Gondwana supercontinent
(c) Collision of tectonic plates
(d) Deposition of sediments
Ans. (b) Erosion of the Gondwana supercontinent - Which is the highest peak of Western Ghats?
(a) Doddabetta
(b) Mullayanagiri
(c) Anamudi
(d) Agasthyamalai
Ans. (c) Anamudi - Are the Western Ghats older than the Himalayas?
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) They are of the same age
(d) None of the above
Ans. (a) Yes - What is the new national highway number for the old NH 1 A and NH 1 D?
(a) NH 2
(b) NH 1
(c) NH 4
(d) NH 19
Answer: (b) NH 1 - NH 1 B has been renumbered as which new national highway?
(a) NH 244
(b) NH 223
(c) NH 50
(d) NH 114
Answer: (a) NH 244 - Which new national highway number corresponds to the old NH 2?
(a) NH 50
(b) NH 19
(c) NH 217
(d) NH 748
Answer: (b) NH 19 - NH 2A is now known as which new national highway?
(a) NH 60
(b) NH 519
(c) NH 4
(d) NH 348
Answer: (b) NH 519 - What is the new number for the old NH 2B?
(a) NH 223
(b) NH 114
(c) NH 5
(d) NH 60
Answer: (b) NH 114 - NH 4 A has been renumbered as which new national highway?
(a) NH 165
(b) NH 748
(c) NH 217
(d) NH 6
Answer: (b) NH 748 - NH 4 B corresponds to which new national highway number?
(a) NH 348
(b) NH 5
(c) NH 6
(d) NH 223
Answer: (a) NH 348 - What is the new number for the old NH 5?
(a) NH 6
(b) NH 49
(c) NH 60
(d) NH 16
Answer: (d) NH 16 - NH 6 has been renumbered to which new highway?
(a) NH 60
(b) NH 223
(c) NH 5
(d) NH 4
Answer: (a) NH 60 - NH 16 (part of the Golden Quadrilateral) is renumbered from which old highway?
(a) NH 217
(b) NH 5
(c) NH 60
(d) NH 2
Answer: (b) NH 5 - Which of the following plains is characterized by gravel and un-assorted sediment deposits and is generally unsuitable for cultivation?
(a) The Tarai Tract
(b) The Bhangar Plains
(c) The Khadar Plains
(d) The Bhabar Plains
Answer: (d) The Bhabar Plains - Which physiographic division of the Great North Indian Plains is known for its high rainfall, excessive humidity, and thick forests, making it rich in humus and organic matter?
(a) The Tarai Tract
(b) The Delta Plains
(c) The Bhangar Plains
(d) The Bhabar Plains
Answer: (a) The Tarai Tract - What is the main characteristic of the Khadar Plains?
(a) They are older alluvial plains.
(b) They consist of gravel and un-assorted sediments.
(c) They are enriched by fresh deposits of silt every year.
(d) They are covered with thick forests.
Answer: (c) They are enriched by fresh deposits of silt every year. - Which of the following areas is known for containing calcium carbonate nodules called ‘Kankars’?
(a) The Khadar Plains
(b) The Bhabar Plains
(c) The Delta Plains
(d) The Bhangar Plains
Answer: (d) The Bhangar Plains - The Delta Plains are an extension of which type of land?
(a) The Tarai Tract
(b) The Khadar Plains
(c) The Bhangar Plains
(d) The Bhabar Plains
Answer: (b) The Khadar Plains - In which division of the Great North Indian Plains is the soil enriched with humus and suitable for crops like wheat, rice, and maize?
(a) The Tarai Tract
(b) The Khadar Plains
(c) The Bhabar Plains
(d) The Bhangar Plains
Answer: (b) The Khadar Plains - The Bhangar Plains were formed during which geological period?
(a) Pleistocene
(b) Holocene
(c) Miocene
(d) Eocene
Answer: (a) Pleistocene - What are the ‘Chars’ and ‘Bills’ in the context of the Delta Plains?
(a) Types of soil
(b) Old and new mud deposits
(c) Uplands and marshy areas
(d) Types of forests
Answer: (c) Uplands and marshy areas - Which physiographic division is described as a marshy tract with a malarial climate and is known for its rich flora and fauna?
(a) The Tarai Tract
(b) The Bhabar Plains
(c) The Bhangar Plains
(d) The Delta Plains
Answer: (a) The Tarai Tract - Which of the following plains is primarily used for the cultivation of crops such as sugarcane, rice, wheat, maize, and oilseeds?
(a) The Bhabar Plains
(b) The Delta Plains
(c) The Khadar Plains
(d) The Bhangar Plains
Answer: (c) The Khadar Plainsy - Which vitamin deficiency causes scurvy?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B1
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Ans: (c) Vitamin C - What is the deficiency disease associated with Vitamin D?
(a) Beriberi
(b) Rickets
(c) Pellagra
(d) Scurvy
Ans: (b) Rickets - Which vitamin is also known as thiamine?
(a) Vitamin B1
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin B3
(d) Vitamin B6
Ans: (a) Vitamin B1 - What deficiency disease is caused by a lack of Vitamin B1?
(a) Pellagra
(b) Beriberi
(c) Scurvy
(d) Rickets
Ans: (b) Beriberi - Which gas is responsible for the greenhouse effect?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen
Ans: (b) Carbon dioxide - What is the basic unit of life?
(a) Cell
(b) Atom
(c) Molecule
(d) Organ
Ans: (a) Cell - What is the SI unit of force?
(a) Joule
(b) Newton
(c) Watt
(d) Ohm
Ans: (b) Newton - Which organelle is responsible for protein synthesis in a cell?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Mitochondrion
(d) Ribosome
Ans: (d) Ribosome - What is the process by which cells divide to form new cells?
(a) Respiration
(b) Digestion
(c) Replication
(d) Mitosis
Ans: (d) Mitosis - Which molecule carries genetic information in a cell?
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) Protein
(d) Lipid
Ans: (a) DNA - What is the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties?
(a) Molecule
(b) Atom
(c) Compound
(d) Ion
Ans: (b) Atom - Which acid is found in citrus fruits?
(a) Sulfuric acid
(b) Nitric acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Ans: (c) Citric acid - What is the pH value of a neutral substance?
(a) 7
(b) 1
(c) 14
(d) 0
Ans: (a) 7 - What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
(a) 300,000 km/s
(b) 150,000 km/s
(c) 3,000 km/s
(d) 30,000 km/s
Ans: (a) 300,000 km/s - What is the phenomenon where a wave bends as it passes from one medium to another?
(a) Diffraction
(b) Dispersion
(c) Reflection
(d) Refraction
Ans: (d) Refraction - What is the energy of motion called?
(a) Potential energy
(b) Kinetic energy
(c) Thermal energy
(d) Mechanical energy
Ans: (b) Kinetic energy - Which molecule carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis?
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) tRNA
(d) rRNA
Ans: (c) tRNA - What is the process by which DNA is copied into mRNA?
(a) Translation
(b) Transcription
(c) Replication
(d) Mutation
Ans: (b) Transcription - Which enzyme is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication?
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) Helicase
(c) Ligase
(d) RNA polymerase
Ans: (b) Helicase - What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
(a) DNA → RNA → Protein
(b) RNA → DNA → Protein
(c) Protein → RNA → DNA
(d) DNA → Protein → RNA
Ans: (a) DNA → RNA → Protein - What is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis?
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) Carotene
(c) Xanthophyll
(d) Anthocyanin
Ans: (a) Chlorophyll - What is the main component of natural gas?
(a) Methane
(b) Ethane
(c) Propane
(d) Butane
Ans: (a) Methane - What is the boiling point of water at sea level?
(a) 90°C
(b) 100°C
(c) 110°C
(d) 120°C
Ans: (b) 100°C - Which planet is known as the Red Planet?
(a) Venus
(b) Mars
(c) Jupiter
(d) Saturn
Ans: (b) Mars - What is the chemical formula for table salt?
(a) NaCl
(b) KCl
(c) NaBr
(d) KBr
Ans: (a) NaCl - What is the hardest natural substance on Earth?
(a) Gold
(b) Iron
(c) Diamond
(d) Platinum
Ans: (c) Diamond - What is the main function of red blood cells?
(a) Transport oxygen
(b) Fight infections
(c) Clot blood
(d) Produce hormones
Ans: (a) Transport oxygen - What is the chemical symbol for iron?
(a) Fe
(b) Ir
(c) In
(d) I
Ans: (a) Fe - What is the powerhouse of the cell?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Ribosome
(c) Mitochondrion
(d) Golgi apparatus
Ans: (c) Mitochondrion - What is the study of fungi called?
(a) Mycology
(b) Bacteriology
(c) Virology
(d) Phycology
Ans: (a) Mycology - What is the unit of electrical resistance?
(a) Volt
b) Ampere
(c) Ohm
(d) Watt
Ans: (c) Ohm - Where was Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj born?
(a) Raigarh
(b) Satara
(c) Shivneri (Poona)
(d) Bijapur
Ans: (c) Shivneri (Poona) - In which year did Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj assume full charge of his jagir?
(a) 1640 CE
(b) 1647 CE
(c) 1650 CE
(d) 1657 CE
Ans: (b) 1647 CE - Who was the Maratha chief from whom Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj conquered Javli?
(a) Shahji Bhonsle
(b) Afzal Khan
(c) Chandra Rao More
(d) Shaista Khan
Ans: (c) Chandra Rao More - Which fort was captured by Maratha troops after the death of Afzal Khan?
(a) Purander
(b) Kondana
(c) Panhala
(d) Torna
Ans: (c) Panhala - Which Mughal governor did Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj carry out a daring night attack on in 1663 CE?
(a) Shaista Khan
(b) Raja Jai Singh
(c) Adil Shah
(d) Aurangzeb
Ans: (a) Shaista Khan - In which year did Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj first attack the Mughal port, Surat?
(a) 1659 CE
(b) 1664 CE
(c) 1667 CE
(d) 1670 CE
Ans: (b) 1664 CE - What was the result of the Treaty of Purander in 1665 CE?
(a) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj surrendered all his forts to the Mughals
(b) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj became an ally of the Bijapur Sultanate
(c) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj retained 12 forts under Mughal service and loyalty
(d) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was imprisoned by Aurangzeb
Ans: (c) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj retained 12 forts under Mughal service and loyalty - In which year did Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj crown himself and assume the title “Chhatrapati”?
(a) 1670 CE
(b) 1674 CE
(c) 1676 CE
(d) 1680 CE
Ans: (b) 1674 CE - Which regions did Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj capture during his expedition into the Carnatic in 1676 CE?
(a) Surat and Berar
(b) Ginjee and Vellore
(c) Purander and Khandesh
(d) Kolhapur and Satara
Ans: (b) Ginjee and Vellore - What major event occurred in Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s life in 1665 CE after visiting Agra?
(a) He was crowned as Chhatrapati
(b) He attacked Surat
(c) He was imprisoned by Aurangzeb but managed to escape
(d) He signed the Treaty of Purander
Ans: (c) He was imprisoned by Aurangzeb but managed to escape - Who was the Nawab of Bengal who opposed the British due to the misuse of dastaks and captured Fort William in 1756 CE?
(a) Alivardi Khan
(b) Mir Jafar
(c) Mir Qasim
(d) Siraj ud Daulah
Answer: (d) Siraj ud Daulah - What significant event occurred on 23rd June 1757 CE?
(a) The signing of the Treaty of Allahabad
(b) The Battle of Buxar
(c) The Battle of Plassey
(d) The capture of Fort William
Answer: (c) The Battle of Plassey - Who was the British commander who emerged victorious at the Battle of Plassey?
(a) Robert Clive
(b) Warren Hastings
(c) Sir John Clive
(d) George Monck
Answer: (a) Robert Clive - What was the main reason for the British victory in the Battle of Plassey?
(a) Superior military tactics
(b) Treachery of Mir Jafar
(c) High morale of British troops
(d) Advanced weaponry
Answer: (b) Treachery of Mir Jafar - What was the outcome of the Battle of Buxar for Mir Qasim?
(a) He was reinstated as Nawab of Bengal
(b) He was defeated and fled to Awadh
(c) He was captured and executed
(d) He successfully allied with the British
Answer: (b) He was defeated and fled to Awadh - On what date did the Battle of Buxar take place?
(a) 22nd October 1764
(b) 23rd June 1757
(c) 17th December 1764
(d) 1st January 1765
Answer: (a) 22nd October 1764 - What was the main administrative change introduced by Robert Clive in Bengal after the Battle of Buxar?
(a) The end of dual government
(b) Establishment of a new tax system
(c) Introduction of Dual Government
(d) Imposition of direct British rule
Answer: (c) Introduction of Dual Government - According to the Treaty of Allahabad, what was the status of Shuja-ud-Daulah and his state?
(a) He retained control of Awadh without any conditions
(b) He was replaced by a British nominee
(c) He had to pay Rs 50 Lakhs and maintain English troops
(d) He was granted a pension by the British
Answer: (c) He had to pay Rs 50 Lakhs and maintain English troops - What rights were granted to the English under the Treaty of Allahabad regarding Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa?
(a) Rights to administer the provinces directly
(b) Rights to collect revenue
(c) Rights to establish military bases
(d) Rights to trade without restrictions
Answer: (b) Rights to collect revenue - Who was the Mughal Emperor that granted the Diwani rights of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to the English?
(a) Shah Alam II
(b) Aurangzeb
(c) Farrukhsiyar
(d) Akbar
Answer: (a) Shah Alam II - Who administered Bengal in place of Mir Jafar during the Battle of Buxar?
(a) Shuja-Ud-Daulah
(b) Shah Alam II
(c) Mir Qasim
(d) Robert Clive
Answer: (c) Mir Qasim
Explanation: Mir Qasim was the Nawab of Bengal who replaced Mir Jafar. He was discontent with the misuse of dastak and farmans by the English and sought to challenge their authority. - Which ruler formed a confederacy with Mir Qasim and Shah Alam II?
(a) Mir Jafar
(b) Shuja-Ud-Daulah
(c) Robert Clive
(d) Hector Munro
Answer: (b) Shuja-Ud-Daulah
Explanation: Shuja-Ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Awadh, joined forces with Mir Qasim and Shah Alam II in an attempt to drive the British out of Bengal. - Who led the English forces in the Battle of Buxar?
(a) Robert Clive
(b) Hector Munro
(c) Mir Jafar
(d) Mir Qasim
Answer: (b) Hector Munro
Explanation: Hector Munro was the British Army Major who commanded the English forces during the Battle of Buxar. - What was the outcome of the Battle of Buxar on October 22, 1764?
(a) The English forces were defeated.
(b) Mir Qasim was victorious.
(c) The English forces won the battle.
(d) The battle ended in a stalemate.
Answer: (c) The English forces won the battle.
Explanation: The English, under Major Hector Munro, emerged victorious in the Battle of Buxar, leading to significant changes in the control of Bengal. - Which treaty concluded the Battle of Buxar?
(a) Treaty of Paris
(b) Treaty of Allahabad
(c) Treaty of Versailles
(d) Treaty of Delhi
Answer: (b) Treaty of Allahabad
Explanation: The Treaty of Allahabad was signed in 1765, marking the end of the conflict and outlining the terms of settlement between the English and the defeated rulers. - What were the key terms of the Treaty of Allahabad between Robert Clive and Shuja-Ud-Daulah?
(a) Shuja-Ud-Daulah had to surrender Midnapore and Chittagong.
(b) Shuja-Ud-Daulah had to pay Rs 50 lakh as war indemnity.
(c) Shuja-Ud-Daulah was granted the Diwani of Bengal.
(d) Shuja-Ud-Daulah had to cede Delhi to the British.
Answer: (b) Shuja-Ud-Daulah had to pay Rs 50 lakh as war indemnity.
Explanation: As part of the treaty terms, Shuja-Ud-Daulah was required to pay a substantial indemnity to the British and surrender Allahabad and Kara to Shah Alam II. - According to the Treaty of Allahabad, what was Shah Alam II required to do?
(a) Cede Bengal to Shuja-Ud-Daulah.
(b) Reside at Allahabad and issue a Farman granting the Diwani of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to the East India Company.
(c) Pay Rs 50 lakh to the Nawab of Awadh.
(d) Hand over Delhi to the English.
Answer: (b) Reside at Allahabad and issue a Farman granting the Diwani of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to the East India Company.
Explanation: Shah Alam II was required to live in Allahabad and issue a Farman that granted the British East India Company control over Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa in exchange for an annual payment. - What was the fate of Mir Jafar after the Battle of Buxar?
(a) He was reinstated as Nawab of Bengal.
(b) He was removed from power and his minor son was appointed Nawab.
(c) He was captured and executed.
(d) He was exiled to England.
Answer: (b) He was removed from power and his minor son was appointed Nawab.
Explanation: After the battle, Mir Jafar was removed from his position, and his minor son, Najimud-Daula, was appointed as Nawab of Bengal, though real power remained with the English. - What was the significance of the Battle of Buxar for the English East India Company?
(a) It marked the end of British influence in India.
(b) It consolidated British control over northern India.
(c) It led to the decline of British military power.
(d) It resulted in the withdrawal of British forces from India.
Answer: (b) It consolidated British control over northern India.
Explanation: The victory at the Battle of Buxar solidified the East India Company’s dominance in northern India and paved the way for greater control over the region. - Which of the following was NOT a term of the Treaty of Allahabad?
(a) Shuja-Ud-Daulah had to surrender Allahabad and Kara.
(b) Shah Alam II was to be granted the Diwani of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa.
(c) The English were allowed duty-free trade in Bengal.
(d) The English were required to pay Rs 53 lakh for Nizamat functions.
Answer: (c) The English were allowed duty-free trade in Bengal.
Explanation: While the English were allowed trade in Bengal with a minor duty on salt, the treaty did not grant them complete duty-free trade. - How many farmers in Andhra Pradesh benefited from the PM Fasal Bima Yojana in 2022-23?
(a) 3,00,000
(b) 3,49,633
(c) 4,00,000
(d) 3,75,000
Ans: (b) 3,49,633 - What innovative installation has Periyar Tiger Reserve recently implemented?
(a) Solar Panels
(b) Geothermal Energy
(c) Wind Turbine
(d) Hydroelectric Dam
Ans: (c) Wind Turbine - How many new sites were added to the UNESCO World Heritage list during the 46th session in New Delhi?
(a) 18
(b) 20
(c) 24
(d) 28
Ans: (c) 24 - In addition to being the 2nd largest aluminium producer, what other rankings does India hold in lime and iron ore production?
(a) 3rd in lime, 4th in iron ore
(b) 4th in lime, 3rd in iron ore
(c) 3rd in lime, 5th in iron ore
(d) 5th in lime, 4th in iron ore
Ans: (a) 3rd in lime, 4th in iron ore - Who announced the launch of the Electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS)?
(a) Prime Minister Narendra Modi
(b) Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman
(c) Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh
(d) Home Minister Amit Shah
Ans: (c) Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh - When and where was the Rashtriya Hindi Vigyan Sammelan 2024 held?
(a) June 25-26, Mumbai
(b) July 30-31, Bhopal
(c) August 15-16, New Delhi
(d) September 10-11, Chennai
Ans: (b) July 30-31, Bhopal - On which date did the CCEA approve the construction of eight new national high-speed corridor projects?
(a) August 2, 2024
(b) July 20, 2024
(c) June 15, 2024
(d) May 10, 2024
Ans: (a) August 2, 2024










