Algebra is a branch of Mathematics that substitutes letters for numbers. In the school education, Algebra Formulas form the foundation of numerous topics of mathematics. Topics like equations, quadratic equations, polynomials, coordinate geometry, calculus, trigonometry, and probability extensively depend on algebraic formulas for understanding and for solving complex problems. Download the Algebra Formulas PDF along with all Algebraic Identities Formula Charts in one place from here.
Algebra Formula
One of the most crucial areas of mathematics is algebra. Numerous disciplines, including quadratic equations, polynomials, coordinate geometry, calculus, trigonometry, probability, and others, can be solved using algebraic formulas. In these formulas, we used numbers along with letters. The most common letters used in algebraic equations and problems are X, Y, A, and B. These formulas enable us to quickly and efficiently tackle time-consuming algebraic problems. Here, we include all significant Algebraic formulas together with their solutions, so that students can access them all in one place.
Algebra Formulas Example
Algebra formulas are basically algebra equations formed by algebraic and mathematical phrases and symbols. These algebraic formulas contain an unknown variable x, which can be generated while simplifying an equation. These algebraic equations efficiently solve complicated algebraic computations.
For example,
(a+b)³ =a³+ 3a²b+3ab²+b³
In the above formulas, both sides are individual algebraic equations. Where ( a³ + 3a²b+3ab²+b³ ) is the simplified expression of (a+b)³.
Algebra Formulas Identities
In algebra formulas, an identity is an equation that is always true regardless of the values assigned to the variables. Algebraic Identity means that the left-hand side (LHS) of the equation is identical to the right-hand side (RHS) of the equation and for all values of the variables. Algebraic identities are solved for the values of unknown variables. Here are some commonly used algebraic identities:
Algebraic Identities Formula
- (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
- (a + b)(a – b) = a2 – b2
- (x + a)(x + b) = x2 + x(a + b) + ab
Algebra Formulas For Squares of Class 10
Here are some important formulas involving squares.
• a²– b² = (a – b)(a + b)
• (a + b)²= a²+ 2ab + b²
• a²+ b²= (a + b)²– 2ab
• (a – b)² = a²– 2ab+ b²
• (a + b + c)² = a² + b² + c²+ 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
• (a – b – c)² = a²+ b²+ c²– 2ab + 2bc – 2ca
Algebra Formulas for Cube
Here are some Algebraic formulas involving cubes.
• (a + b)³ = a³+ 3a²b + 3ab²+ b³
• (a + b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3ab(a + b)
• (a – b)³= a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³
• (a – b)³= a³ – b³ – 3ab(a – b)
• a³ – b³ = (a – b)(a²+ ab + b²)
• a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a²– ab + b²)
Some more Algebra formulas are –
• (a + b)⁴= a⁴+ 4a³b + 6a²b² + 4ab³ + b²
• (a – b)⁴= a4 – 4a³b + 6a²b² – 4ab³+ b⁴
• a⁴ – b⁴= (a – b)(a + b)(a² + b²)
• a⁵ – b⁵= (a – b)(a⁴ + a³b + a²b² + ab³+ b⁴)
Algebra Formula for Natural Numbers
Algebra formulas for Natural Numbers. Except for 0 and negative numbers, the rest of the numbers [ 2 to infinity] in the number system that humans can count are known as Natural Numbers. Some algebraic formulas are applied when performing operations on natural numbers. They are.
Consider n to be a natural number.
- (an – bn )= (a – b)(an-1 + an-2b+…+ bn-2a + bn-1)
- ( an + bn)= (a + b)(an-1 – an-2b +…+ bn-2a – bn-1) [ where n is even , (n = k + 1) ]
- (an + bn )= (a + b)(an-1 – an-2b +an-3b2…- bn-2a + bn-1) [ where n is odd , (n = 2k + 1) ]
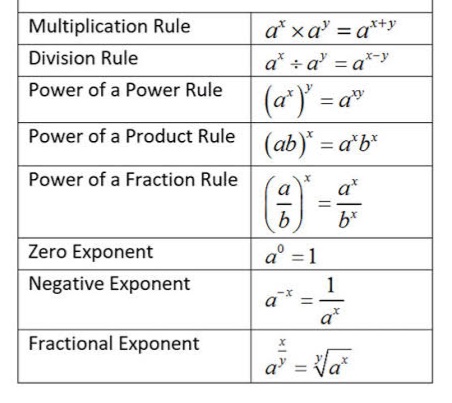
Laws of Exponents
In Algebra, An Exponent or power is used to demonstrate the repeated multiplication of a number. Such as 3×3×3×3 can be written as 3⁴ where 4 is the exponent of 3. In general, exponents or powers indicate how many times a number can be multiplied. There are various rules to operate an exponent for addition, subtraction, and multiplication, which are easily solved by algebraic formulas.
Algebra Formulas for Quadric equations
Quadratic equations are one of the most important topics in the syllabus of classes 9 and 10. To find the root of the given quadratic equations, we used the following formulas
If ax²+bx+c =0 is a quadratic equation, then
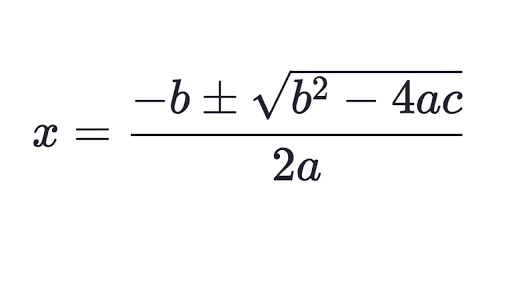
From the above formula we can conclude that , If the roots of the quadric equation are α and β
1. The equation will be (x − α)(x − β) = 0,
2. The value of (α + β ) = (-b / a) and α × β = (c / a).
Algebra Formulas For Irrational Numbers
The formulas used to solve equations based on Irrational Numbers are as follows
- √ab = √a √b
- √a/b =√a / √b
- ( √a +√b ) ( √a – √b ) = a-b
- ( √a +√b )²= a + 2 √ab + b
- ( a +√b )( a -√b )= a² – b
Algebra Formulas List/Chart
Here is a list of all important Algebraic formulas. Students must go through the list to solve difficult algebraic equations very quickly.
| Important Formulas | |
| 1 | a²– b² = (a – b)(a + b) |
| 2 | (a + b)²= a²+ 2ab + b² |
| 3 | a²+ b²= (a + b)²– 2ab |
| 4 | (a – b)² = a²– 2ab+ b² |
| 5 | (a + b + c)² = a² + b² + c²+ 2ab + 2bc + 2ca |
| 6 | (a – b – c)² = a²+ b²+ c²– 2ab + 2bc – 2ca |
| 7 | (a + b)³ = a³+ 3a²b + 3ab²+ b³ |
| 8 | (a + b)³ = a³ + b³ + 3ab(a + b) |
| 9 | (a – b)³= a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³ |
| 10 | (a – b)³= a³ – b³ – 3ab(a – b) |
| 11 | a³ – b³ = (a – b)(a²+ ab + b²) |
| 12 | a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a²– ab + b²) |
| 13 | (a + b)⁴= a⁴+ 4a³b + 6a²b² + 4ab³ + b² |
| 14 | (a – b)⁴= a4 – 4a³b + 6a²b² – 4ab³+ b⁴ |
| 15 | a⁴ – b⁴= (a – b)(a + b)(a² + b²) |
| 16 | a⁵ – b⁵= (a – b)(a⁴ + a³b + a²b² + ab³+ b⁴) |
Some commonly used Algebraic formulas in maths
Below, we have shared some derivations of frequently used Algebra formulas for your better understanding.
a+b+c Whole Square Formula- (a+b+c)^2 Formula
The square of the sum of three terms can be expanded using the formula for the square of a trinomial:
So, is equal to the sum of the squares of the individual terms (, , ) and twice the products of the pairs of terms (, , ).
This expansion holds true for any values of, , and.
a-b Whole Square
The square of the difference between two terms can be expanded using the formula for the square of a binomial:
So, is equal to the square of the first term (), minus twice the product of the two terms (), and the square of the second term ().
This expansion holds true for any values of and.
a+b Whole Square
The square of the sum of two terms, , can be expanded using the formula for the square of a binomial:
So, is equal to the sum of the squares of the individual terms ( and ) and twice the product of the terms ().
This expansion holds true for any values of a and .
Implementation of Algebra All Formulas with Examples
Example 1 : Find the value 20²- 15²
Solution: To solve the equation ,the formula we use is
a² -b² = (a+b) (a-b)
= (20+15)(20-15)
= 35 × 5
= 175 (Answer)
Example 2 : (x-y) =2 and x²+ y² =20 then find the value of x and y [ where x,y >0 ]
Solution: Here , x²+ y² =20
(x-y)² +2xy =20
Or, (2)²+ 2xy =20
Or, 2xy = 20-4 = 16
Or,xy = 8
Now, (x+y)²= (x-y)² +4xy = (2)² +4.8 =36
Or,x+y = ± 6
So, x+y = 6 [x,y >0 ] ….(1)
We also get , x- y =2 ……(2)
Solving two equations we get ,
x = 4 and y = 2 (Answer)
Example 3 : Divide( a³ + b³ + c³ – 3abc )by( a+b+c )and the quotient.Determine the magnitude.
Solution: a+b³ + c3 – 3abc
=(a+b+c)(a²+b²+c2-ab-ac-bc)
Determinant quotient =
[(a+b+c)(a²+b²+c²-ab-ac-bc)] ÷ (a+b+c)
= a²+b²+c²-ab-be-ca.
Magnitude of quotient is 2. (Answer)
Example 4
Find their successive product (x + y), (x – y), (x² + y²).
Solution :Determinant serial product =
(x + y) (x – y) (x² + y²)
= (x²-y²)(x² + y²)
= (x²)² – (y²)²
= x⁴ – y ⁴.( Answer)
Some Questions of Algebra Formula
1. If x+y = 3 and xy = 2, what is the value of (x – y) ² ?
2. If a+b = 8 and ab = 15, what will be the values of a and b?
3. If a+b = 5 and ab = 6, Find the value of a² – b² ?
4. If x = 29 and y = 14, what is the value of (4x² + 9y²+ 12xy )?
All Algebraic Identities
Algebraic identities are equations that are true for all values of the variables involved. Here are some of the most important algebraic identities:
1. Basic Algebraic Identities
- Square of a Sum:
- Square of a Difference:
- Product of a Sum and Difference:
- Cubic of a Sum:
- Cubic of a Difference:
- Sum of Cubes:
- Difference of Cubes:
2. Multinomial Algebraic Identities
- Square of a Trinomial:
- Cubic of a Trinomial:
3. Special Algebraic Identities
- General Binomial Theorem:
- (a + b + c)² Expanded:
- Sum of Powers of Roots:
4. Quadratic Algebraic Identities
- For any quadratic polynomial:
whereand b are the roots of the equation
5. Important Algebraic Products
- Sum of squares of two numbers:
- Product of four numbers:
6. Miscellaneous Algebraic Identities
- Lagrange’s Identity:
- Expression for
These identities are useful in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and performing algebraic manipulations.Algebraic Formulas PDF
Check Out The Algebraic Formulas PDF for Class 10 Students. Click Here- Math Algebra Formulas PDF
Related Post:








 CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...














