Calcium Hydroxide Formula: Calcium Hydroxide is a colorless compound found in crystalline form. Ca(OH)2 is the calcium hydroxide formula. Ionic interactions between the calcium ion Ca2+ and two hydroxide ions OH¯ hold calcium hydroxide molecules together. In general, calcium hydroxide is made by combining calcium oxide (commonly known as quicklime) and water. Calcium hydroxide has a wide range of applications. It is widely utilized in the construction industry, particularly in the manufacture of cement, mortar, and plaster. Read the entire article to learn about the calcium hydroxide formula structure, chemical and physical properties, applications, and more.
Calcium Hydroxide Formula
In the chemical industry, calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) is a common raw ingredient. Ca(OH)2 is the chemical calcium hydroxide formula, often known as lime that has been slaked or hydrated lime. In its solid state, it is a white inorganic compound with a powdery appearance. It is made up of one calcium ion (Ca2+) coupled with two hydroxide ions (OH-). It is also used to regulate pH and eliminate pollutants in water and wastewater treatment. Calcium hydroxide is used as a soil additive in agriculture to adjust soil pH. Exposure to concentrated Ca(OH)2 can cause lung damage and possibly blindness.
Calcium Hydroxide Formula Structure
When calcium oxide and water combine, Calcium Hydroxide is created. For each calcium ion (Ca2+), the chemical contains two hydroxide ions (OH). Both molecules are ionic, creating calcium ions and hydroxide ions in both aqueous and electrolytic dissociations. Calcium hydroxide has a molecular structure that consists of a calcium cation (Ca2+) surrounded by two hydroxide anions (OH-). The calcium ion is in the center, and the hydroxide ions are arranged around it. Each hydroxide ion is made up of one oxygen atom that is linked to one hydrogen atom. A Ca(OH)2 Calcium Hydroxide formula structure is shown below.
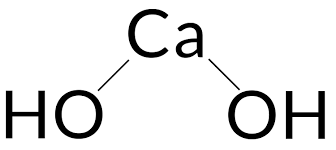
Calcium Hydroxide Formula by Criss Cross Method
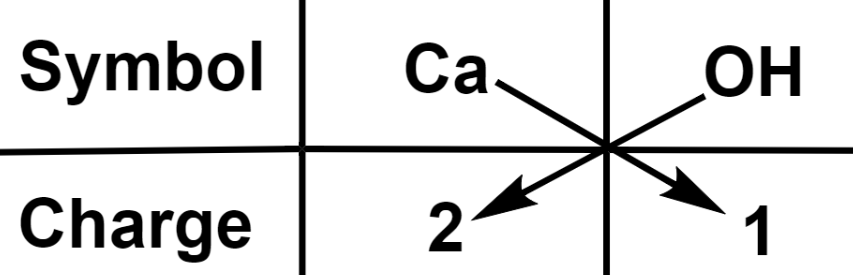
The crisscross valence method is a popular and very simple way of writing the chemical formula of a specific molecule. We may acquire the calcium Hydroxide formula by crisis cross Method with is – Ca(OH)2. Let’s look at how we can acquire the crisscross formula of any compound.
- We’re going to start with valence, the valence of an element is heavily dependent on the group in which it sits; the valence of a specific group remains constant throughout the group. For example, halogens (group 17) have a valence of -1, which means they only need one electron to achieve the stability of the next noble gas.
- We shall simply exchange the valence of one atom for the valence (or charge) of another, (1 valence = 1 atom, 2 valences = 2 atoms, 3 valences = 3atoms….. n valence = n atoms) because we are utilizing the criss-cross valence approach.
- Now understand with an Example: Hydroxide ion (OH) has a -1 charge, whereas we know calcium’s valence is +2 (group 2). As a result of crisscrossing for the chemical formula of calcium hydroxide, we will require one atom of calcium and two molecules of hydroxide ion, and the chemical formula can be represented as Ca(OH)2.
Calcium Hydroxide Preparation
Calcium hydroxide was initially utilised in root canal fillings around 1920. Any exposed tooth pulp was treated with calcium hydroxide, and capping dental pulp with calcium hydroxide became routine practise in the mid-20th century. Calcium hydroxide is a key element in adhesive for bricks and stone, plaster, and cement in the building industry. Many significant industries also make use of calcium hydroxide. Let’s look at how calcium hydroxide is produced.
- Calcium hydroxide is often formed by reacting calcium oxide (CaO) with water (H2O).
CaO + H2OCa(OH)2
- This reaction is very exothermic, which means it generates a lot of heat.
- When water is added to dry Portland cement to form concrete, the material warms up and releases heat.
- An alternative method of manufacturing employs an aqueous double displacement reaction between sodium hydroxide and calcium chloride. Sodium chloride is also formed in this process.
Calcium Hydroxide Physical Properties
Let’s have a look at some of the physical features of calcium hydroxide, which are mentioned below:
- Calcium hydroxide is a crystal white powder or solid. It can also take on the appearance of a colorless or slightly off-white material.
- Calcium hydroxide dissolves in glycerol and acids, but very slightly in water.
- Its solubility decreases as temperature rises. Assume its solubility at solubility is 1.73 g/L at 20°C and 1.89 g/L at 0°C.
- Limewater is a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide that combines with acids to generate salts.
- At temperatures close to its melting point, this compound also loses water and decomposes.
- The calcium hydroxide solubility product (Ksp) can be calculated as 5.5 * 10-6.
- Calcium hydroxide has a density of about 2.21 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3).
- Contact with calcium hydroxide can cause chemical burns if the skin is not properly protected. Long-term exposure can result in lung damage.
Chemical Properties of Calcium Hydroxide
The following are the calcium hydroxide’s chemical characteristics.
- It also combines with carbon dioxide (CO2) to generate calcium carbonate (CaCO3). This reaction is known as carbonation in general. This is in charge of the hardening and stabilization of calcium hydroxide in building materials like mortar and plaster.
- Calcium hydroxide is an alkaline base with strong base characteristics. When dissociated in water, it releases hydroxide ions, which can combine with acids to create salts and water.
- When calcium hydroxide dissolves in water, it produces an alkaline or basic solution. A saturated calcium hydroxide solution has a pH of 12-13.
Calcium Hydroxide Formula & Uses
Calcium hydroxide is used in a variety of industries, including building, water treatment, agriculture, and food processing. It is just slightly soluble in water and has alkaline characteristics. There are several applications and uses for calcium hydroxide, and a few of them are discussed below.
- calcium hydroxide is used as a binder in the production of cement, mortar, and plaster, where it improves the strength and longevity of these products.
- Calcium hydroxide is also used in the production of various insecticides, paints, and waterproofing compounds, and as an addition to oils and lubricants to increase their flowability. Calcium hydroxide is used as an accelerator in the manufacture of rubber and polymers.
- It is also used in the paper industry to treat wood so that it can be converted into pulp more easily.
- Calcium hydroxide is one of several chemicals used in industrial scrubbers to remove nitrogen and sulphur oxides from exhaust gases produced by a variety of industrial operations. Removing these oxides contributes to a reduction in the amount of acid rain produced by industrial pollution.
- In wastewater and water treatment operations, calcium hydroxide is used to raise the pH and remove pollutants via precipitation reactions.
- It is used as a soil amendment to balance the pH of the soil and deliver necessary nutrients to crops.
- Calcium hydroxide is employed as a neutralizing chemical because, in a twofold displacement reaction, it combines with acids to produce water and salt. This neutralization might take place in farm soils to aid plant development or in rivers to mitigate the impacts of acid rain.
- In food processing, calcium hydroxide is used as a firming agent in pickling and canning, as well as for food preservation.









 NEET UG 2026 Registration: NTA releases ...
NEET UG 2026 Registration: NTA releases ...
 CUET UG 2026 Online Registration Started...
CUET UG 2026 Online Registration Started...
 CUET 2026 Free Batches Launched by CUET ...
CUET 2026 Free Batches Launched by CUET ...














