The CBSE class 12 chemistry exam 2025 is over and students can now access the official question paper along with the answer key for sets 1, 2, 3. The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam was held from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM today, February 27. As per students’ initial reaction, the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper was of moderate difficulty with a balanced combination of conceptual, numerical, and application-based problems. Our subject matter experts have solved the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2025 to provide you with the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry answer key 2025 for all sets.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2025 Answer Key with Questions
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry question paper 2025 consisted of questions from physical, inorganic and inorganic chemistry. The CBSE 12th chemistry question paper 2025 had a good mix of questions from all three sub-domains. The initial review of the question paper suggests that the paper was of the moderate difficulty level. The CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Question Paper 2025 PDF is now available with us for all sets 1, 2, 3.
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Question Paper 2025 (With Answer Key) PDF Download
As the CBSE 12th Chemistry board exam 2025 is over, the official question papers for all sets is available in PDF format. Students can download the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2025 PDF Set 1, 2, 3 in the table below for free. In addition, we have also offered a thorough analysis of the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam 2025 analysis based on inputs from students and subject experts.
| CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2025 PDF Download | |
| Question Paper Set | CBSE 12th Chemistry Question Paper PDF Download Link |
| Set 1 | Click Here to Download Question Paper PDF |
| Set 2 | Click Here to Download Question Paper PDF |
| Set 3 | Click Here to Download Question Paper PDF |
Key Highlights For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam Pattern 2025
| Section | Type of Questions | Number of Questions | Marks per Question | Total Marks |
| A | Multiple Choice | 16 | 1 | 16 |
| B | Short Answer | 5 | 2 | 10 |
| C | Short Answer | 7 | 3 | 21 |
| D | Case Study | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| E | Long Answer | 3 | 5 | 15 |
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2025 for All Sets
Our in house experts at Adda247 have prepared the accurate answers for all questions asked in the CBSE Class 12th Chemistry 2025 exam. We have uploaded the CBSE Class 12th Chemistry answer key 2025 for all sets 1, 2, 3 on this page to help students match their responses and know their exam performance. The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry paper questions and solutions 2025 will serve as a valuable preparation tool for future board exam students.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2025 Set 1
SECTION – A
16 × 1 = 16
Questions No. 1 to 16 are Multiple Choice type questions carrying 1 mark each.
| Question Number | Options | Correct Answer |
| 1. The charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of MnO4− to MnO2 is | (A) 1 F, (B) 3 F, (C) 5 F, (D) 6 F | (B) 3 F |
| 2. Which among the following is a false statement? | (A) Rate of zero-order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
(B) Half-life of a zero-order reaction is inversely proportional to the rate constant. (C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. (D) For a first-order reaction, t1/2 = 0.693/k. |
(C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. |
| 3. The number of molecules that react with each other in an elementary reaction is a measure of the | (A) the activation energy of the reaction, (B) stoichiometry of the reaction, (C) the molecularity of the reaction, (D) order of the reaction. | (C) molecularity of the reaction |
| 4. The element having [Ar] 3d10 4s2 electronic configuration is | (A) Cu, (B) Zn, (C) Cr, (D) Mn | (B) Zn |
| 5. The complex ions [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+ are called | (A) Ionization isomers, (B) Linkage isomers, (C) Co-ordination isomers, (D) Geometrical isomers | (B) Linkage isomers |
| 6. The diamagnetic species is: | (A) [Ni(CN)4]2−, (B) [NiCl4]2−, (C) [Fe(CN)6]3−, (D) [CoF6]3− | (A) [Ni(CN)4]2− |
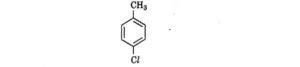
| 7. Which is the correct IUPAC name for the given compound?
|
(A) Methylchlorobenzene, (B) Toluene, (C) 1-Chloro-4-Methylbenzene, (D) 1-Methyl-4-Chlorobenzene | (C) 1-Chloro-4-Methylbenzene |
| 8. What will be formed after the oxidation reaction of secondary alcohol with chromic anhydride (CrO3)? | (A) Aldehyde, (B) Ketone, (C) Carboxylic acid, (D) Ester | (B) Ketone |
| 9. The conversion of phenol to salicylic acid can be accomplished by | (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction, (B) Friedel-Crafts reaction, (C) Kolbe reaction, (D) Coupling reaction | (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction |
| 10. Which of the following is/are examples of denaturation of protein? | (A) Coagulation of egg white, (B) Curdling of milk, (C) Clotting of blood, (D) Both (A) and (B) | (D) Both (A) and (B) |
| 11. Nucleotides are joined together by | (A) Glycosidic linkage, (B) Peptide linkage, (C) Hydrogen bonding, (D) Phosphodiester linkage | (D) Phosphodiester linkage |
| 12. Scurvy is caused due to deficiency of | (A) Vitamin B1, (B) Vitamin B2, (C) Ascorbic acid, (D) Glutamic acid | (C) Ascorbic acid |
| 13. Assertion (A): In a first-order reaction, if the concentration of the reactant is doubled, its half-life is also doubled.
Reason (R): The half-life of a reaction does not depend upon the initial concentration of the reactant in a first-order reaction. |
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
| 14. Assertion (A): Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Cu has a positive electrode potential. |
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
| 15. Assertion (A): Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with the anion formed by phthalimide.
|
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
| 16. Assertion (A): Vitamin D cannot be stored in our body.
Reason (R): Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin and is not excreted from the body in urine. |
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2025 with Answer Key 2025 Set 2
SECTION – A
| Question No. | Question | Options | Answer |
| 1 | Assertion (A): Vitamin D cannot be stored in our body. Reason (R): Vitamin D is fat soluble vitamin and is not excreted from the body in urine. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. | (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. |
| 2 | Assertion (A): Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis. Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with the anion formed by phthalimide. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
| 3 | Assertion (A): Cu cannot liberate H₂ on reaction with dilute mineral acids. Reason (R): Cu has positive electrode potential. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. | (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). |
| 4 | Assertion (A): In a first order reaction, if the concentration of the reactant is doubled, its half-life is also doubled. Reason (R): The half-life of a reaction does not depend upon the initial concentration of the reactant in a first order reaction. | (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. | (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. |
| 5 | Scurvy is caused due to deficiency of | (A) Vitamin B1 (B) Vitamin B2 (C) Ascorbic acid (D) Glutamic acid | (C) Ascorbic acid |
| 6 | Nucleotides are joined together by | (A) Glycosidic linkage (B) Peptide linkage (C) Hydrogen bonding (D) Phosphodiester linkage | (D) Phosphodiester linkage |
| 7 | Which of the following is/are examples of denaturation of protein? | (A) Coagulation of egg white (B) Curdling of milk (C) Clotting of blood (D) Both (A) and (B) | (D) Both (A) and (B) |
| 8 | The conversion of phenol to salicylic acid can be accomplished by | (A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction (B) Friedel-Crafts reaction (C) Kolbe reaction (D) Coupling reaction | (C) Kolbe reaction |
| 9 | What will be formed after oxidation reaction of secondary alcohol with chromic anhydride (CrO3)? | (A) Aldehyde (B) Ketone (C) Carboxylic acid (D) Ester | (B) Ketone |
| 11 | The diamagnetic species is: | (A) [Ni(CN)]²⁻ (B) [NiCl₄]²⁻ (C) [Fe(CN)₆]³⁻ (D) [CoF] | (A) [Ni(CN)]²⁻ |
| 12 | The complex ions [Co(NH₃)₅ (NO₂)]²⁺ and [Co(NH₃)₅ (ONO)]²⁺ are called | (A) Ionization isomers (B) Linkage isomers (C) Co-ordination isomers (D) Geometrical isomers | (B) Linkage isomers |
| 13 | The element having [Ar]3d¹⁰4s¹ electronic configuration is | (A) Cu (B) Zn (C) Cr (D) Mn | (A) Cu |
| 14 | The number of molecules that react with each other in an elementary reaction is a measure of the: | (A) Activation energy of the reaction (B) Stoichiometry of the reaction (C) Molecularity of the reaction (D) Order of the reaction | (C) Molecularity of the reaction |
| 15 | Which among the following is a false statement? | (A) Rate of zero order reaction is independent of initial concentration of reactant. (B) Half-life of a zero order reaction is inversely proportional to the rate constant. (C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. (D) For a first order reaction, t₁/₂ = 0.693/k. | (C) Molecularity of a reaction may be zero. |
| 16 | The charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of MnO₄ to MnO₂ is | (A) 1 F (B) 3 F (C) 5 F (D) 6 F | (C) 5 F |
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Answer Key 2025 (Set 56/5/3)
Check the questions and answers of Section A of the class 12 chemistry set 3 question paper below.
| S.No | Question | Answer |
| 1 | CH₃CH₂CHO and CH₃CH₂COOH can be distinguished by | Sodium bicarbonate test |
| 2 | While doing qualitative analysis in the chemistry lab, Abhishek added yellow coloured potassium chromate solution into a test tube. He was surprised to see the colour of the solution changing immediately to orange. He realised that the test tube was not clean and contained a few drops of the same liquid. Which of the following substances will be the most likely liquid to be present in the test tube before adding potassium chromate solution? | HCL Solution |
| 3 | The role of a catalyst is to change | Activation energy of reaction |
| 4 | Which of the following molecules is chiral in nature? | 2-chlorobutane |
| 5 | CH₃C₂OH can be converted to CH₃CHO by: | Treatment with PCC |
| 6 | The IUPAC name for CH₃-CH₂-N(CH₃)-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃ is: | N-ethyl-N-methylpropan-1-amine |
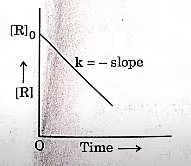
| 7 | A plot between concentration of reactant [R] and time ‘t’ is shown below. Which of the given order of reaction is indicated by the graph?
|
Zero order |
| 8 | The treatment of ethyl bromide with alcoholic silver nitrite gives: | Nitroethane |
| 9 | Which of the following aqueous solutions will have the highest freezing point? | 1.0 M KCl |
| 10 | Which of the following aldehydes will undergo Cannizzaro reaction? | (CH₃)₃C CHO |
| 11 | In which of the following groups are both ions coloured in aqueous solutions | CO²+ and FE²+ |
| 12 | Match the following of column I with column II | i. Lead storage cell – d. inverter
ii. Mercury Cell- c. Wrist watch iii. Dry cell- a. Wall clock iv. Fuel cell- b. Apollo Space Program |
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Question Paper 2025 Analysis
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry question paper 2025 analysis based on the students’ reaction and expert feedback is available now. Check them below.
Feedback from Students
We have refreshed the students’ feedback on the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam:
- The general level of difficulty of the exam was average.
- The MCQ questions were straightforward. Nevertheless, a few of the questions relied on calculations and took a considerable amount of time.
- The brief answer questions ranged from easy to moderate. The majority of the questions were not time-intensive.
- The challenge level of the Case-Based Questions was also moderate.
- Students perceived the long answer questions as somewhat lengthy. The majority of the students could not respond to all the questions in the allotted time.
- The questions that relied on diagrams were lengthy.
Analysis by Experts
Expert teachers think that students can do well on this test if they have a firm grasp of the concepts and practice answering numerical problems on a regular basis. Teachers praised the exam format, emphasizing that:
- The paper followed the CBSE syllabus and was balanced.
- Instead of requiring memorization, case-based and assertion-reasoning questions demanded conceptual comprehension.
- The paper would be manageable for those who concentrated on NCERT textbooks and past years’ papers.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2025 Difficulty Level
Based on the detailed review by the subject matter expert and students, we are providing the difficulty level for every section and question paper sets for CBSE Class 12 chemistry 2025 exam below.
|
Parameter
|
Class 12 Chemistry Exam Analysis 2025 CBSE
|
|
Overall difficulty level of the paper
|
Moderate to Tough
|
|
Difficulty Level of Section A
|
Moderate
|
|
Difficulty Level of Section B
|
Tough
|
|
Difficulty Level of Section C
|
Moderate
|
|
Difficulty Level of Section D
|
Moderate
|
|
Difficulty Level of Section E
|
Moderate to Tough
|
|
Expected Good Score
|
55+
|
|
Lengthiest Question (If any)
|
Assertion-reasoning and case-based questions
|
|
Topics with more weightage in the exam
|
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
|
|
Time-Consuming Section (If any)
|
Physical Chemistry
|
How to Use CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2025
Students can use the CBSE Class 12 chemistry answer key 2025 to compute their score. Follow the process given below to calculate your score using answer key.
Step 1: Use the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2025 given above and ensure you have your chemistry question paper prepared.
Step 2: Verify your responses by comparing them with those provided in the answer key.
Step 3: Assign yourself marks for every correct response and subtract marks for incorrect ones, if necessary, according to the grading guidelines.
Step 4: Sum all the marks to calculate your overall score after going through all the responses.









 CUET Economics Previous Year Question Pa...
CUET Economics Previous Year Question Pa...
 CUET Maths Previous Year Question Paper,...
CUET Maths Previous Year Question Paper,...
 CUET Geography Previous Year Question Pa...
CUET Geography Previous Year Question Pa...








