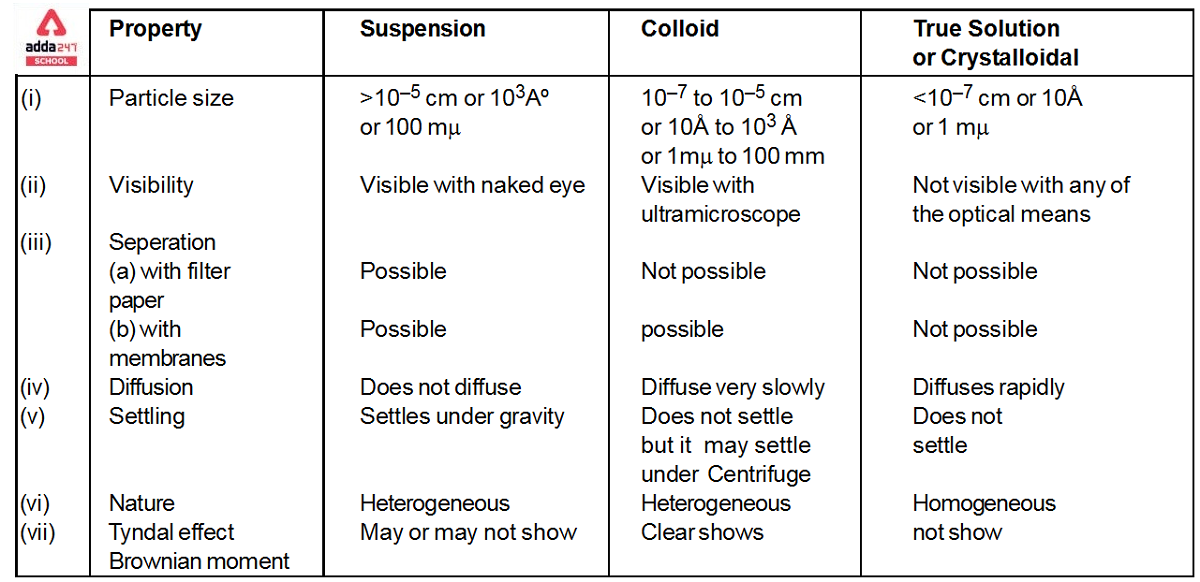
Colloidal Solution
Colloidal Solution: Colloids (also known as colloidal solutions or colloidal systems) are mixed in which insoluble particles of one substance are suspended in another substance at a microscopic level. In a colloidal solution, the size of the suspended particles can range from 1 to 1000 nanometres (10-9 meters). The suspended particles in a combination must not settle in order to be categorized as a colloid (in the manner that the particles of suspensions settle at the bottom of the container if left undisturbed). The Tyndall Effect is a phenomenon in which light beams incident on colloids are scattered due to interactions between the light and the colloidal particles. Colloidal particles are the tiniest particles. colloidal solution, on the other hand, are essentially solutions with solute particle sizes ranging from 1nm to 1000nm. colloidal solution are naturally diverse.
Read More About:
- Endothermic Reaction – Definition, Equation, Examples, Formula
- Dielectric Constant- Definition, Formula, Meaning In Chemistry
- Limestone- Chemical Formula, Uses, Meaning
- Cannizzaro Reaction – Definition, Examples, Mechanism
What is Colloidal Solution Definition?
colloidal solutions are defined as a mixture in which one of the components is broken down into very small particles that are spread throughout a second material. A colloid is a combination in which one ingredient is suspended throughout another substance by microscopically distributed insoluble particles. The particles must be spread in a liquid, according to some definitions. Interface and colloid science is concerned with colloidal suspensions. Italian chemist Francesco Selmi first developed this topic of study in 1845, while Scottish scientist Thomas Graham has been researching it since 1861.
Colloidal Solution Examples
colloidal solutions are not all kinds of mixes. colloidal solutions are mixtures in which the suspended particles do not settle at the button and are equally disseminated in another substance. The following are some examples of colloidal solutions:
- Blood
- Whipped cream
- Paints
- Flame retardants
- Butter
- Cheese
- Perfume
- Gelatin
- Dirty water
- Starch solution
and many other substances.
Properties of Colloidal Solution
The colloidal solution exhibits a wide range of properties which are classified into three broad types discussed below:
OPTICAL Properties of colloidal solution:
- When a powerful beam of light is sent through a colloidal sol, the light scattering by the colloidal particles produces a visible cone. The Faraday–Tyndall effect is what causes this.
- The electron microscope, which can provide images of actual particles, even those reaching molecular dimensions, is now routinely used to examine colloidal particle size, shape, and structure. The electron microscope’s success can be attributed to its great resolving power, which is measured in terms of ‘d,’ the lowest distance between two objects that allows them to be distinguished. The smaller the wavelength of the radiation employed, the lower the value of ‘d’ and the higher the resolving power.
- The optical microscope’s radiation source is visible light, which can only discern two particles at a time of roughly 20 nanoseconds. The electron microscope’s radiation source is a stream of high-energy electrons with wavelengths in the 0.01 nm range.
- The above-mentioned Faraday-Tyndall Effect is used to explain the light scattering property of colloidal solution particles. The blue colour of the sky, which is visible to human eyes due to the scattering of blue wavelength light by colloidal particles in the atmosphere, is a wonderful illustration of this. The molecular weight of colloidal particles is determined by this feature.
KINETIC Properties of colloidal solution:
- The random movement of colloidal particles is described by Brownian motion. The irregular motion, which can be seen with particles as large as 5 m, was attributed to the particles being bombarded by the molecules of the dispersion medium. Because the molecules are too small to perceive, their motion cannot be monitored. The velocity of the particles increases as the particle size decreases. The Brownian movement is reduced and eventually stopped by increasing the viscosity of the medium, which can be performed by adding glycerin.
- Colloidal particles diffuse naturally from a high-concentration zone to a low-concentration region until the system’s concentration is uniform throughout. The Brownian movement is a direct effect of diffusion. Colloidal particle diffusion is governed by Fick’s first law of diffusion, which states that the amount of material diffusing across a plane of area at any given time is directly proportional to the change in concentration on both sides.
- The Van’t Hoff Equation, where is the osmotic pressure, c is the concentration of the solute in the system, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature, describes the osmotic pressure of colloidal particles. The osmotic pressure of colloidal particles is directly proportional to all of these components, according to this equation.
- Because the colloidal particles are always in Brownian motion, as previously stated, they have no tendency to silt. The colloidal particles’ Brownian motion is sufficient to counteract the gravitational force acting on them. As a result, a larger force is required to achieve quantitative and detectable sedimentation of colloidal particles. The ultracentrifuge, which can produce a force one million times that of gravity, is used to do this.
- Viscosity is a measure of a system’s resistance to flow when it is subjected to a force. When a liquid is more viscous, it takes more force to get it moving and keep it moving at a consistent rate. y, o is the viscosity of the dispersion medium, is the viscosity of the dispersion, and is the volume fraction, and is the viscosity of the colloidal solution is given by an equation developed by Einstein, = o(1 + 2.5), where y, o is the viscosity of the dispersion medium, is the viscosity of the dispersion, and is the volume fraction.
ELECTRIC Properties of colloidal solution:
- The essential idea underpinning four electrokinetic phenomena is the movement of a charged surface with regard to an adjacent liquid phase: electrophoresis, electro-osmosis, sedimentation potential, and streaming potential. Electrophoresis is the phenomenon of charged particles moving across a liquid media when a potential difference is applied. Electro-osmosis is a phenomena in which a charged particle moves relative to a stationary liquid when a potential is applied to it. The formation of a potential difference when charged particles sediment is known as sedimentation potential. The streaming potential is different from electro-osmosis in that it is created by pushing a liquid to flow through a stopper or bed of particles.
- When sodium chloride is placed in a solution on one side of a semipermeable membrane and a negatively charged colloid with its counter ions R-Na+ is placed on the other, the sodium and chloride ions can freely travel over the barrier, but the colloidal anionic particles cannot.
Examples of Colloidal Solution Purification Methods
There are mainly two major ways for purificationof colloidal solution, i.e., by condensation method (chemical techniques) and by dispersion method (physical techniques).
Condensation Method
Purification of the colloidal solution by condensation method uses the following chemical techniques: Oxidation, Double decomposition, Hydrolysis, Excessive cooling, Exchange of solvent, Change of physical state, etc.
Dispersion Method
The dispersion method for purification of colloids mainly includes the following physical methods: Mechanical dispersion, Bredig’s Arc Method or by Electrical Dispersion, Peptization.
Colloidal Solution Particle Size
Colloidal particles are larger than simple molecules but small enough to remain suspended. Their colloidal solution particle size range of diameters is between 1 and 1000 nm, i.e. from 10–9 to 10–6 m.
Related Post:
- Lifecycle Of Silkworm- Diagram, Drawing, Project
- Scattering Of Light- Examples, Definition, Discovery, Prism
- Highest Dam In India
- Which Is The Longest Dam In India?
- Aufbau Principle Definition, Formula, Example, Limitation








 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














