Decomposition reactions are the breakdown of chemical species into simpler components. Typically, decomposition reactions necessitate the addition of energy. The breakdown of potassium chlorate (KClO3) by heat, for example, is a typical way of creating oxygen gas in the laboratory.
Decomposition Reaction Definition
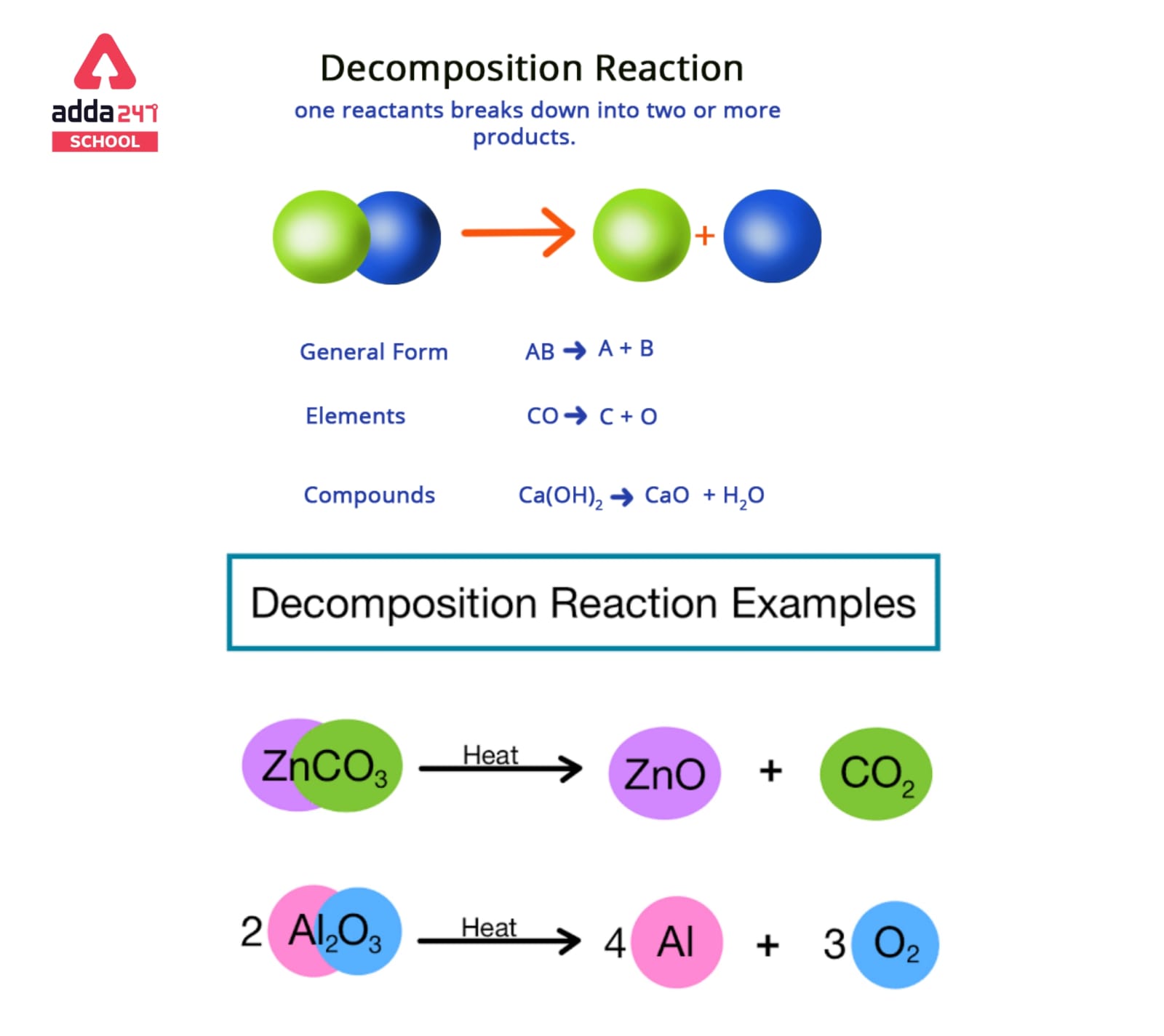
Decomposition reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which a single compound is broken down into two or more simpler compounds or elements. These reactions typically involve the breaking of chemical bonds, and they can be either endothermic or exothermic.
Decomposition Reaction Example
One common example of a decomposition reaction is the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen through the process of electrolysis. Another example is the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Decomposition Reaction Types
There are Three main types of decomposition reactions: thermal decomposition and electrolytic decomposition.
Thermal Decomposition
Thermal decomposition occurs when a compound is broken down by heat. This type of decomposition is often exothermic, meaning it releases heat energy. Thermal decomposition is often used in the production of metals and other materials.
Thermal Decomposition Reaction Example
Thermal decomposition is a type of chemical reaction in which a compound breaks down into simpler substances when heated. Here’s an example of a thermal decomposition reaction:
Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3):
CaCO3(s) -> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
In this reaction, calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which is commonly found in the form of limestone or marble, decomposes when heated to form calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. This reaction is commonly used in industries such as cement production and in the creation of lime for various applications. When you heat calcium carbonate, it undergoes thermal decomposition to produce these two new substances.
Electrolytic Decomposition
Electrolytic decomposition occurs when an electric current is passed through a compound, causing it to break down into simpler compounds or elements. This type of decomposition is often endothermic, meaning it requires the input of heat energy. It is used in the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
Electrolytic Decomposition Example
In general, a decomposition reaction can be represented by the general equation:
AB → A + B
where A and B represent the simpler products formed from the original compound AB.
Decomposition reactions are important in various industrial processes, such as the production of fertilizers, the extraction of metals, and the production of chemicals. The decomposition of compounds can also be used for purification and analysis of substances.
Photolytic Decomposition
Photolytic decomposition, also known as photodecomposition or photolysis, is a chemical reaction in which a compound is broken down into simpler substances under the influence of light. This process occurs when the energy from photons (particles of light) is absorbed by the molecules of the compound, causing them to undergo chemical changes.
Photolytic decomposition is often seen in organic compounds and is a fundamental process in various natural and artificial systems.
Photolytic Decomposition Examples
Here are a few examples:
- Photosynthesis: In photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic organisms use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process involves the photolytic decomposition of water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions (protons).
- Photodegradation of Organic Compounds: Sunlight can lead to the photodegradation of organic molecules, such as plastics, dyes, and pesticides. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can break down the chemical bonds in these substances, causing them to decompose into simpler, often less harmful compounds.
- Photolysis of Ozone: In the Earth’s stratosphere, ozone (O3) molecules can undergo photolytic decomposition when they absorb high-energy UV radiation. This process plays a crucial role in the ozone layer’s maintenance and can release oxygen molecules (O2) and oxygen atoms (O) as products.
- Photodecomposition in Photography: In traditional film photography, photodecomposition is used to create images. When light strikes a photosensitive material like film or photographic paper, it triggers chemical reactions that result in the formation of an image.
- Photolysis in Environmental Cleanup: Photolytic decomposition can be employed in environmental cleanup processes. For example, in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), UV light is used to break down pollutants and contaminants in water and air, transforming them into less harmful substances.
The specific mechanism of photolytic decomposition can vary widely depending on the compound involved and the type of light (UV, visible, etc.) used. It is an important area of study in both chemistry and environmental science, as understanding how compounds react to light can have significant implications for various fields, including energy production, pollution control, and materials science.
It’s important to note that Decomposition reactions can also be catalyzed by various agents such as light, catalysts, and enzymes.
Decomposition Reaction Formula
|
2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) |
Another breakdown reaction is the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (NaCl) at high temperatures to produce sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl2).
|
2NaCl (l) → 2Na (l) + Cl2(g) |
The decomposition of mercury oxide (HgO) with heat to give mercury metal (Hg) and oxygen gas is a very important decomposition process in the history of chemistry. Carl Wilhelm Scheele, Joseph Priestley, and Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier employed this reaction in their investigations on oxygen in the 18th century.
|
2HgO(s) → 2Hg (l) + O2(g) |
Read More About:
- Heron’s Formula For Area Of Triangle, Proof And Example
- Rutherford Atomic Model- Experiments, Postulates, Diagram And Its Drawbacks
- Colloidal Solution- Definition, Properties, Examples, Particle Size
- Endothermic Reaction – Definition, Equation, Examples, Formula
- Dielectric Constant- Definition, Formula, Meaning In Chemistry
Decomposition Reaction- Format for General Reactions
A decomposition reaction’s general format is shown below.
AB -> A + B
The parent molecule (reactant) is AB, while the resultant molecules are A and B.
Decomposition Reaction Examples for Class 10
Decomposition reactions occur all around us, although we are generally unaware of them. The following are some common instances of decomposition reactions.
The chemical equation
|
H2CO3 → H2O + CO2 |
can be used to depict the decomposition of carbonic acid in soft drinks.
Water is electrolyzed to produce hydrogen and oxygen.
Decomposition Reaction- Inverse Reaction
A combination reaction is the polar opposite of a decomposition process. The creation of a single product from two or more reactants is the goal of these reactions.
Decomposition Reactions- Applications
The extraction of metals from their ores is one of the most common uses of decomposition processes. Zinc, for example, can be extracted from calamine by a decomposition reaction. Sodium can also be created from sodium chloride in a similar way (NaCl).
Decomposition Reaction- Reaction of Double Decomposition
A double decomposition reaction occurs when two constituent reactants exchange positive and negative ions, resulting in the formation of two new compounds.
Example
|
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + HOH(l) |
Examples of Decomposition Reaction for Class 10
The following are the three main types of breakdown reactions:
Decomposition Reaction of thermal degradation
A decomposition reaction that is activated by thermal energy is known as a thermal decomposition reaction. To put it another way, a thermal decomposition reaction necessitates the delivery of energy to the reactants in the form of heat. Because energy is required to break chemical bonds and separate the constituent elements, such reactions are usually endothermic. The following is an example of a thermal breakdown reaction.
|
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 |
Calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide when heated. This procedure is used to make quick lime, which is a critical ingredient in a variety of industries.
Decomposition Reaction of electrolytic decomposition
The activation energy for decomposition in an electrolytic decomposition reaction is delivered in the form of electrical energy. The electrolysis of water is an example of an electrolytic breakdown reaction, which can be represented by the chemical equation:
|
2H2O→ 2H2 + O2 |
Photo decomposition/ Photolytic breakdown/ Photochemical decomposition
A photodecomposition reaction is a sort of decomposition reaction in which the reaction absorbs energy from photons and breaks down into its parts. The decomposition of dioxygen and an oxygen radical, as indicated by the chemical equation below, is an example of a photo decomposition reaction.
|
O3 + hv → O2 + O |
Related Post:
- Limestone- Chemical Formula, Uses, Meaning
- Cannizzaro Reaction – Definition, Examples, Mechanism
- Lifecycle Of Silkworm- Diagram, Drawing, Project
- Scattering Of Light- Examples, Definition, Discovery, Prism
10 Easy Examples of Decomposition Reaction Class 10
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2) is an example of a decomposition reaction: 2H2O2 –> 2H2O + O2
- The decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen through the process of electrolysis is another example of a decomposition reaction: 2H2O –> 2H2 + O2
- The decomposition of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) into nitrogen gas (N2) and water vapor (H2O) is another example: NH4NO3 –> N2 + H2O
- The decomposition of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) also represents a decomposition reaction: CaCO3 –> CaO + CO2
- The decomposition of potassium chlorate (KClO3) into potassium chloride (KCl) and oxygen (O2) is another example: KClO3 –> KCl + 3O2
- The decomposition of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) into manganese dioxide (MnO2) and oxygen (O2) is another example: 2KMnO4 –> 2KMnO2 + O2
- The decomposition of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) into sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) also represents a decomposition reaction: NaHCO3 –> Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
- The decomposition of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) into sulfur dioxide (SO2) and water (H2O) is another example: 2H2SO4 –> 2SO2 + 2H2O
- The decomposition of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) into sulfur (S) and water (H2O) is another example: H2S –> S + H2O
- The decomposition of nitric oxide (NO) into nitrogen gas (N2) and oxygen (O2) is another example: 2NO –> N2 + O2
These are just a few examples of decomposition reactions, but there are many more that occur in nature and in various industrial processes.








 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














