Difference between osmosis and diffusion: Osmosis and diffusion are two types of transport processes that are used to move molecules into and out of cells. Despite the fact that both are kinds of passive transport, there are some differences between osmosis and diffusion. We frequently notice various events in nature that corroborate the evidence for osmosis and diffusion processes. We have often observed while spraying room fresheners in the room; the fragrance of the fresheners diffuses and you can detect the odor. However, we get mixed up between the two terms, diffusion and osmosis. To fully grasp the notion, it is vital to comprehend the difference between Osmosis and diffusion.
Difference between osmosis and diffusion Class 9
Biological transport is critical in a living cell since it participates in numerous physiological processes such as nutrition intake, waste elimination, and cell signaling. Biological transport is the movement of molecules, ions, and other substances across and within cell membranes. The two types of biological transport are diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of particles in the presence of a concentration gradient, whereas Osmosis is the migration of solvent particles from a diluted solution to a more concentrated solution.
Now the question arises What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion? In this article, we are going to learn the difference between osmosis and diffusion in detail, but before that, we must know the Meaning of diffusion and osmosis.
Difference between osmosis and diffusion: What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is a sort of biological transport in which a substance passes a semipermeable membrane from a greater concentration of the solvent to a lower concentration of the solvent. Furthermore, this mechanism is critical for maintaining water balance in cells and tissues because it is driven by the inclination of water molecules to shift from areas of higher free energy to areas of lower free energy. Osmosis occurs spontaneously and without the use of any cell energy. In the Osmosis transport, Only lipids, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, are permeable to these semipermeable membranes. Ions, proteins, and other molecular substances cannot flow across these membranes. Osmosis is also involved in other physiological functions, including blood pressure regulation, nutrition absorption from the digestive system, and transport. of water in plants.
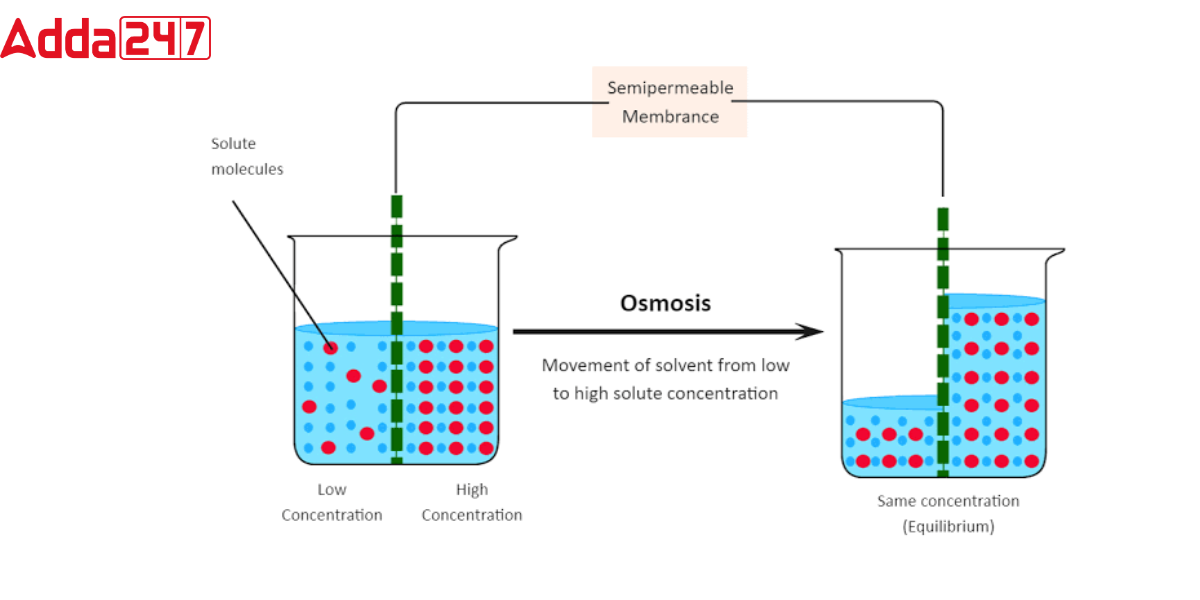
Difference between osmosis and diffusion: What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the movement of particles from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration area until equilibrium is attained. This mechanism, which is powered by random thermal motion, does not require any energy. Conditions such as pressure, temperature, and the particles’ size and shape all influence the diffusion rate. This phenomenon happens in gases, liquids, and solids and is a fundamental mechanism for many natural phenomena such as molecular flow within cells, odor dispersion through air, and solute mixing in a solution.
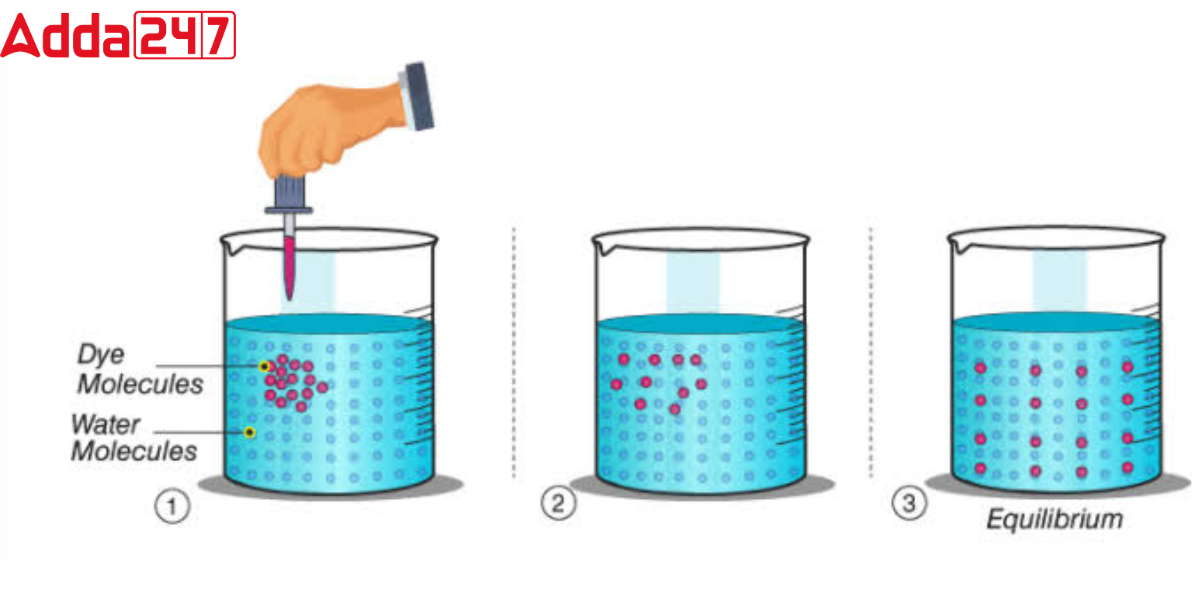
Difference between osmosis and diffusion in Tabular form
The Main difference between osmosis and diffusion is that in Osmosis, the water or solvent goes from a lower concentration to a higher concentration, but in diffusion, the solvent particles move from a higher concentration to a lower concentration. Let’s explore more differences between osmosis and diffusion discussed in the below table.
| Difference between osmosis and diffusion | ||
| Point of difference | Osmosis | Diffusion |
| Process | It is described as the phenomenon of solvent particles moving over a semi-permeable barrier | It is described as the movement of particles from a higher concentration zone to a lower concentration region. |
| Membrane | It needs the use of a semi-permeable membrane. | It does not require a semi-permeable membrane. |
| Type of Medium | Diffusion can happen only in a liquid medium. | Diffusion can happen between any medium, including gas to gas, liquid to liquid, liquid to gas, solid to solid, and solid to liquid. |
| Direction | Particles can only flow in one direction. | The movement of particles occurs in all directions. |
| Water requirement | Water is required for particle mobility. | Water is not required for particle mobility. |
| Type of substance | Only water or another solvent can travel from a higher concentration zone to a lower concentration region. | Any material can travel from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration area. |
| Types of Solution | Only occurs between solutions of similar types. | Occurs between solutions that are similar and solutions that are dissimilar. |
| Concentration | The concentration of the solvent does not become equal on both sides of the membrane. | The concentration of the diffusion substance equalizes to fill the available space. |
| Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure and turgor pressure | These two pressures work against osmosis. | These two pressures are not generally associated with diffusion. |
| Dependence | It is determined by the solute potential. Furthermore, it is mostly determined by the amount of solute particles present in the solvent. | It is not affected by the solute potential, the water potential, or the pressure potential. it is primarily determined by the existence of other particles. |
| Examples |
|
|
Other Related Posts –








 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...






