The cell is one of the fundamental units of a living body, which is responsible for all metabolic activities. Plants and animals, as we know, are made up of millions of cells that share certain similarities and distinctions. There are many distinctions and similarities between plant and animal cells. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells, thus their cell architecture and organelles are very similar. Nonetheless, there are significant differences between plant and animal cells. Here we discuss all facts and difference between plant cell and animal cell.
Difference Between Plant cell and Animal cell
The cell is the basic unit of life, and cells are responsible for almost all of life’s functions. Multicellular organisms have a huge number of cells, whereas unicellular species have only one cell. Unicellular organisms are thought to be one of the first forms of life on Earth, with more sophisticated multicellular species subsequently evolving from them. Specialized cells are seen in multicellular organisms. Cell organelles in multicellular organisms are complex. Complex cell organelles are uncommon in unicellular species.
The basic difference between plant cell and animal cell is Plants play the job of producer in an ecosystem, whilst animals play the role of consumer, which explains why their daily activities and functions differ. Not only that, but their cell structures are also diverse. Plants and animals have different cell structures and organelles. They are classified mostly according to their function. Plants and animals differ due to differences in their cell makeup, and as a result, their structure and functions differ as well.
The another difference between plant cell and animal cell is Each cell organelle has a specific purpose, and while some of the cell organelles are found in both plant and animal cells, others may be exclusive to only one.
Each cell organelle has a specific purpose, and while some of the cell organelles are found in both plant and animal cells, others may be exclusive to only one.
It might be the fact that all living species are made up of cells with similar structures, but still, there remain variances in the architectures of plant and animal cells.
The cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, and vacuoles are all structures found in both plant and animal cells, however, the cell wall and chloroplasts are two structures that are just present in plants.
Difference Between Animal Cell and Plant Cell
Some important difference between animal cell and plant cell are given below.
- Plant cells have a cell wall. On the other hand, Animal cells lack a cell wall. However, Plants rely on their cell walls for stability.
- Plants use chloroplasts to perform photosynthesis, which allows them to produce food, and thus they have it, however, Animal cells lack chloroplasts.
- Animal cells contain smaller vacuoles (if any) and are irregular or spherical, whereas plant cells have one or more big vacuoles and are square or rectangular in appearance. Large vacuoles assist the plant to maintain its shape and allow it to store water and food for later use.
- A plant cell’s nucleus is present and located on one side of the cell, whereas an animal cell’s nucleus is located in the centre.
- Lysosomes are present in plant cells but are very rare, whereas they are present and can be plentiful in animal cells.
- Centrosomes are not present in plant cells, however, they are present in animal cells.
Both cell types have cytoplasm, as well as ribosomes and the Golgi Apparatus. - Plastids can be found in plant cells, however, they are not seen in animal cells.
- In a plant cell, Cilia is lacking, although it is found in the majority of animal cells.
- Mitochondria are present in plant cells but in fewer numbers than in animal cells.
- A plant cell’s mode of nutrition is largely autotrophic, whereas an animal cell’s mode of nutrition is heterotrophic.
- Plant and animal cells both feature membrane-bound organelles including the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, the nucleus, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, and lysosomes, as well as membranes like cytoskeletal elements and cytoplasm. Plant cells have the potential to be larger than animal cells. Animal cells have a normal range of 10 to 30 micrometres, while plant cells have a range of 10 to 100 micrometres.
Basic Difference Between Plant and Animal Cell
Plant and animal cells are the basic units of life, but there are some differences between the two.
Plant cells have several unique features that animal cells do not have. some points are given below.
- Cell Wall: Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose, which provides support and protection for the cell.
- Chloroplasts: Plant cells have chloroplasts, which are organelles that contain chlorophyll and are involved in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is a pigment that helps plants to capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy.
- Large Central Vacuole: Plant cells have a large central vacuole, which stores water and other substances. This is important for maintaining the turgor pressure of the cell.
In other way we say, animal cells have several features that plant cells do not have. some points are given below
- Centrioles: Animal cells have centrioles, which are involved in cell division.
- Lysosomes: Animal cells have lysosomes, which are organelles that contain digestive enzymes.
- Cilia and Flagella: Some animal cells have cilia or flagella, which are structures that are involved in the movement.
10 Differences Between Plants and Animals Cells
10 key differences between plant and animal cells:
Cell Wall:
Plant Cells: Have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, which provides structure and support.
Animal Cells: Do not have a cell wall, only a flexible plasma membrane.
Chloroplasts:
Plant Cells: Contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Animal Cells: Lack chloroplasts; they do not perform photosynthesis.
Vacuoles:
Plant Cells: Have a large central vacuole that maintains cell turgor and stores nutrients.
Animal Cells: Have small, temporary vacuoles or may lack them entirely.
Shape:
Plant Cells: Generally rectangular or cubic in shape due to the rigid cell wall.
Animal Cells: Typically round or irregular in shape due to the lack of a cell wall.
Centrioles:
Plant Cells: Usually do not have centrioles (except in lower plants).
Animal Cells: Contain centrioles that play a role in cell division.
Lysosomes:
Plant Cells: Rare or absent, as plants typically rely on vacuoles for waste breakdown.
Animal Cells: Common and involved in digestion and waste removal.
Plasmodesmata:
Plant Cells: Have plasmodesmata, channels between cells for communication.
Animal Cells: Lack plasmodesmata; instead, they communicate through gap junctions.
Energy Storage:
Plant Cells: Store energy as starch.
Animal Cells: Store energy as glycogen.
Cilia and Flagella:
Plant Cells: Rarely have cilia or flagella (mostly found in reproductive cells).
Animal Cells: May have cilia or flagella for movement (e.g., sperm cells).
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts:
Plant Cells: Have both mitochondria (for respiration) and chloroplasts (for photosynthesis).
Animal Cells: Have only mitochondria for energy production.
Diagram of Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell for Class 9
Here is a diagram that showing some basic differences between plant and animal cells:
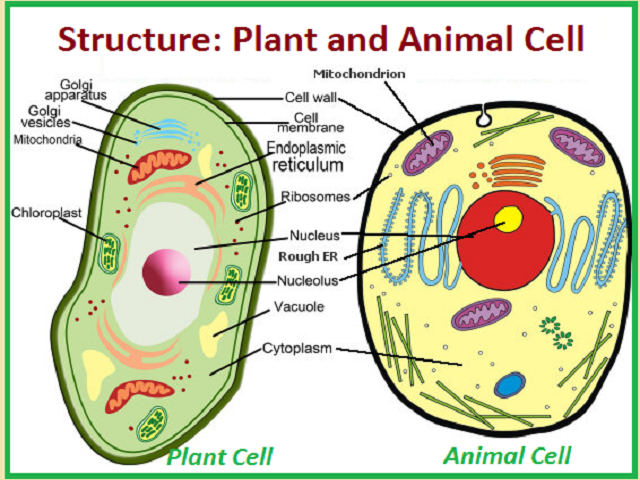
As you can see from the diagram, plant cells have a more rigid and rectangular shape due to their cell wall, while animal cells have a more rounded shape. Plant cells also have a larger central vacuole and chloroplasts, while animal cells have centrioles and lysosomes.
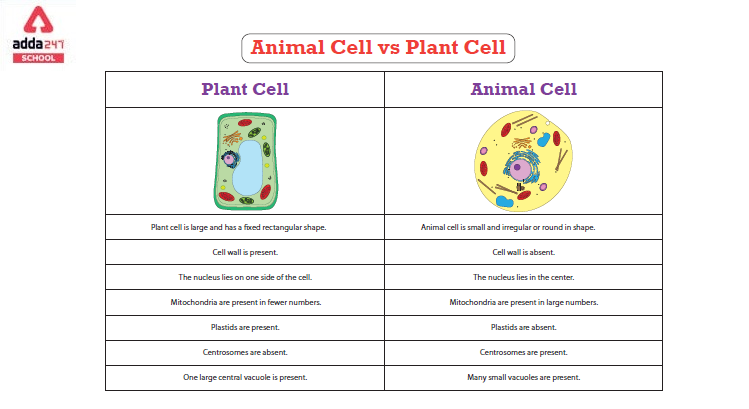
Major Plant Cell and Animal Cell Difference in Table
Here’s a table comparing the differences between plant cells and animal cells:
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (made of cellulose) | Absent |
| Shape | Generally rectangular or cubic | Generally round or irregular |
| Chloroplasts | Present (for photosynthesis) | Absent |
| Vacuole | Large central vacuole (often one large one) | Small or absent |
| Plastids | Present (chloroplasts, leucoplasts, etc.) | Absent |
| Centrioles | Absent | Present |
| Lysosomes | Rarely present | Commonly present |
| Plasma Membrane | Present, inside the cell wall | Present, outermost layer |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Golgi Apparatus | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Present (both smooth and rough) | Present (both smooth and rough) |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
Plant cell and Animal cell Difference in Hindi
कोशिका और पशु कोशिका के बीच अंतर
कोशिका जीवन की मूल इकाई है, और कोशिकाएँ जीवन के लगभग सभी कार्यों के लिए जिम्मेदार होती हैं। बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में बड़ी संख्या में कोशिकाएँ होती हैं, जबकि एककोशिकीय प्रजातियों में केवल एक कोशिका होती है।
एककोशिकीय जीवों को पृथ्वी पर जीवन के पहले रूपों में से एक माना जाता है, और अधिक परिष्कृत बहुकोशिकीय प्रजातियां बाद में उनसे विकसित होती हैं। बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में विशिष्ट कोशिकाएँ देखी जाती हैं। बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में कोशिकांग जटिल होते हैं। एककोशिकीय प्रजातियों में जटिल कोशिका अंग असामान्य हैं।
एक पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र में पौधे उत्पादक की भूमिका निभाते हैं, जबकि जानवर उपभोक्ता की भूमिका निभाते हैं, जो बताता है कि उनकी दैनिक गतिविधियां और कार्य अलग-अलग क्यों हैं। इतना ही नहीं, बल्कि उनकी कोशिका संरचना भी विविध हैं। पौधों और जानवरों में अलग-अलग कोशिका संरचनाएं और अंग होते हैं। उन्हें ज्यादातर उनके कार्य के अनुसार वर्गीकृत किया जाता है। पौधे और जानवर अपने सेल मेकअप में अंतर के कारण भिन्न होते हैं, और परिणामस्वरूप, उनकी संरचना और कार्य भी भिन्न होते हैं।
प्रत्येक कोशिका अंग का एक विशिष्ट उद्देश्य होता है, और जबकि कुछ कोशिका अंग पौधे और पशु कोशिकाओं दोनों में पाए जाते हैं, अन्य केवल एक के लिए अनन्य हो सकते हैं।
प्रत्येक कोशिका अंग का एक विशिष्ट उद्देश्य होता है, और जबकि कुछ कोशिका अंग पौधे और पशु कोशिकाओं दोनों में पाए जाते हैं, अन्य केवल एक के लिए अनन्य हो सकते हैं।
यह तथ्य हो सकता है कि सभी जीवित प्रजातियां समान संरचनाओं वाली कोशिकाओं से बनी होती हैं, लेकिन फिर भी, पौधों और जानवरों की कोशिकाओं की वास्तुकला में भिन्नताएं होती हैं।
कोशिका झिल्ली, नाभिक, माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया और रिक्तिकाएं सभी संरचनाएं हैं जो पौधे और पशु कोशिकाओं दोनों में पाई जाती हैं, हालांकि, कोशिका भित्ति और क्लोरोप्लास्ट दो संरचनाएं हैं जो पौधों में मौजूद हैं।
अब, हम उन मुख्य अंतरों को जानेंगे जो पादप कोशिका और जंतु कोशिका दोनों में होते हैं।
Other Related Posts –








 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Notes fo...
Breathing and Exchange of Gases Notes fo...
 Omnivores Animals- Definition, Name List...
Omnivores Animals- Definition, Name List...
 Nephron: Definition, Diagram, Structure,...
Nephron: Definition, Diagram, Structure,...














