The concept of Electronic Configuration is very crucial in the physics as well as in the quantum chemistry. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals of an atom or molecule. Each atom has a unique Configuration of electrons. Each electron in an orbital moves independently in an average field created by all other orbitals, according to electronic configurations. In this article we are going to learn about the Electron Configuration of elements more in detail by going through the Electronic Configuration examples of first 30 elements in the periodic table.
Electron Configuration
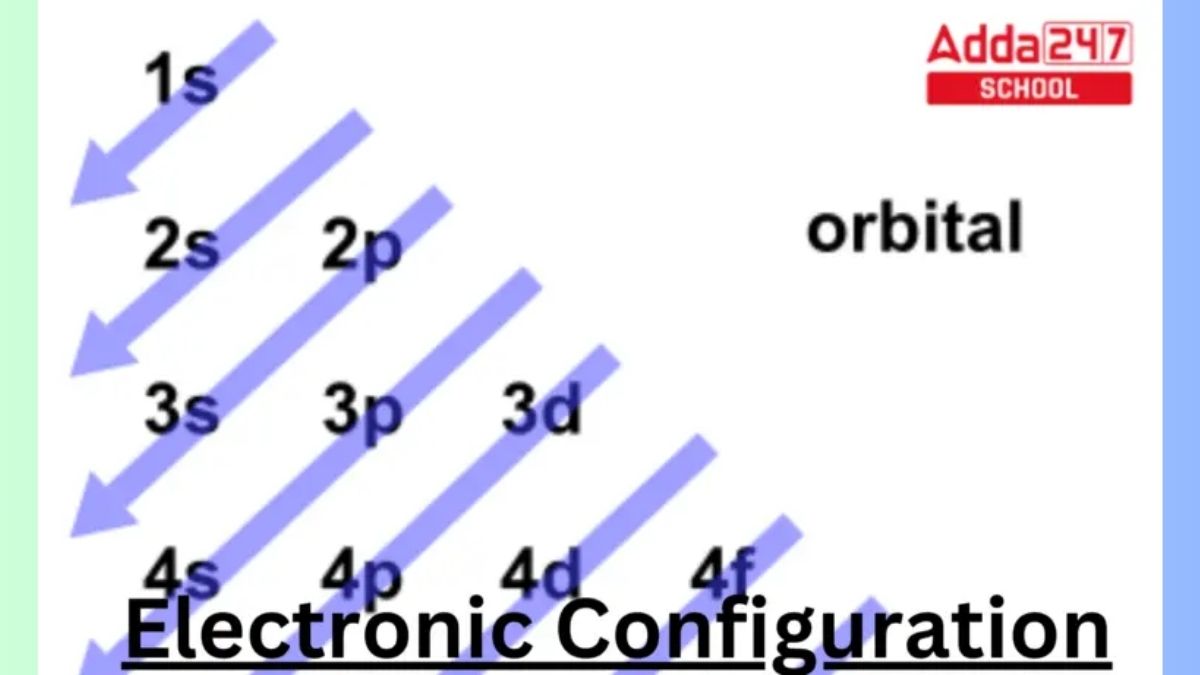
In simple words Electronic Configuration is the arrangements of electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals of an atom. Atomic electron configurations are represented by a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells are ordered. Atomic orbitals make up these subshells. s, p, d, and f are the four subshell labels that are employed. Each of these subshells has a maximum number of electrons of 2, 6, 10, and 14 accordingly. The electronic configuration of the neon atom, for example, is 1s2 2s2 2p6, which means that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by 2, 2, and 6 electrons, respectively. For example:
Neon (Ne) – 1s22s22p6
Electronic Configuration Definition
The way in which electrons are organized in orbitals surrounding the nucleus of an atom In the quantum-mechanical model, the electronic configuration of an atom is described by listing the occupied orbitals in the order they are filled, with the number of electrons in each orbital noted as a superscript.
Using this notation, sodium is arranged in orbitals as 2-8-1 with the electronic configuration of 1s22s22p63s1. Frequently, a abbreviated technique is utilized which only includes the electrons exceeding the noble gas configuration of the prior atom in the periodic table. An instance of this is sodium, which has an additional 3s electron compared to the noble gas neon (Ne, atomic number 10), represented as [Ne]3s1 in shorthand notation.
Electron Configuration of Elements 1 to 30
Take a look at the Electronic configuration of first 30 elements of the periodic table below.
| Atomic Number | Name of the Element |
Electronic Configuration
|
| 1 | Hydrogen (H) | 1s1 |
| 2 | Helium (He) | 1s2 |
| 3 | Lithium (Li) | [He] 2s1 |
| 4 | Beryllium (Be) | [He] 2s2 |
| 5 | Boron (B) | [He] 2s2 2p1 |
| 6 | Carbon (C) | [He] 2s2 2p2 |
| 7 | Nitrogen (N) | [He] 2s2 2p3 |
| 8 | Oxygen (O) | [He] 2s2 2p4 |
| 9 | Fluorine (F) | [He] 2s2 2p5 |
| 10 | Neon (Ne) | [He] 2s2 2p6 |
| 11 | Sodium (Na) | [Ne] 3s1 |
| 12 | Magnesium (Mg) | [Ne] 3s2 |
| 13 | Aluminium (Al) | [Ne] 3s2 3p1 |
| 14 | Silicon (Si) | [Ne] 3s2 3p2 |
| 15 | Phosphorus (P) | [Ne] 3s2 3p3 |
| 16 | Sulphur (S) | [Ne] 3s2 3p4 |
| 17 | Chlorine (Cl) | [Ne] 3s2 3p5 |
| 18 | Argon (Ar) | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 |
| 19 | Potassium (K) | [Ar] 4s1 |
| 20 | Calcium (Ca) | [Ar] 4s2 |
| 21 | Scandium (Sc) | [Ar] 3d1 4s2 |
| 22 | Titanium (Ti) | [Ar] 3d2 4s2 |
| 23 | Vanadium (V) | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
| 24 | Chromium (Cr) | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 |
| 25 | Manganese (Mn) | [Ar] 3d5 4s2 |
| 26 | Iron (Fe) | [Ar] 3d6 4s2 |
| 27 | Cobalt (Co) | [Ar] 3d7 4s2 |
| 28 | Nickel (Ni) | [Ar] 3d8 4s2 |
| 29 | Copper (Cu) | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 |
| 30 | Zinc (Zn) | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 |
Electron Configuration of Elements
The distribution of electrons in an element’s atomic orbitals is described by the element’s electron configuration. Atomic electronic configurations adhere to a standard nomenclature in which all atomic subshells that contain electrons are arranged in a sequence with the number of electrons they each hold expressed in superscript. For instance, the distribution of electrons in sodium atom can be given as 1s22s22p63s1
Electron Configuration of Carbon
The first two electrons will be placed in the 1s orbital when writing the electron configuration for carbon. The following two electrons for Carbon (C) are placed in the 2s orbital because 1s can only accommodate two electrons. The 2p orbital will house the final two electrons. The electronic configuration of carbon will therefore be 1s22s22p2.
Electron Configuration of Oxygen
The periodic table shows that oxygen has eight electrons. These 8 electrons would fill in the following order: 1s, 2s, and finally 2p, according to the aforementioned fill order. 1s22s22p4 would be O or oxygen’s electron configuration.
Electron Configuration of Chlorine
It will be 1s22s22p63s23p5 for the electron configuration of chlorine. The configuration notation gives scientists a simple way to express and record how electrons are organised around an atom’s nucleus.
Atomic Mass of Elements 1 to 30 with Symbol and PDF
Electron Configuration of Potassium
Potassium (K) has a complete electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p64s1. [Ar]4s1 is an acronym for the electron configuration of argon (Ar), plus one additional electron in the 4s orbital. The 18 electrons in argon. Potassium has 19 electrons, and the last electron arrangement completes the picture.
Electron Configuration of Calcium
The electron arrangement for calcium will be 1s22s22p63s23p64s2. The configuration notation gives scientists a simple way to express and record how electrons are organised around an atom’s nucleus. As a result, it is simpler to comprehend and forecast how atoms will cooperate to form chemical bonds.
| Related Posts | |
| Electron Configuration | Aufbau Principle |
| Periodic Table | Chemistry Investigatory Project |
| Hybridization Rules | Net Ionic Equations |









 Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
 CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
 CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...
CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...














