Sense organs are specialized organs in the body that help us receive and process information from the environment through our senses. There are 5 types of sense organs present in our body. These sense organs are the Eyes, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Skin. Kids are required to learn the sense organs name as they are vital for the proper functioning of our body. Sense organs respond to certain physical phenomena by providing the necessary information for interpretation through a network of nerves and different organs. Our associations and interactions with the world are controlled by these senses. In this article, we will cover the detailed concept of sense organs along with sense organs name and their functionalities.
Sense Organs
Sensory neurons make up sense organs, which are specialized organs. It aids our perception of and response to our surroundings. There are five sensory organs in the human body. Sense organ are vital for many processes and aid in our ability to perceive our environment. These are essential components of our bodies that provide us the ability to perceive our surroundings. Numerous stimuli are triggered by sense organs and their receptors, which then send messages to the brain.
What are the Sense Organs?
Sense organs are specialized organs of the human body that help to perceive the world around us. Sense Organs are an integral part of our lives and Sense Organ is the only sway that enables us to perceive the environment. There are two types of receptors found in sense organ: general receptors and special receptors. These receptors have the ability to send a signal to a sensory neuron. Specialized sense organ, such as the tongue for taste, the nose for smell, the ears for hearing and balance, and the eyes for vision, are known as special receptors.
Five Sense Organs Name
The five sense organs are the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. 5 Sense organs are specialized organs that aid in our perception of the world around us and are an important part of our daily life. They are the only means by which we may comprehend our surroundings.
Sense organ give the necessary info, which is then interpreted by other organs and a network of nerves. They all function in reaction to a certain physical phenomenon.
A sense is a biological mechanism that an organism uses for sensation, information collecting, and response to stimuli. The brain gets signals from the senses, which are constantly receiving information from the environment, interprets these signals, and causes the body to respond, and sense organ collect numerous stimuli for transduction during a sensation. Almost every aspect of an organism’s life revolves around sensation and perception. Our associations and interactions with the world around us are governed by these senses.
Function of Sense Organs For Class 1
There are five sensory organs in the human body. These five sense organs can receive and convey sensory information to the brain, allowing an organism to perceive its surroundings. The following are the several sensory organs:
Eyes
The eyes are our body’s visual sensory organs, and they are sensitive to light images. The colour of our eyes varies based on the amount of melanin in our bodies, and they aid in our sense of sight by detecting and focusing on light images.
The iris is the colored portion of the eye that governs the pupil’s size and diameter. The amount of light that enters the eyes is influenced by the size of the pupil.
The vitreous body, which is filled with a gelatinous fluid called vitreous humour and gives shape to the eyeball, is located behind the lens of the eye. It also transfers light to the retina, which is located at the very rear of the eyeball. Photoreceptors can be found in this retina. Light is detected by photoreceptors.
Ears
The auditory sense organs of our body, the ears, assist us in perceiving noises. Vibrations in the air are detected by our auditory system.
The outer ear, inner ear, and middle ear are the three parts of the ear. These vibrations are transferred from the outer ear into the ear canal, where they are converted into meaningful sound by the brain. This sense is also crucial for maintaining our body’s balance or homeostasis.
Tongue
The tongue aids in the perception of diverse tastes and flavours, and the taste buds located between the papillae on the tongue aid in the detection of distinct tastes. Gustation is the scientific term for the sense of taste.
The senses of smell and taste are intertwined, and if you can’t smell something, you won’t be able to taste it either.
Chemoreceptors are taste buds on the tongue. Both taste buds and the nasal cavity have chemoreceptors, but the chemoreceptors in the nose can sense any form of smell, whereas taste buds only have four different types. Each of the four may sense various flavours such as sweetness, sourness, bitterness, and saltiness.
Nose
The nose is an olfactory organ that aids our sense of taste as well as helps us perceive distinct aromas. The top of the nasal cavity is lined with olfactory cells, which contain cilia that protrude into the nasal cavity. The olfactory nerve fibres are located on the cell’s other end.
Chemoreceptors are olfactory cells that can sense small variations in chemicals. These molecules adhere to the cilia, which transmits a nerve signal to the brain, where it is translated into a recognisable odour. The body creates mucus during a cold, which inhibits the sense of smell.
Skin
The largest organ in our body, the skin is linked to our sense of touch.
Touch, pain, pressure, and temperature are all detected by general receptors in the skin, which are found throughout the body. When skin receptors are triggered, an impulse is sent to the spinal cord and ultimately to the brain.
Other Organs that Help us Sense for Kids
Apart from the five sense organs mentioned above, there are other organs too that assist us in sensing things around us:
Vestibular System
The vestibular system serves as a sensory system for the body, delivering information about motions, head position, and spatial orientation to the brain. In addition, this system is involved in motor functions. It aids in maintaining body posture, body balance, head and body stabilisation during movement, and even understanding our bodies’ orientation and posture with respect to the environment.
Proprioception system
The proprioception system aids the body in identifying the muscles, joints, and limbs located in 3D space, as well as the direction it is moving in respect to the body, whether it is conscious or unconscious.
5 Sense Organs Name with Pictures
All 5 sense organs are given here in this picture.
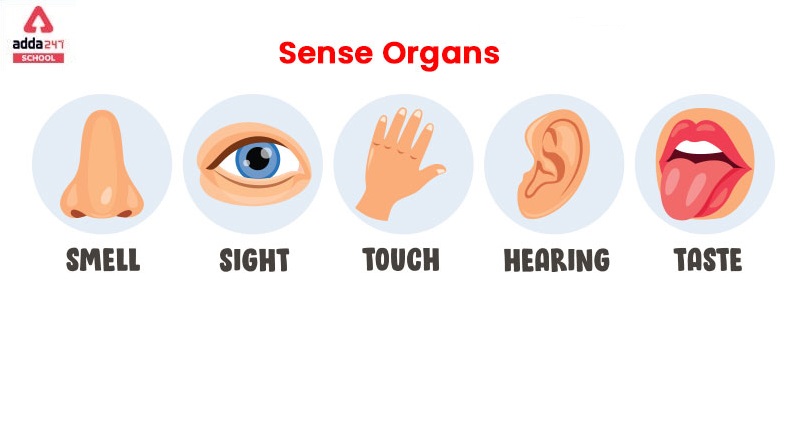
5 Sense Organs Images
five sense organs chart is given below. students do check for their project work.
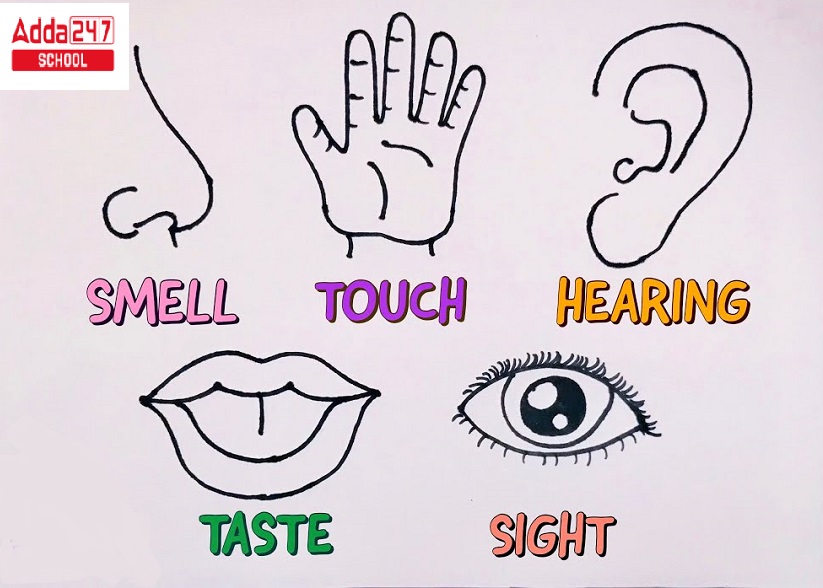
How to keep the Sense Organs healthy?
Maintaining healthy sense organs is important for overall well-being. Here are some general tips to help keep your sense organs healthy:
- Eyes:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Foods like leafy greens, carrots, and fish can be beneficial for eye health.
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds to reduce eye strain.
- Protect your eyes from harmful UV rays by wearing sunglasses when outdoors.
- Avoid smoking, as it can increase the risk of eye diseases like cataracts and macular degeneration.
- Get regular eye check-ups to detect any issues early.
- Ears:
- Avoid prolonged exposure to loud noises, as it can lead to hearing loss. Use ear protection in noisy environments.
- Clean your ears gently and do not insert objects like cotton swabs into the ear canal, as this can damage the ear.
- If you’re prone to ear infections, keep your ears dry and clean, and seek medical attention if you experience pain or discomfort.
- Nose:
- Keep the nasal passages moisturized to prevent dryness and discomfort. Use saline nasal sprays if necessary.
- Avoid excessive use of nasal decongestant sprays, as they can lead to a rebound effect and worsen congestion.
- If you have allergies, manage them properly to prevent nasal inflammation and congestion.
- Taste and Smell:
- Eat a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support your taste buds and maintain your sense of taste.
- Avoid smoking, as it can affect your sense of taste and smell.
- Be cautious with hot foods and liquids to prevent burns that could affect your ability to taste.
- Skin (Sense of Touch):
- Practice good skin hygiene by keeping your skin clean and moisturized.
- Protect your skin from excessive sun exposure by using sunscreen and protective clothing.
- Check your skin regularly for any changes or unusual growths that could indicate skin issues.
- Mindfulness and Stress Management:
- Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and stress reduction techniques can indirectly contribute to the health of your sense organs by promoting overall well-being.
Remember that individual health needs can vary, so it’s always a good idea to consult with healthcare professionals or specialists if you have specific concerns about your sense organs’ health.
5 Sense Organs Name in Hindi
संवेदी न्यूरॉन्स संवेदी अंग बनाते हैं, जो विशेष अंग हैं। यह हमारे आस-पास की हमारी धारणा और प्रतिक्रिया में सहायता करता है। मानव शरीर में पांच संवेदी अंग होते हैं। पांच संवेदी अंग आंख, कान, नाक, जीभ और त्वचा हैं।
इंद्रिय अंग विशेष अंग हैं जो हमारे आस-पास की दुनिया की हमारी धारणा में सहायता करते हैं और हमारे दैनिक जीवन का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। वे ही एकमात्र साधन हैं जिनके द्वारा हम अपने परिवेश को समझ सकते हैं।
इंद्रिय अंग आवश्यक जानकारी देते हैं, जिसकी व्याख्या अन्य अंगों और तंत्रिकाओं के एक नेटवर्क द्वारा की जाती है। वे सभी एक निश्चित भौतिक घटना की प्रतिक्रिया में कार्य करते हैं।
एक भावना एक जैविक तंत्र है जो एक जीव संवेदना, सूचना एकत्र करने और उत्तेजनाओं की प्रतिक्रिया के लिए उपयोग करता है। मस्तिष्क को इंद्रियों से संकेत मिलते हैं, जो लगातार पर्यावरण से जानकारी प्राप्त कर रहे हैं, इन संकेतों की व्याख्या करते हैं, और शरीर को प्रतिक्रिया देने का कारण बनते हैं, और संवेदी अंग एक सनसनी के दौरान पारगमन के लिए कई उत्तेजना एकत्र करते हैं। एक जीव के जीवन का लगभग हर पहलू संवेदना और धारणा के इर्द-गिर्द घूमता है। हमारे आस-पास की दुनिया के साथ हमारे जुड़ाव और अंतःक्रियाएं इन इंद्रियों द्वारा नियंत्रित होती हैं।
Sense Organs Meaning in Hindi
पांच ज्ञानेंद्रियों के नाम और उनके कार्य: मानव शरीर में पांच संवेदी अंग होते हैं। ये पांच इंद्रिय अंग मस्तिष्क को संवेदी जानकारी प्राप्त कर सकते हैं और भेज सकते हैं, जिससे जीव अपने परिवेश को देख सकता है। निम्नलिखित कई संवेदी अंग हैं:
1. आंखें
आंखें हमारे शरीर के दृश्य संवेदी अंग हैं, और वे प्रकाश छवियों के प्रति संवेदनशील हैं। हमारी आंखों का रंग हमारे शरीर में मेलेनिन की मात्रा के आधार पर भिन्न होता है, और वे प्रकाश छवियों का पता लगाने और उन पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके हमारी दृष्टि की भावना में सहायता करते हैं।
परितारिका आंख का रंगीन भाग है जो पुतली के आकार और व्यास को नियंत्रित करता है। आंखों में प्रवेश करने वाले प्रकाश की मात्रा पुतली के आकार से प्रभावित होती है।
कांच का शरीर, जो एक जिलेटिनस तरल पदार्थ से भरा होता है जिसे कांच का हास्य कहा जाता है और नेत्रगोलक को आकार देता है, आंख के लेंस के पीछे स्थित होता है। यह प्रकाश को रेटिना में भी स्थानांतरित करता है, जो नेत्रगोलक के बिल्कुल पीछे स्थित होता है। इस रेटिना में फोटोरिसेप्टर पाए जा सकते हैं। प्रकाश का पता फोटोरिसेप्टर द्वारा लगाया जाता है।
2. कान
हमारे शरीर के श्रवण इंद्रिय अंग, कान, शोर को समझने में हमारी सहायता करते हैं। हवा में कंपन का पता हमारे श्रवण तंत्र द्वारा लगाया जाता है।
बाहरी कान, भीतरी कान और मध्य कान कान के तीन भाग हैं। इन कंपनों को बाहरी कान से कान नहर में स्थानांतरित किया जाता है, जहां वे मस्तिष्क द्वारा सार्थक ध्वनि में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं। यह भाव हमारे शरीर के संतुलन या होमियोस्टैसिस को बनाए रखने के लिए भी महत्वपूर्ण है।
3. जीभ
जीभ विविध स्वादों और स्वादों की धारणा में सहायता करती है, और जीभ पर पैपिला के बीच स्थित स्वाद कलिकाएं अलग-अलग स्वादों का पता लगाने में सहायता करती हैं। Gustaoception स्वाद की भावना के लिए वैज्ञानिक शब्द है।
गंध और स्वाद की इंद्रियां आपस में जुड़ी हुई हैं, और यदि आप किसी चीज को सूंघ नहीं सकते हैं, तो आप उसका स्वाद भी नहीं ले पाएंगे।
केमोरिसेप्टर जीभ पर स्वाद कलिकाएँ होती हैं। स्वाद कलिकाएं और नाक गुहा दोनों में केमोरिसेप्टर होते हैं, लेकिन नाक में केमोरिसेप्टर गंध के किसी भी रूप को समझ सकते हैं, जबकि स्वाद कलियों में केवल चार अलग-अलग प्रकार होते हैं। चारों में से प्रत्येक मिठास, खटास, कड़वाहट और नमकीनता जैसे विभिन्न स्वादों को महसूस कर सकता है।
4. नाक
नाक एक घ्राण अंग है जो स्वाद की हमारी समझ में सहायता करता है और साथ ही हमें अलग-अलग सुगंधों को समझने में मदद करता है। नाक गुहा के शीर्ष को घ्राण कोशिकाओं के साथ पंक्तिबद्ध किया जाता है, जिसमें सिलिया होता है जो नाक गुहा में फैलता है। घ्राण तंत्रिका तंतु कोशिका के दूसरे छोर पर स्थित होते हैं।
केमोरिसेप्टर घ्राण कोशिकाएं हैं जो रसायनों में छोटे बदलावों को महसूस कर सकती हैं। ये अणु सिलिया का पालन करते हैं, जो मस्तिष्क को एक तंत्रिका संकेत पहुंचाता है, जहां इसे एक पहचानने योग्य गंध में अनुवादित किया जाता है। सर्दी के दौरान शरीर में बलगम का निर्माण होता है, जो गंध की भावना को रोकता है।
5. त्वचा
हमारे शरीर का सबसे बड़ा अंग, त्वचा हमारे स्पर्श की भावना से जुड़ा है।
स्पर्श, दर्द, दबाव और तापमान सभी का पता त्वचा में सामान्य रिसेप्टर्स द्वारा लगाया जाता है, जो पूरे शरीर में पाए जाते हैं। जब त्वचा के रिसेप्टर्स ट्रिगर होते हैं, तो एक आवेग रीढ़ की हड्डी और अंत में मस्तिष्क को भेजा जाता है।








 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
 CUET PG 2026 Registration Form OUT at ex...
CUET PG 2026 Registration Form OUT at ex...














