With the advent of your time, the modern computer began to take shape. The development of the computer had begun in the sixteenth century. Numerous improvements were made to the original computer. It continued to advance in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and cost in order to push the design of the current-day computer. In this article, we will cover all the computer generations along with their characteristics in detail. We have also included the chart of all Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with Pictures along with their brief description.
Generation of Computer
The generation of computers along with their defining characteristics and advancements. From the sixteenth century onward, computers underwent a long and continuous state of evolution. Computer generations refer to the many stages of this extended duration. The period from 1940 to 1956 saw the development of the first generation of computers, which was followed by the second generation from 1956 to 1963, the third generation from 1964 to 1971, the fourth generation from 1971 to the present, and the fifth generation, which is now under development. It’s important to note that there may be some variation in the classification of generations depending on different sources, but this is a commonly accepted overview.
How Many Generation of Computer
- First Generation (1940s-1950s): The first generation of computers used vacuum tubes as the primary electronic component. These machines were large, expensive, and consumed a significant amount of electricity. They were mainly programmed using machine language and assembly language. Examples include the ENIAC and UNIVAC I.
- Second Generation (1950s-1960s): The second generation of computers introduced the use of transistors, which replaced vacuum tubes. Transistors were smaller, faster, more reliable, and consumed less power. This advancement led to the development of smaller and more affordable computers. High-level programming languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL were developed during this period.
- Third Generation (1960s-1970s): The third generation of computers witnessed the invention of integrated circuits (ICs) or chips. ICs allowed for the placement of multiple transistors and electronic components on a single chip, leading to further miniaturization and increased processing power. This generation saw the emergence of mainframe and minicomputers, as well as the development of operating systems and time-sharing.
- Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): The fourth generation of computers brought about the advent of microprocessors. Microprocessors combined the processing power of a complete CPU onto a single chip, enabling the creation of personal computers (PCs). The development of microcomputers and the use of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) marked this era. High-level programming languages, such as C and Pascal, became more popular.
- Fifth Generation (1980s-Present): The fifth generation of computers is characterized by the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and parallel processing. This generation focuses on creating computer systems that can mimic human intelligence, including natural language processing and expert systems. Some key technologies associated with this generation include neural networks, genetic algorithms, and supercomputers.
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th
The generation of computer 1st to 5th long period is often conveniently divided into the subsequent phases called generations of computers.
| Generation of Computer | Time-Period | Evolving Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| First Generation | 1940s – 1950s | Vacuum Tube Based |
| Second Generation | 1950s – 1960s | Transistor Based |
| Third Generation | 1960s – 1970s | Integrated Circuit Based |
| Fourth Generation | 1970s – Present | Microprocessor Based |
| Fifth Generation | Present – Future | Artificial Intelligence Based |
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with Pictures
Here we will discuss all the generations of computers 1st to 5th in detail. It will help students as well as competitive exam aspirants in their exam preparation.
First Generation of Computer (1940s-1950s)
Vacuum tubes served as the primary electronic component of the first generations of computers. Vacuum tubes were big, heavy things that used a lot of electricity. These computers had only a few kilohertz of speed, which was also quite slow.
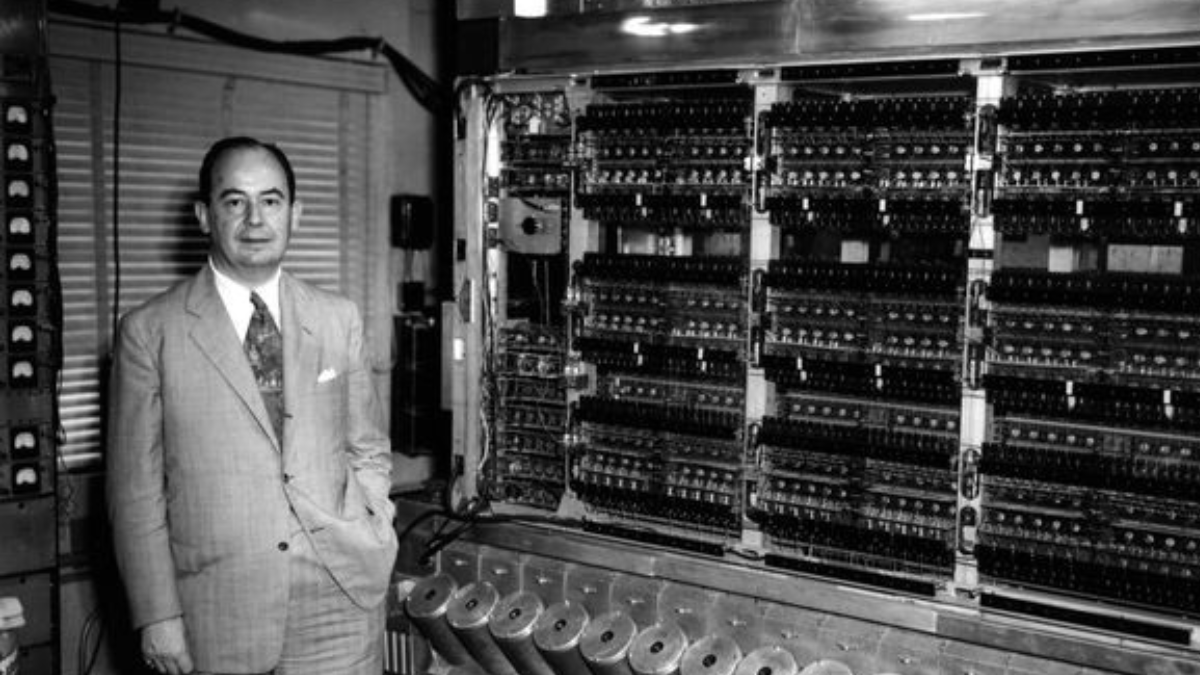
Characteristics of First Generation of Computer
The table given below consists of characteristics of first generation of computer.
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Vacuum tube |
| Programming language | Machine language |
| Main memory | Magnetic tapes and magnetic drums |
| Input/output devices | Paper tape and punched cards |
| Speed and size | Very slow and very large (often taking up an entire room) |
| Examples of the first generation | IBM 650, IBM 701, ENIAC, UNIVAC1, etc. |
Second Generation of Computer (1950s-1960s)
Transistors, as opposed to vacuum tubes, were employed in the second generation of computers. Compared to vacuum tubes, transistors were quicker, more efficient, and smaller. Smaller, more potent computers could be created as a result.
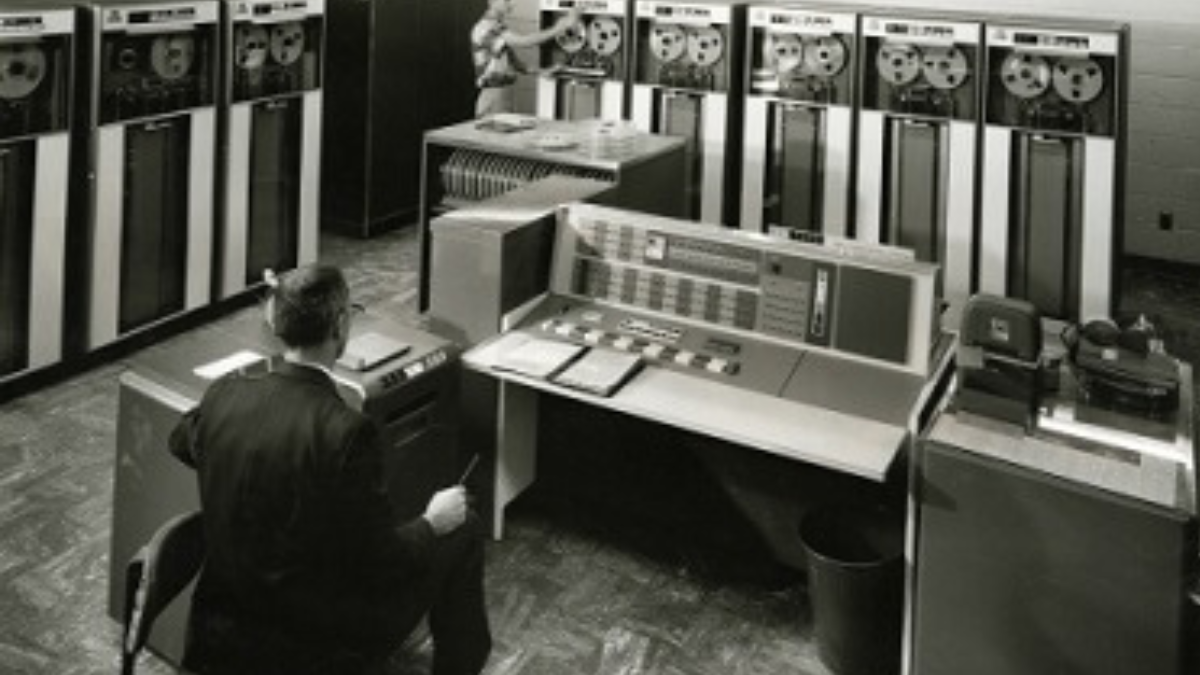

Characteristics of Second Generation of Computer
The table given below consists of the characteristics of the second generation of Computer.
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Transistor |
| Programming language | Machine language and assembly language |
| Memory | Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk |
| Input/output devices | Magnetic tape and punched cards |
| Power and size | Smaller in size, had low power consumption, and generated less heat (in comparison with the first-generation computers) |
| Examples of the second generation | PDP-8, IBM1400 series, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, CDC 3600, etc. |
Third Generation of Computer (1960s-1970s)
Integrated circuits (ICs) served as the primary electronic component of the third generation of computers. Transistors are built into integrated circuits (ICs) and are engraved onto a single chip. This made it possible to create increasingly more compact and potent computers.
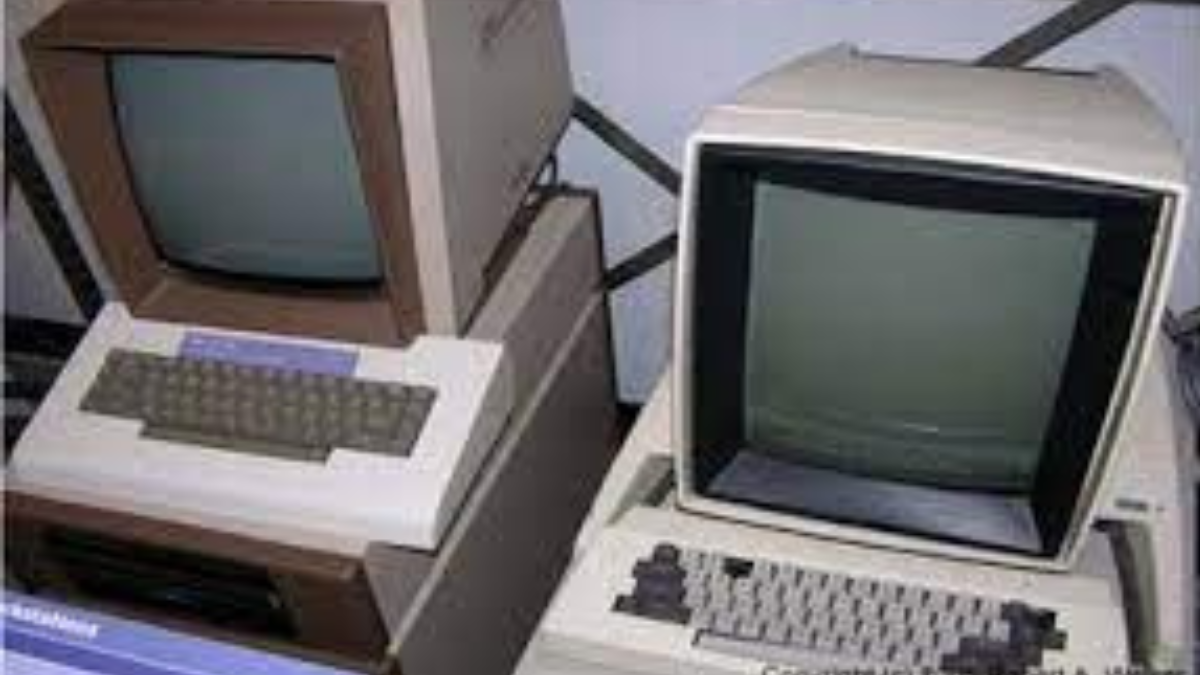

Characteristics of the Third Generation of Computer
The table given below consists of the characteristics of the third generation of Computer.
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Integrated circuits (ICs) |
| Programming language | High-level language |
| Memory | Large magnetic core, magnetic tape/disk |
| Input/output devices | Magnetic tape, monitor, keyboard, printer, etc. |
| Examples of the third generation | IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, NCR 395, B6500, UNIVAC 1108, etc. |
Fourth Generation of Computer (1970s-1980s)
Microprocessors are the primary electronic component used in computers that belong to the fourth generation. Single chips called microprocessors house the central processing unit (CPU), memory, and other parts. Personal computers (PCs) and other compact, cheap computers were made possible as a result.
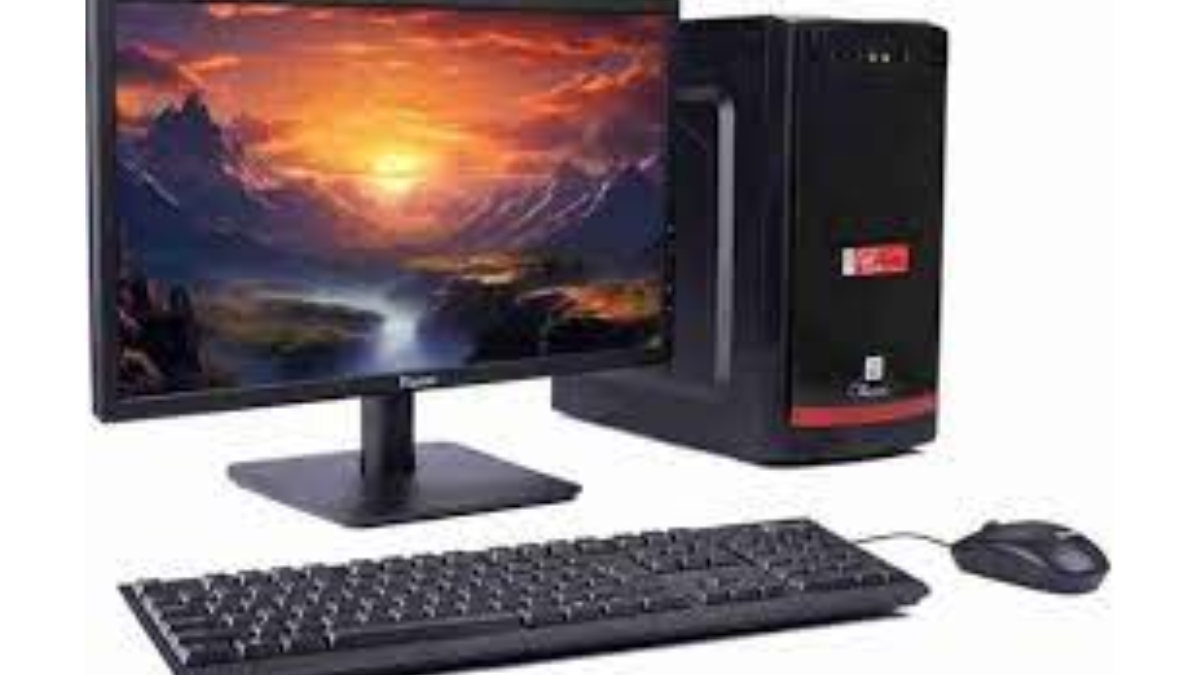

Characteristics of The Fourth Generation of Computer
The table given below consists of the characteristics of the fourth Generation of Computers.
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Very-large-scale integration (VLSI) and the microprocessor (VLSI has thousands of transistors on a single microchip) |
| Memory | Semiconductor memory (such as RAM, ROM, etc.) |
| Input/output devices | Pointing devices, optical scanning, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc. |
| Examples of the fourth generation | IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, Altair 8800, etc. |
Fifth Generation of Computer (1980s-Present)
The fifth generation of computers, which is currently being developed, is concentrated on parallel processing and artificial intelligence (AI). AI refers to a computer’s capacity to learn and think like a human. The capacity of computers to carry out several tasks at once is known as parallel processing.

Characteristics of Fifth and Current Generations of Computer
The table given below consists of characteristics of fifth generation.
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Based on artificial intelligence, uses Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method |
| Language | Understands natural language (human language) |
| Size | Portable and small in size |
| Input/output devices | Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (voice recognition), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc. |
| Example of the fifth generation | Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc. |
Computer Generation Chart
The Chart below summarizes the different computer generation chart.
| Generation | Main electronic component | Speed | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| First generation | Vacuum tubes | Few kilohertz | Large, bulky |
| Second generation | Transistors | Millions of hertz | Smaller, more powerful |
| Third generation | Integrated circuits (ICs) | Billions of hertz | Very small, powerful |
| Fourth generation | Microprocessors | Gigahertz | Personal computers |
| Fifth generation | Artificial intelligence (AI) and parallel processing | Tremendous speed and power | Still in development |
Generations of Computer Chart
Below we have provided a chart listing all generations of computers. The chart also shows their operating time period and the technology used in them. The computer generations chart is given below. check all computers generations.
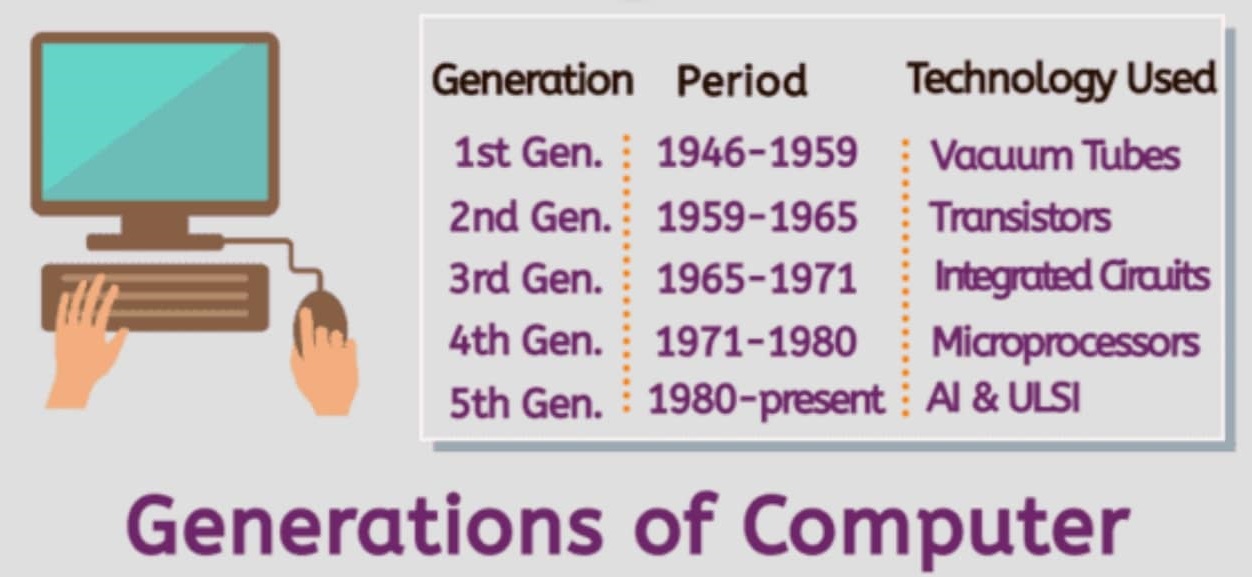
How many Generations of Computer?
Computers can be categorized into five generations of computer based on their technological advancements and key developments. These generations are number from 1 to 5. Computer system development is typically discussed in terms of multiple generations of development. As successive generations came into being, computer technology advanced.
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th PDF Download
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf for the students to better understand the all functions of the computers. This generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf download will assist students in their studies.
Click here for Generation of Computer 1st to 5th Pdf Download
| Related Articles | |
| What is a Flowchart in Computer? | Components of a Computer |
| Types of Computers | Fundamentals of Computers |









 All Input and Output Devices of Computer
All Input and Output Devices of Computer
 BTech Computer Science Syllabus 2025 Out...
BTech Computer Science Syllabus 2025 Out...
 Data Science Course Syllabus 2025, Check...
Data Science Course Syllabus 2025, Check...














