ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24: The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE) releases the ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 on its official website. It is one of the two main central boards apart from the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). Candidates who are going to take the ICSE Class 10 board Exam in 2024 must go through the ICSE Maths Syllabus 2023-24 Class 10. Knowing what to study is the best way to score good marks in the examination. CISCE has made no modifications to their Maths syllabus class 10 icse 2023-24 academic year. Students must download the Maths Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2023-24 PDF given on the page and pass the exam with flying colors.
Maths Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2023-24
The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE) is anticipated to conduct the Class 10 exams 2024 in February – March 2024, therefore it is a very crucial Time to gear up preparation for the ICSE 2024 board exams While studying and preparing for Class 10 maths, students can refer to the most recent maths syllabus class 10 icse 2023-24 which will help them to familiar with the course structure’s topics/chapters. By following the detailed syllabus, one can easily score good marks in the examination.
The maths syllabus class 10 icse 2023-24 includes crucial topics like Commercial Maths, Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry . Students can find the ICSE Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2023-24 chapter-wise and topics explained on this page.
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 Exam Pattern
Candidates who are going to take the ICSE class 10 board Exams in 2024 must familiar with the ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 as well the Question paper design. Go through the Key highlights of the ICSE Class 10 Maths Qusetion paper.
1. There will be one two-and-a-half-hour paper worth 80 points and one internal assessment worth 20 points.
2. The exam will be divided into two halves, Section I (40 points) and Section II (40 points).
3. Section I will be made up of mandatory short answer questions.
4. Section II: Candidates must answer four out of seven questions.
ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 Pdf Download
The ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 PDF is now available to download at the official website of CISCE. Candidates who are going to sit in the upcoming Class 10 board Exam download the ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 Pdf and start preparing accordingly. For convenience of the students, we have provided the direct link to download the ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024 PDF below.
ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 Download PDF
Syllabus of Maths Class 10 ICSE 2023-24
Maths is one of the Scoring subjects in the Class 10 Curriculum. However, few students find difficulty in it because of its huge calculations. The Main Mantra to secure to good Score in Maths is to practice practice and Practice nothing else. Candidates must study all the Topics in the ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 in detail and revise the concept again and again. check out the Topics and subjects included in the ICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2023-24 are as follows.
Maths Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2023-24 Chapter 1. Commercial Mathematics
(i) Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Computation of tax including problems involving discounts, list price, profit, loss,
basic/cost price including inverse cases. Candidates are also expected to find the price
paid by the consumer after paying State Goods and Service Tax (SGST) and Central
Goods and Service Tax (CGST) – the different rates as in vogue on different types
of items will be provided. Problems based on corresponding inverse cases are also included.
(ii) Banking
Recurring Deposit Accounts: computation of interest and maturity value using the
formula:
Maths Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2023-24 Chapter 2. Algebra
(i) Linear Inequations
Linear Inequations in one unknown for x ∈ N, W, Z, R. Solving:
- Algebraically and writing the solution in set notation form.
- Representation of solution on the number line.
(ii) Quadratic Equations in one variable
(a) Nature of roots
- Two distinct real roots if b2 – 4ac > 0
- Two equal real roots if b² – 4ac = 0
- No real roots if b² – 4ac < 0
(b) Solving Quadratic equations by:
- Factorisation
- Using Formula.
(c) Solving simple quadratic equation problems.
(iii)Ratio and Proportion
(a) Proportion, Continued proportion, mean proportion
(b) Componendo, dividendo, alternendo, invertendo properties and their combinations.
(iv) Factorisation of polynomials:
(a) Factor Theorem.
(b) Remainder Theorem.
(c) Factorising a polynomial completely after obtaining one factor by factor theorem.
Note: f (x) not to exceed degree 3.
(v) Matrices
(a) Order of a matrix. Row and column matrices.
(b) Compatibility for addition and multiplication.
(c) Null and Identity matrices.
(d) Addition and subtraction of 2×2 matrices.
(e) Multiplication of a 2×2 matrix by
- a non-zero rational number
- a matrix.
(vi) Arithmetic Progression
Finding the General term of an A.P.
Finding Sum of first ‘n’ terms of an A.P.
(vii) Co-ordinate Geometry
(a) Reflection
(i) Reflection of a point in a line:
x=0, y =0, x= a, y=a, the origin.
(ii) Reflection of a point in the origin.
(iii)Invariant points.
(b) Co-ordinates expressed as (x, y), Section formula, Midpoint formula, Concept of slope, equation of a line, Various forms of straight lines.
(i) Section and Mid-point formula (Internal section only, co-ordinates of the centroid of a triangle included).
(ii) Equation of a line:
- Slope –intercept form y = mx + c
- Two- point form (y-y1) = m(x-x1)
Geometric understanding of ‘m’ as slope/ gradient/ tanθ where θ is the angle the line makes with the positive direction of the x axis. Geometric understanding of ‘c’ as the y intercept/the ordinate of the point where the line intercepts the y axis/ the point on
the line where x=0. - Conditions for two lines to be parallel or perpendicular.
Maths Syllabus Class 10 ICSE 2023-24 Chapter 3. Geometry
(a) Similarity
Similarity, conditions of similar triangles.
(i) Comparison with congruency, keyword being proportionality.
(ii) Three conditions: SSS, SAS, AA. Simple applications (proof not included).
(iii)Applications of Basic Proportionality Theorem.
(b) Circles
(i) Angle Properties
- The angle that an arc of a circle subtends at the center is double that which it subtends at any point on the remaining part of the circle
- Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.
- The angle in a semi-circle is a right angle.
(ii) Cyclic Properties:
- Opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary
- The exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the opposite interior angle.
(iii)Tangent and Secant Properties:
- The tangent at any point of a circle and the radius through the point are
perpendicular to each other. - If two circles touch, the point of contact lies on the straight line joining their centres.
- From any point outside a circle, two tangents can be drawn, and they are
equal in length. - If two chords intersect internally or externally then the product of the lengths of the segments are equal.
- If a chord and a tangent intersect externally, then the product of the lengths of segments of the chord is equal to the square of the length of the tangent from the point of contact
to the point of intersection. - If a line touches a circle and from the point of contact, a chord is drawn, the angles between the tangent and the chord are respectively equal to the angles in the corresponding
alternate segments.
[ Note: Proofs of the theorems are not required. Applications of all Circle Theorems in
solving numerical and theoretical problems are included.]
(iv) Constructions
(a) Construction of tangents to a circle from an external point
(b) Circumscribing and inscribing a circle on a triangle and a regular hexagon.
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter 4. Mensuration
Area and volume of solids – Cylinder, Cone and Sphere.
Three-dimensional solids – right circular cylinder, right circular cone and sphere: Area (total surface and curved surface) and Volume.
Direct application problems including cost, Inner and Outer volume and melting and recasting
method to find the volume or surface area of a new solid. Combination of solids included.
Note: Problems on Frustum are not included.
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter 5. Trigonometry
(a) Using Identities to prove simple algebraic trigonometric expressions
sin²A + cos² A = 1
1 + tan² A = sec² A
1+cot²A = cosec²A; 0 ≤ A ≤ 90°
(b) Heights and distances: Solving 2-D problems involving angles of elevation and depression
using trigonometric tables.
Note: Cases involving more than two right angled triangles excluded.
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter 6. Statistics
Statistics – basic concepts, Mean, Median, Mode.
Histograms and Ogive.
(a) Computation of:
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean*, median class, and modal class for
grouped data (only continuous data).
* Mean by all 3 methods included:
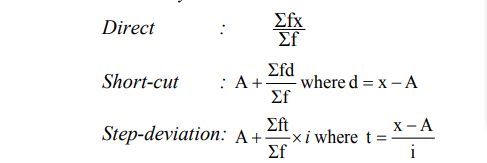
(b) Graphical Representation. Histograms and Less than Ogive.
- Finding the mode from the histogram, the upper quartile, lower Quartile and
median etc. from the ogive.
• Calculation of inter Quartile range.
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024 Chapter 7. Probability
Random experiments, Sample space, Events, definition of probability, Simple problems on
single events.
SI UNITS, SIGNS, SYMBOLS AND ABBREVIATIONS
(1) Agreed conventions
(a) Units may be written in full or using the agreed symbols, but no other abbreviation may be used.
(b) The letter ‘s’ is never added to symbols to indicate the plural form.
(c) A full stop is not written after symbols for units unless it occurs at the end of a sentence.
(d) When unit symbols are combined as a quotient, e.g., meter per second, it is recommended that it should be written as m/s, or as m
.
(e) Three decimal signs are in common international use: the full point, the mid-point and the comma. Since the full point is sometimes used for multiplication and the comma for spacing digits in large numbers, it is recommended that the mid-point be used for decimals.
(2) Names and symbols
ICSE Maths Syllabus 2024: Internal Assessment
The minimum number of assignments: Two assignments as prescribed by the teacher.
Suggested Assignments
- Comparative newspaper coverage of different items.
- Survey of various types of Bank accounts, and rates of interest offered.
- Planning a home budget.
- Conduct a survey in your locality to study the mode of conveyance / Price of various essential
commodities / favourite sports. Represent the data using a bar graph / histogram and estimate
the mode. - To use a newspaper to study and report on shares and dividends.
- Set up a dropper with ink in it vertical at a height say 20 cm above a horizontally placed sheet of plain paper. Release one ink drop; observe the pattern, if any, on the paper. Vary the vertical
distance and repeat. Discover any pattern of relationship between the vertical height and the
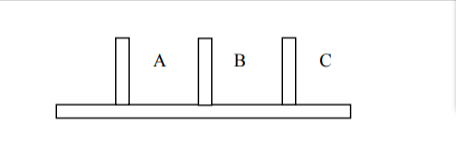
ink drop observed. - You are provided (or you construct a model as shown) – three vertical sticks (size of a pencil)
stuck to a horizontal board. You should also have discs of varying sizes with holes (like a
doughnut). Start with one disc; place it on (in) stick A. Transfer it to another stick (B or C); this
is one move (m). Now try with two discs placed in A such that the large disc is below, and the
smaller disc is above (number of discs = n=2 now). Now transfer them one at a time in B or C
to obtain a similar situation (larger disc below). How many moves? Try with more discs (n = 1, 2, 3, etc.) and generalize.
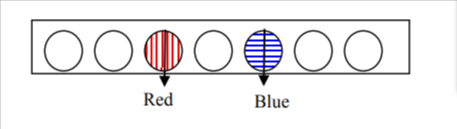
- The board has some holes to hold marbles, red on
one side and blue on the other. Start with one
pair. Interchange the positions by making one
move at a time. A marble can jump over another
to fill the hole behind. The move (m) equal 3.
Try with 2 (n=2) and more. Find the relationship
between n and m.
- Take a square sheet of paper of side 10 cm. Four small squares are to be cut from the corners of
the square sheet and then the paper is folded at the cuts to form an open box. What should be the
size of the squares cut so that the volume of the open box is maximum? - Take an open box, four sets of marbles (ensuring that marbles in each set are of the same size), and some water. By placing the marbles and water in the box, attempt to answer the question: do
larger marbles or smaller marbles occupy more volume in a given space? - An eccentric artist says that the best paintings have the same area as their perimeter (numerically). Let us not argue whether such sizes increase the viewer’s appreciation, but only try and find what sides (in integers only) a rectangle must have if its area and perimeter are to be equal (Note: there are only two such rectangles).
- Find by constructing the center of a circle, using only a 60-30 set square and a pencil.
- Various types of “cryptarithm”.
| Related Articles | |
| ICSE Class 10 History and Civics Syllabus | ICSE Class 10 Physics Syllabus |
| ICSE Class 10 English Syllabus | ICSE Class 10 Biology Syllabus |









 CUET Commerce Syllabus 2026, Download Su...
CUET Commerce Syllabus 2026, Download Su...
 CUET PG Hindi Syllabus 2026, Download CU...
CUET PG Hindi Syllabus 2026, Download CU...
 NIMCET Syllabus 2026, Download Subject-w...
NIMCET Syllabus 2026, Download Subject-w...














