The logarithm Formula is one of the most widely used formulas used for solving complex calculations. Logarithm, also known commonly by the name log, is basically an alternative way to write the exponents. Mathematical calculations and many other scientific disciplines depend heavily on logarithms. A mathematical idea known as the logarithm is utilized frequently in fields including physics, engineering, computer science, and finance to assist in simplifying complicated computations. This formula is used to find the values related to logs.
Logarithm Formula
The logarithm formula is an important formula for solving complex problems in higher classes related to exponents. This formula is used whenever the concept of logarithm comes into play. Before understanding this formula, let us first have a deeper look about logarithms.
What are Logarithms?
Logarithms are another method in which an exponential number can be expressed. It is the opposite function of the exponential function just like the division is opposite that of the multiplication. Simply put, it is the power to which a base number of the logarithm must be raised to get the given number. You will have a clear understanding of this concept by going through the explanation given below.
The formula of logarithm for an exponential expression ab= c is given by loga (c) = b. Some of the examples of exponent form to log form is given below.
36 = 729 can be written in logarithm form as log3(729) = 6
44 = 256 can be written in logarithm form as log4(256) = 4
pq = a can be written in logarithm form as logp(a) = q
210 = 1024 can be written in logarithm form as log2(1024) = 10
Log Formula Explanation
This formula is used to derive the values of exponential functions by converting them into the logarithmic functions. It makes calculation quite easy, hence saving a lot of effort. Let us understand this formula in detail.
The logarithmic form of an exponent is written in the following way.
Let us suppose we have been given xy= z
then, the logarithm of the above exponential function becomes
logx (z) = y
where, x is known as the base of the log
z is known as the argument of the log
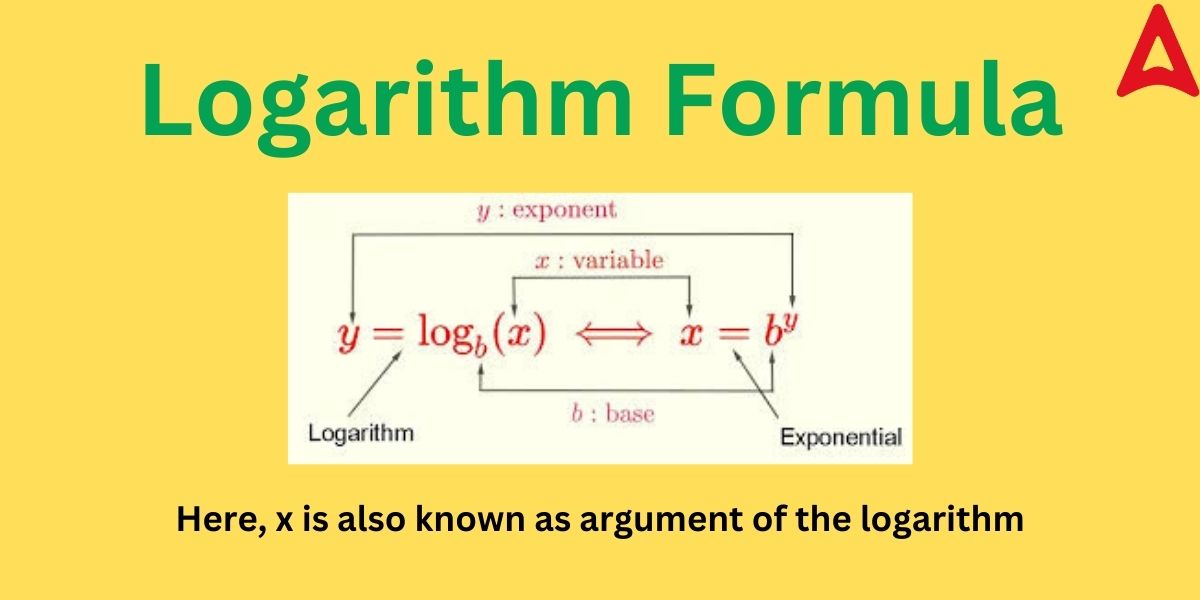
As you can observe from the above formula and diagram, the base of the log is the number to which the exponent is raised.
Formula of Logarithm in Hindi
Logarithm को हिंदी में लघुगणक कहते हैं| लघुगणक सूत्र का उपयोग घातीय कार्यों को लघुगणकीय कार्यों में परिवर्तित करके उनके मान प्राप्त करने के लिए किया जाता है। यह गणना को काफी आसान बना देता है, जिससे बहुत सारा प्रयास बच जाता है। आइए इस फॉर्मूले को विस्तार से समझते हैं.
किसी घातांक का लघुगणकीय रूप निम्नलिखित प्रकार से लिखा जाता है।
मान लीजिए कि हमें ab= c दिया गया है
फिर, उपरोक्त घातीय फलन का लघुगणक बन जाता है
loga (c) = b
जहां, a को लघुगणक के आधार के रूप में जाना जाता है
c को लघुगणक के तर्क के रूप में जाना जाता है
जिसे अंग्रेजी भाषा में Argument कहते हैं, उसे हिन्दी भाषा में तर्क कहा जाता है जबकी base को हिन्दी भाषा में आधार कहा जाता है|
जैसा कि आप उपरोक्त सूत्र से देख सकते हैं, लघुगणक का आधार वह संख्या है जिस पर घातांक बढ़ा हुआ है।
Logarithm Types
There are basically two types of logarithms. The value for both these types of logarithms can be found using this formula. The two types of logarithm are stated below.
1) Natural Logarithm: Natural logarithm are those logarithm that always contain a constant “e” in its base. This constant is known as Euler’s constant. It is therefore also recognized as base “e” constant. It is denoted by loge or ln. The value of “e” is about 2.718. In other words, by what power the “e” must be raised to get the desired number is defined by the natural logarithm.
Example: ln(2) = 0.693
ln(5) = 1.61
2) Common Logarithm: The common logarithm are those logarithm that has base as 10. It is denoted as log10 or simply log. It is therefore also recognized as base 10 logarithms. In simple words, by what power 10 must be raised so as to get the desired number is defined by the common logarithm.
Example: log (100) = 2
log10 (1000) = 3
Common and Natural Logarithmic Formula Relation
The common logarithm and the natural logarithm are connected to each other.
The relation between them is given by the formula:
ln = 2.303 x log
where, ln = natural logarithm
log = common logarithm with base 10
Logarithmic Formulas Properties
There exist some unique properties in the formula of logarithm that is useful in understanding various logarithmic problems. Some of the unique properties of the fomula of logarithm is given below:
loga(a) = 1, i.e., if the base and argument is same then the answer is always 1
log 1 = 0
log 0 = undefined
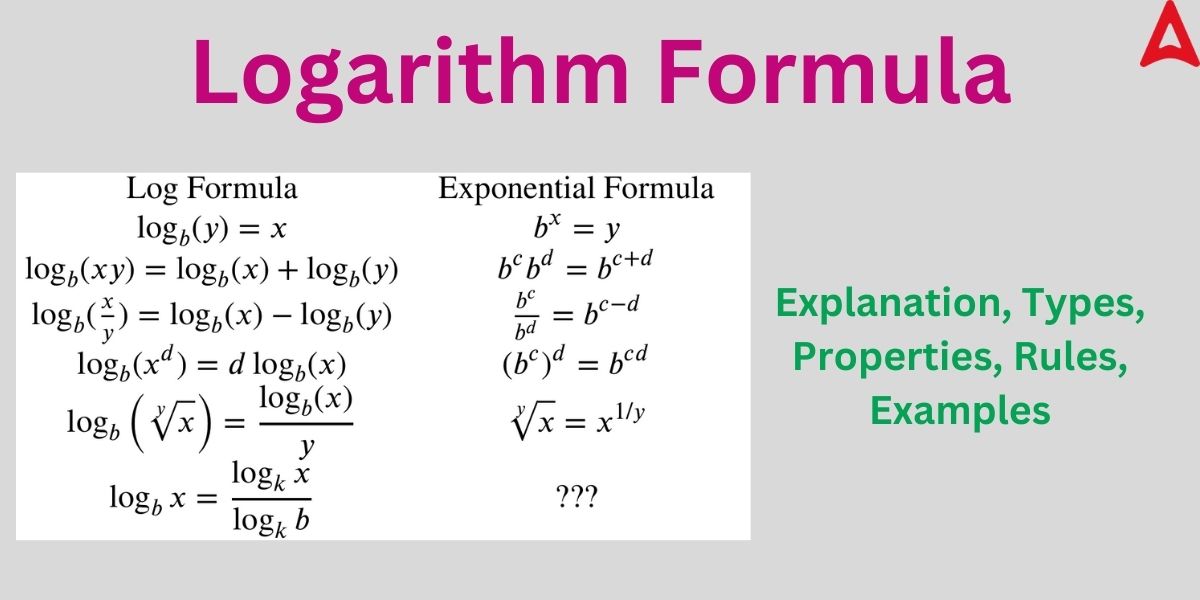
Basic Log Formulas
Some of the log formulas are used ubiquitously to solve various problems. These are also known as basic formulas in the logarithmic world. These basic formulas are listed below.
- log(ab) = log(a) + log(b)
- log(a/b) = log(a) – log(b)
-
log(a)b = b log(a)
- log(√a) = log (a)1/2 = (1/2) log(a)
- log(ax/by) = x log(a) – y log(b)
- log(axby) = x log(a) + y log(b)
Log Formulas Class 11 and Class 12
The log formula is extensively used in various calculations in class 11 and class 12. Students of these classes must be familiar with these formulas so as to solve various complex problems. Some formulas related to logarithm essential for class 11 and class 12 students are given below:
log 1 = 0
log(ab) = log(a) + log(b)
log(a/b) = log(a) – log(b)
log 0 = undefined
log(a + b) = log a + log(1+ba)
log(a – b) = log a + log (1-b/a)
loga(a) = 1
log(a)b = b log(a)
log(
) = (1/m) log(b)
Logarithm Formulas Rules
The logarithm formula is governed by some rules. These rules are used to deduce the values of logs in different cases. Some of these rules are stated herein:
1) Base Switch Rule
Using this rule, we can switch the base of the log with the argument.
loga(b) = 1/logb(a)
2) Log Integral Rule
This rule states the value of log in case of integration.
∫loga(y)dy = y( loga(y) – 1/ln(a) ) + C
3) Log Derivative Rule
This rule helps us to find the derivative of a logarithm function
If f(y) = loga(y)
Then, the derivative of f(y), i.e., f'(y) will be
f'(y) = 1/(y (ln(a)))
4) Log Product Rule
This rule deals with the cases when two numbers are in multiplication in the logarithm
log(ab) = log(a) + log(b)
5) Log Division Rule
As per log division rule:
log (a/b) = log(a) – log(b)
6) Log Identity Rule
It states that if the base and argument of the log is same then the answer is always 1
loga(a) = 1
7) Log exponential Rule
log(a)b = b log(a)
8) Logarithm in Power Rule
According to this rule, if a logarithm with base “a” is raised to the power “a”, then the answer will be equal to the argument of the log function.
Mathematically, alog(x) = x
where log(x) has the base “a”
9) Log Zero Value Rule
The value of Log 1 is always 0 no matter what the base is.
log (1) = 0
10) Log Undefined Rule
log (0) = undefined
Log a/b Formula for JEE
The competitive examination of JEE (Joint Entrance Examination) involves several complex calculations. The fornula of logarithm comes as a handy tool for such calculations. So, it is advisable for students of JEE to prepare and memorize the log formulas given below to ace their examinations.
- log(ab) = log(a) + log(b)
- log(a/b) = log(a) – log(b)
-
log(a)b = b log(a)
- log(√a) = log (a)1/2 = (1/2) log(a)
- log(ax/by) = x log(a) – y log(b)
- log(axby) = x log(a) + y log(b)
- loga(a) = 1
- log (1) = 0
- log (0) = undefined
- log(a + b) = log a + log(1+ba)
- log(a – b) = log a + log (1-b/a)
Log Formula Solved Examples
Some of the solved examples on the log formula is given below. These solved questions will help students understand this topic in a better way.
Example 1: What will be the value of log (4) where the base of the log is 2?
Solution: Given that base of the log is 2
so, log2(4) = log2(2)²
As we know log(a)b = b log(a)
Hence, log2(2)² =2 log2(2)
As loga(a) = 1
Hence, log2(2) = 1
So, log2(2)² =2 x 1
Therefore, log2(4) = 2
Example 2: Given that log3(a) = 4, what will be the value of a?
Solution: As we know if logx (z) = y, then xy= z
Using this rule we can write log3(a) = 4 as
a = 34
Hence, a = 81
Example 3: What will be the value of log(14) if log(2) is 0.301 and log(7) is 0.845?
Solution: Given log(2) = 0.301
log(7) = 0.845
we can write log(14) as log(2 x 7)
Using the log product rule of log(ab) = log(a) + log(b), we get
log(14) = 1og(2) + log(7)
log(14) = 0.301 + 0.845
Hence, log(14) = 1.146
Example 4: What will be the value of log25(25)?
Solution: As we know, loga(a) = 1
Hence, log25(25) = 1
Example 5: Find the value of log3(729).
Solution: We have been given log3(729)
log3(729) = log3(36)
using the rule log(a)b = b log(a), we get
6 x log3(3)
using the identity rule loga(a) = 1, we get
6 x 1
Hence, log3(729) = 6
Benefits of formula of log in Maths
The formula of logarithms in mathematics offers several benefits, making it an essential tool in various fields. Here are some key advantages:
1. Simplifies Complex Calculations
Logarithms transform multiplication and division into addition and subtraction, simplifying calculations.
2. Helps Solve Exponential Equations
Logarithms are used to solve equations involving exponential terms,
3. Reduces Scale of Numbers
Logarithms compress large or small numbers into a manageable range, making them useful in scientific and engineering calculations (e.g., decibels in sound, pH in chemistry).
4. Supports Graphical Representation
Logarithmic scales are used to plot data that spans several orders of magnitude, such as in earthquake magnitudes or population growth charts.
5. Enables Logarithmic Differentiation
Logarithmic differentiation is a technique used in calculus to simplify differentiation of functions involving products, quotients, or powers.
6. Useful in Growth and Decay Problems
Logarithms are essential in modeling real-world scenarios like population growth, radioactive decay, and compound interest.
7. Foundation for Algorithms and Computers
The concept of logarithms underpins algorithms and computer science, especially in complexity analysis, where terms like
log𝑛 appear frequently.
8. Application in Data Science
Logarithmic transformations normalize data, making it easier to interpret and analyze trends, particularly in regression analysis.
By leveraging the properties and formulas of logarithms, mathematicians and scientists can address complex problems efficiently.








 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














