The Modern periodic table is an updated and enhanced version of various models proposed by scientists in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Dimitri Mendeleev proposed his periodic table based on the discoveries of previous scientists such as John Newlands and Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier.
Periodic Table
Mendeleev, on the other hand, is awarded sole credit for developing the periodic table. In the modern periodic table, all known elements are organized in order of increasing atomic number and repeating chemical characteristics. They are organized in a tabular format, with columns representing a group and a row representing a period. Dimitri Mendeleev, commonly regarded as the father of the periodic table, proposed the initial iteration of the periodic table, which is still in use today. In this article, we will discuss all the details of the modern periodic table, stay tuned with us and read the complete article. Bookmark this page to get all the latest articles.
Mendeleev’s Table Vs Modern Periodic Table
Dimitri Mendeleev, commonly regarded as the father of the periodic table, proposed the initial iteration of the table, which is still in use today. Mendeleev’s periodic law differs from the modern periodic 118 element table in the following way.
- Mendeleev based his table on increasing atomic mass, but the modern table is based on increasing atomic number order.
- Mendeleev’s periodic table, despite being based on atomic weight, was able to anticipate the discovery and qualities of some elements. During his time, just roughly half of the elements presently known to us were known, and much of the information we had on the elements was incorrect.
Periodic Table of Names and Symbols
We can say that the periodic table is a work of art in terms of organized chemical information, and the evolution of chemistry’s table into its modern form is an amazing feat. The first 94 elements of the table occur naturally, but the remaining elements from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories or nuclear reactors. Elements in groups have qualities that are similar in some ways.
Periodic Table Chart
There is no one optimal periodic table structure, although by whatever consensus exists, the form employed here is the most popular and useful. Periods (presented horizontally) and groups (shown vertically) are included in the typical form of the Modern periodic table illustrated below.
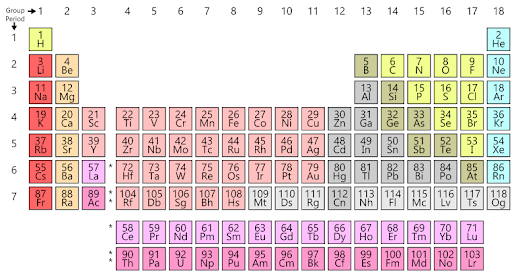
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an element is a fundamental property that defines the identity of that element. It is represented by the symbol “Z” and is equal to the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of that element. In a neutral atom, the atomic number also corresponds to the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.
The atomic number is a unique identifier for each element on the periodic table. For example:
- Hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, which means it has one proton in its nucleus.
- Helium (He) has an atomic number of 2, indicating it has two protons.
- Carbon (C) has an atomic number of 6, meaning it contains six protons in its nucleus.
- Oxygen (O) has an atomic number of 8, signifying eight protons.
The atomic number determines an element’s chemical properties and its position on the periodic table. Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, which results in elements with similar chemical properties being grouped together in columns called “groups” or “families.”
Atomic Number 1 to 30 Elements
Atomic numbers 1 to 30 are very important in chemistry.
Here are the atomic numbers and corresponding elements from atomic number 1 to 30 elements name list:
- Hydrogen (H)
- Helium (He)
- Lithium (Li)
- Beryllium (Be)
- Boron (B)
- Carbon (C)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
- Neon (Ne)
- Sodium (Na)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silicon (Si)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Sulfur (S)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Argon (Ar)
- Potassium (K)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Scandium (Sc)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Vanadium (V)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Manganese (Mn)
- Iron (Fe)
- Cobalt (Co)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)
These elements make up the first three rows of the periodic table and include some of the most common elements found in nature.
The charge number of an atomic nucleus is the chemical element’s atomic number, also known as nuclear charge number (symbol Z). This is equivalent to the proton number (np), or the number of protons present in the nucleus of each atom of that element, for conventional nuclei. Ordinary chemical elements can be uniquely identified by their atomic number. The atomic number and the number of electrons are both equal in a regular, uncharged atom.
Atomic Number of Elements From 1 to 30
Here is the list of 30 elements from Hydrogen to Ununquadium.
| Atomic Number | Symbol of Element | Element |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen |
| 2 | He | Helium |
| 3 | Li | Lithium |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium |
| 5 | B | Boron |
| 6 | C | Carbon |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen |
| 8 | O | Oxygen |
| 9 | F | Fluorine |
| 10 | Ne | Neon |
| 11 | Na | Sodium |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum |
| 14 | Si | Silicon |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus |
| 16 | S | Sulfur |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine |
| 18 | Ar | Argon |
| 19 | K | Potassium |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium |
| 23 | V | Vanadium |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese |
| 26 | Fe | Iron |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel |
| 29 | Cu | Copper |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium |
| 33 | As | Arsenic |
| 34 | Se | Selenium |
| 35 | Br | Bromine |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium |
| 47 | Ag | Silver |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium |
| 49 | In | Indium |
| 50 | Sn | Tin |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium |
| 53 | I | Iodine |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon |
| 55 | Cs | Cesium |
| 56 | Ba | Barium |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium |
| 63 | Eu | Europium |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium |
| 68 | Er | Erbium |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum |
| 74 | W | Tungsten |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium |
| 76 | Os | Osmium |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum |
| 79 | Au | Gold |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium |
| 82 | Pb | Lead |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth |
| 84 | Po | Polonium |
| 85 | At | Astatine |
| 86 | Rn | Radon |
| 87 | Fr | Francium |
| 88 | Ra | Radium |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium |
| 90 | Th | Thorium |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium |
| 92 | U | Uranium |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium |
| 95 | Am | Americium |
| 96 | Cm | Curium |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium |
| 98 | Cf | Californium |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium |
| 102 | No | Nobelium |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium |
| 112 | Uub | Ununbiium |
| 113 | — | —— |
| 114 | Uuq | Ununquadium |
Atomic Number 1 to 30 List
Checkout 30 elements from periodic table below.
| Atomic Number | Symbol of Element | Element |
| 1 | H | Hydrogen |
| 2 | He | Helium |
| 3 | Li | Lithium |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium |
| 5 | B | Boron |
| 6 | C | Carbon |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen |
| 8 | O | Oxygen |
| 9 | F | Fluorine |
| 10 | Ne | Neon |
| 11 | Na | Sodium |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum |
| 14 | Si | Silicon |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus |
| 16 | S | Sulfur |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine |
| 18 | Ar | Argon |
| 19 | K | Potassium |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium |
| 23 | V | Vanadium |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese |
| 26 | Fe | Iron |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel |
| 29 | Cu | Copper |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc |
Atomic Number of Silver
The chemical element of silver has the atomic number 47 and the symbol Ag. It is a transition metal that is soft, white, and lustrous and has the highest electrical, thermal, and reflectivity of any metal.
Atomic Number of Oxygen
The chemical element with the atomic number 8 and symbol O is called oxygen. It belongs to the periodic table’s chalcogen group, is a very reactive nonmetal, and is an oxidizing agent that easily produces oxides with most elements as well as other compounds.
Atomic Number of Iron
The chemical element iron has the atomic number 26 and the symbol Fe. It is a metal that is found in group 8 of the periodic table and the first transition series. It makes up a large portion of both the Earth’s outer and inner core and is, by mass, the second-most prevalent element on Earth after oxygen.
Atomic Number of Carbon
Chemical element carbon has the atomic number six and the letter C assigned to it. It has a tetravalent atom, which means that four of its electrons can be used to create covalent chemical bonds. It is nonmetallic. The periodic table’s group 14 includes it. The crust of the Earth contains barely 0.025 percent carbon.
Atomic Number of Silicon
Chemical element silicon has the chemical symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor that has a blue-grey metallic sheen and is a hard, brittle crystalline solid. It belongs to the periodic table’s group 14
Atomic Number of Sulphur
Chemical element sulphur has the letter S and atomic number 16. It is multivalent, nonmetallic, and plentiful. Sulfur atoms normally combine to create cyclic octatomic molecules, which have the chemical formula S8. At room temperature, elemental sulphur is a crystalline solid that is brilliant yellow.
Atomic Number of Barium
Chemical element barium has the chemical symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal and the fifth element in group 2. Barium is not a free element in nature due to its great chemical reactivity.
Atomic Number of Magnesium
The chemical element magnesium has the atomic number 12 and the letter Mg as its symbol. It is a solid that has a lustrous grey color and many of the same physical and chemical characteristics as the other five alkaline earth metals.
The contemporary or modern periodic table, which we presently use, is a revised and enhanced version of specific models proposed by scientists in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The periodic table organizes all known elements in order of increasing atomic number and recurring chemical properties. Some of the of the periodic table of elements’ characteristics are detailed below.
- In the modern periodic table, periods are the horizontal rows.
- The periodic table contains seven periods.
- From top to bottom, they are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
- The sixth period, on the other hand, is made up of 32 components.
- Four new elements have been added to the periodic table’s seventh period. 113-Nihonium, 115-Moscovium, 117-Tennessine, and 118-Oganesson are the elements. With this addition, the 7th period now includes 32 components.
- The first period comprises only two elements: hydrogen and helium.
- The second and third periods each include eight components.
- The fourth and fifth periods each include 18
Modern Periodic Table Groups
Modern Periodic Tables of Elements are organized in a tabular format, with a row representing a period and a column representing a group. Elements are ordered in increasing atomic number order from left to right and top to bottom. Elements of the same group will therefore have the same valence electron configuration and, as a result, identical chemical characteristics. The Modern periodic table groups are given below.
- In the modern periodic table, groups are the vertical columns.
- The periodic table is divided into 18 groups.
- These groupings are numbered 1 to 18.
Periodic Table with Names
There are 118 Elements in the modern periodic table. periodic table with names are listed below:
- Element 1: H-Hydrogen
- Element 2: He-Helium
- Element 3: Li-Lithium
- Element 4: Be-Beryllium
- Element 5: B-Boron
- Element 6: C-Carbon
- Element 7: N-Nitrogen
- Element 8: O-Oxygen
- Element 9: F-Fluorine
- Element 10: Ne-Neon
- Element 11: Na-Sodium
- Element 12: Mg-Magnesium
- Element 13 : Al-Aluminum
- Element 14 : Si-Silicon
- Element 15 : P-Phosphorus
- Element 16 : S-Sulfur
- Element 17 : Cl-Chlorine
- Element 18 : Ar-Argon
- Element 19 : K-Potassium
- Element 20 : Ca-Calcium
- Element 21 : Sc-Scandium
- Element 22 : Ti-Titanium
- Element 23 : V-Vanadium
- Element 24 : Cr-Chromium
- Element 25 : Mn-Manganese
- Element 26 : Fe-Iron
- Element 27 : Co-Cobalt
- Element 28 : Ni-Nickel
- Element 29 : Cu-Copper
- Element 30 : Zn-Zinc
- Element 31 : Ga-Gallium
- Element 32 : Ge-Germanium
- Element 33 : As-Arsenic
- Element 34 : Se-SeleniumElement
- 35 : Br-BromineElement
- 36 : Kr-Krypton
- Element 37 : Rb-Rubidium
- Element 38 : Sr-Strontium
- Element 39 : Y-Yttrium
- Element 40 : Zr-Zirconium
- Element 41 : Nb-Niobium
- Element 42 : Mo-Molybdenum
- Element 43 : Tc-Technetium
- Element 44 : Ru-Ruthenium
- Element 45 : Rh-Rhodium
- Element 46 : Pd-Palladium
- Element 47 : Ag-Silver
- Element 48 : Cd-Cadmium
- Element 49 : In-Indium
- Element 50 : Sn-Tin
- Element 51 : Sb-Antimony
- Element 52 : Te-Tellurium
- Element 53 : I-Iodine
- Element 54 : Xe-Xenon
- Element 55 : Cs-Cesium
- Element 56: Ba-Barium
- Element 57: La-Lanthanum
- Element 58: Ce-Cerium
- Element 59 : Pr-Praseodymium
- Element 60: Nd-Neodymium
- Element 61: Pm-Promethium
- Element 62: Sm-Samarium
- Element 63: Eu-Europium
- Element 64 : Gd-Gadolinium
- Element 65: Tb-Terbium
- Element 66 : Dy-Dysprosium
- Element 67: Ho-Holmium
- Element 68: Er-Erbium
- Element 69: Tm-Thulium
- Element 70: Yb-Ytterbium
- Element 71: Lu-Lutetium
- Element 72: Hf-Hafnium
- Element 73: Ta-Tantalum
- Element 74: W-Tungsten
- Element 75: Re-Rhenium
- Element 76: Os-Osmium
- Element 77: Ir-Iridium
- Element 78: Pt-Platinum
- Element 79 : Au-Gold
- Element 80: Hg-Mercury
- Element 81: Tl-Thallium
- Element 82: Pb-Lead
- Element 83: Bi-Bismuth
- Element 84: Po-Polonium
- Element 85: At-Astatine
- Element 86: Rn-Radon
- Element 87: Fr-Francium
- Element 88: Ra-Radium
- Element 89: Ac-Actinium
- Element 90: Th-Thorium
- Element 91: Pa-Protactinium
- Element 92: U-Uranium
- Element 93: Np-Neptunium
- Element 94: Pu-Plutonium
- Element 95: Am-Americium
- Element 96: Cm-Curium
- Element 97: Bk-Berkelium
- Element 98: Cf-Californium
- Element 99: Es-Ensteinium
- Element 100: Fm-Fermium
- Element 101: Md-Mendelevium
- Element 102: No-Nobelium
- Element 103: Lr-Lawrencium
- Element 104: Rf-Rutherfordium
- Element 105: Db-Dubnium
- Element 106: Sg-Seaborgium
- Element 107: Bh-Bohrium
- Element 108: Hs-Hassium
- Element 109 : Mt-Meitnerium
- Element 110 : Ds-Darmstadtium
- Element 111 : Rg-Roentgenium
- Element 112 : Cn-Copernicium
- Element 113: Nh-Nihonium
- Element 114: Fl-Flerovium
- Element 115: Mc-Moscovium
- Element 116 : Lv-Livermorium
- Element 117: Ts-Tennessine
- Element 118: Og-Oganesson
Periodic Table of Elements in Hindi
आधुनिक आवर्त सारणी में 118 तत्व हैं। सभी तत्व नीचे सूचीबद्ध हैं:
तत्व 1: एच-हाइड्रोजन
तत्व 2: ही-हीलियम
तत्व 3: ली-लिथियम
तत्व 4: बे-बेरीलियम
तत्व 5: बी-बोरोन
तत्व 6: सी-कार्बन
तत्व 7: एन-नाइट्रोजन
तत्व 8: ओ-ऑक्सीजन
तत्व 9: एफ-फ्लोरीन
तत्व 10: ने-नियॉन
तत्व 11: ना-सोडियम
तत्व 12: एमजी-मैग्नीशियम
तत्व 13: अल-एल्यूमीनियम
तत्व 14: सी-सिलिकॉन
तत्व 15: पी-फॉस्फोरस
तत्व 16: एस-सल्फर
तत्व 17: Cl-क्लोरीन
तत्व 18: अर-आर्गन
तत्व 19: के-पोटेशियम
तत्व 20 : Ca-कैल्शियम
तत्व 21: एससी-स्कैंडियम
तत्व 22: Ti-टाइटेनियम
तत्व 23: वी-वैनेडियम
तत्व 24: सीआर-क्रोमियम
तत्व 25: एमएन-मैंगनीज
तत्व 26: फे-आयरन
तत्व 27: सह-कोबाल्ट
तत्व 28: नी-निकेल
तत्व 29: Cu-कॉपर
तत्व 30: Zn-Zinc
तत्व 31: गा-गैलियम
तत्व 32: जीई-जर्मेनियम
तत्व 33: एस-आर्सेनिक
तत्व 34: से-सेलेनियम एलिमेंट
35 : Br-BromineElement
36 : क्र-क्रिप्टन
तत्व 37: आरबी-रूबिडियम
तत्व 38: सीनियर-स्ट्रोंटियम
तत्व 39: Y-Yttrium
तत्व 40: Zr-Zirconium
तत्व 41: नायब-निओबियम
तत्व 42: मो-मोलिब्डेनम
तत्व 43: टीसी-टेक्नेटियम
तत्व 44: रु-रूथेनियम
तत्व 45: Rh-रोडियम
तत्व 46: पीडी-पैलेडियम
तत्व 47: एजी-सिल्वर
तत्व 48: सीडी-कैडमियम
तत्व 49: इन-इंडियम
तत्व 50: एसएन-टिन
तत्व 51: एसबी-एंटीमोनी
तत्व 52: टी-टेल्यूरियम
तत्व 53: आई-आयोडीन
तत्व 54: ज़ी-क्सीनन
तत्व 55: सीएस-सीज़ियम
तत्व 56: बा-बेरियम
तत्व 57: ला-लान्थेनम
तत्व 58: सीई-सेरियम
तत्व 59: पीआर-प्रेजोडायमियम
तत्व 60: एनडी-नियोडिमियम
तत्व 61: पीएम-प्रोमेथियम
तत्व 62: एसएम-समैरियम
तत्व 63: ईयू-यूरोपियम
तत्व 64: जीडी-गैडोलिनियम
तत्व 65: टीबी-टेरबियम
तत्व 66: डाई-डिस्प्रोसियम
तत्व 67: हो-होल्मियम
तत्व 68: एर-एरबियम
तत्व 69: टीएम-थुलियम
तत्व 70: Yb-Ytterbium
तत्व 71: लू-लुटेटियम
तत्व 72: एचएफ-हाफनियम
तत्व 73: टा-टैंटलम
तत्व 74: डब्ल्यू-टंगस्टन
तत्व 75: पुन: रेनियम
तत्व 76: ओस-ऑस्मियम
तत्व 77: इर-इरिडियम
तत्व 78: पीटी-प्लैटिनम
तत्व 79: औ-गोल्ड
तत्व 80: पारा-बुध
तत्व 81: टीएल-थैलियम
तत्व 82: पीबी-लीड
तत्व 83: द्वि-बिस्मथ
तत्व 84: पो-पोलोनियम
तत्व 85: एट-एस्टेटिन
तत्व 86: आरएन-रेडॉन
तत्व 87: Fr-Francium
तत्व 88: रा-रेडियम
तत्व 89: एसी-एक्टिनियम
तत्व 90: गु-थोरियम
तत्व 91: पा-प्रोटैक्टीनियम
तत्व 92: यू-यूरेनियम
तत्व 93: एनपी-नेप्च्यूनियम
तत्व 94: पु-प्लूटोनियम
तत्व 95: Am-Americium
तत्व 96: सेमी-क्यूरियम
तत्व 97: बीके-बर्केलियम
तत्व 98: सीएफ-कैलिफोर्निया
तत्व 99: एस-एनस्टीनियम
तत्व 100: एफएम-फर्मियम
तत्व 101: एमडी-मेंडेलीवियम
तत्व 102: नो-नोबेलियम
तत्व 103: एलआर-लॉरेंसियम
तत्व 104: आरएफ-रदरफोर्डियम
तत्व 105: डीबी-डबनियम
तत्व 106: एसजी-सीबोर्गियम
तत्व 107: भ-बोहरियम
तत्व 108: एचएस-हसियम
तत्व 109: माउंट-मीटनेरियम
तत्व 110: डीएस-डार्मस्टेडियम
तत्व 111: आरजी-रोएंटजेनियम
तत्व 112: सीएन-कॉपरनिकियम
तत्व 113: एनएच-निहोनियम
तत्व 114: फ्लो-फ्लेरोवियम
तत्व 115: मैक-मोस्कोवियम
तत्व 116: लव-लिवरमोरियम
तत्व 117: Ts-Tennessine
तत्व 118: ओग-ओगनेसन
| Also Read | |
| CaCO3- Chemical & Common Name | Difference Between Mass And Weight |
| Viscosity of Water | Barriers of communication |








 Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
 CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
 CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...
CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...














