The Nitrogen Dioxide is one of the most important compounds formed by Nitrogen. The Dioxide of Nitrogen, as the name suggests, is formed when the Nitrogen reacts with oxygen molecule. The dioxide of Nitrogen plays many important roles in human lives and it is also known to be highly deleterious. In this article, we will learn about Dioxide of Nitrogen by going through its definition, NO2 Structure, formula, uses and properties.
Nitrogen Dioxide- NO2
You must have heard about different oxides of Nitrogen, the Nitrogen Dioxide is one of them. The other oxides of Nitrogen includes nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, nitrogen pentoxide, etc. The oxides of nitrogen are generally a mixture of gases that are composed of nitrogen and oxygen.
Nitrogen is an element found in nature that is crucial for the development and breeding of plants and animals. It is described as an element with a atomic number of 7, making up about 78 percent of our planet’s atmosphere. This gas has no color, smell, or reaction. Subjecting it to distillation from liquid air results in the transformation into liquid nitrogen, which has a boiling point of 77.4 Kelvin (195.8 °C) and is commonly used as a refrigerant.
Nitrogen Dioxide Definition
Nitrogen Oxide, chemically denoted as NO2, is formed from the combination of a single Nitrogen atom with a molecule of oxygen. It is also known as nitrogen (IV) oxide or Deutoxide of nitrogen. It is one of the main air pollutants that absorbs UV radiation and prevents it from reaching the surface of the planet earth.
When compressed, nitrogen (IV) oxide is a reddish-brown gas or a yellowish-brown liquid. Its vapors are denser than those of air. Nitrogen dioxide and manganese dioxide (MnO2) are instances of oxides that contain two oxygen atoms, each connected directly to an atom of a different element, in this instance being nitrogen (NO2).
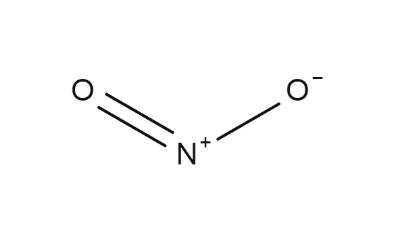
NO2 Structure (Structure of No2)
The structure of Nitrogen dioxide is bent or V-Shaped. The NO2 covalent molecule is composed of a central nitrogen atom, one oxygen atom bonded by a single bond, and another oxygen atom bonded by a double bond. The structure of nitrogen (IV) oxide is given below.
Nitrogen Dioxide Formula
The Chemical Formula for the Nitrogen Dioxide is NO2. It is classified as one of a few nitric oxides, such as nitric oxide and nitrous oxide, made up of nitrogen and oxygen. Chemical formulas can be either empirical or molecular, where the empirical formula indicates the amount of each element in a molecule, and the molecular formula gives the specific number of atoms per element.
For Deutoxide of Nitrogen, the empirical and molecular formula is NO2, representing a 1:2 ratio of nitrogen to oxygen atoms. The dioxide of Nitrogen, also called nitric oxide (IV), is a major air pollutant that can absorb UV light and lead to skin cancer.
Sources of NO2
More than 98 percent of anthropogenic NO, emissions come from combustion, mainly from stationary sources. Oxides of nitrogen produced by combustion are mainly released as nitric oxide, NO, which is a relatively harmless gas but quickly changes into the toxic nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere.
Research is currently being done on the health effects of nitrate serosols and nitrosamines, which are created with the help of NO2. Due to the amount produced and their ability to cause widespread harm to public health and well-being, nitrogen oxides are one of the air pollutants that the U.S. has set standards and regulations for.
Nitrogen Dioxide Uses
The NO2 has a wide range of uses, demonstrating its adaptability across multiple industries. Check the primary uses of Dioxide of Nitrogen below:
- In Rocket Propulsion, NO2 is used as an oxidizer, necessary for combustion reactions to generate thrust for spacecraft and rockets in space travel.
- NO2 acts as a strong oxidant and flour bleaching agent, playing a vital role in both chemical reactions and the food industry. It is used to bleach flour in order to improve the appearance and quality of different food items.
- NO2 plays a crucial role in the creation of explosives, aiding in the development of powerful compounds utilized in various applications, such as military and industrial purposes.
- Nitric acid Synthesis: NO2 is a key component in the chemical synthesis of nitric acid, which produces this vital industrial chemical.
- Part of Oxidized Cellulose Compounds: It plays a vital role in the production of oxidized cellulose compounds, aiding in the creation of materials with certain characteristics and uses.
- Catalyst: Because of its catalytic qualities, NO2 can speed up a number of industrial processes by facilitating chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed.
- Creation of Sulfuric Acid: It is used as a necessary ingredient in the complex chemical reactions that result in the creation of sulfuric acid, which is an essential and frequently used acid.
Properties of NO2
Check the physical and chemical properties of NO2 below:
Physical Properties of Nitrogen Dioxide
- Chemical Formula: NO2 acts as both the empirical and molecular formula.
- Molecular weight: 46 g/mol is determined by adding the molecular weights of nitrogen and oxygen in the given compound. This can be calculated as 14 g/mol for nitrogen and 16 g/mol for oxygen, resulting in a total of 46 g/mol.
- Density: 1.880 grams per cubic decimeter
- The boiling point of Dioxide of Nitrogen is 21.15 °C
- The melting point of NO2 is -9.3 degrees Celsius.
Chemical Properties of NO2
The primary chemical properties of Deutoxide of Nitrogen is given hereunder.
1) Hydrolysis reaction – Hydrolysis reaction of NO2 produces nitrous acid and nitric acid.
2 NO2 (N2O4) + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
2)Thermal properties – The NO2 exists as dinitrogen tetroxide gas in equilibrium.
2 NO2 ⇌ N2O4
3) Formation of nitrites – corresponding nitrites of NO2 are formed by alkyl and metal iodides.
2 CH3I + 2 NO2 → 2 CH3NO2 + I2
TiI4 + 4 NO2 → Ti(NO2)4 + 2 I2
4) Works as an oxidizer – Due to the weakness of the N–O bond in the nitric oxide (IV), NO2 is a strong oxidizer
5) At low levels of NO2, the reaction is extremely slow, i.e., it shows inert property.
Health Problems Due to Nitrous Dioxide
Serious exposure to nitrogen dioxide can result in death. When touching it, it results in a stinging feeling in the eyes and skin. When it is in a liquid state, it can result in frostbite. It is said to interact with the blood in order to create methemoglobin. When exposed to high temperatures for decomposition, it emits harmful nitrogen oxide fumes. High concentrations of NO2 cause irritation of the airways because it is an inflammatory gas.
NO2 primarily impacts respiratory conditions by inducing elevated levels of inflammation in the airways. Extended periods of exposure will lead to lower lung capacity, higher likelihood of respiratory issues, and increased sensitivity to allergies. NO2 also plays a role in generating tiny particles (PM) and ground-level ozone, both linked to negative environmental impacts.
Environmental Effects of NO2
NO2 and other NOx combine with water, oxygen, and other substances in the atmosphere to create acid rain. Acid rain negatively impacts delicate ecosystems like lakes and forests. The nitrate particles created by NOx cause the air to become hazy and make it hard to see through. This impacts the numerous national parks we frequent for their scenery. NOx presence in the air is a factor in the nutrient pollution found in coastal waters.
| Related Articles | |
| Chemical Kinetics Notes | 118 Elements Name and Properties |
| Aufbau Principle | Theoretical Yield Formula |
| Endothermic Reactions | Solutions Notes |











 Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12...
 CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions w...
 CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...
CUET Chemistry Syllabus 2026, Download O...














