A genus of microscopic unicellular ciliates called Paramecium is commonly found in freshwater habitats, such as ponds, lakes, and streams. These microscopic organisms, which range in length from 50 to 350 micrometers, are amazing illustrations of the diversity and complexity of life at the cellular level. Paramecium are remarkable examples of the wonders of the microscopic world because of their complex cellular organization, variety of reproductive strategies, and important ecological importance. Their research sheds light on the underlying ideas of life and the relationships between different organisms in ecosystems.
Paramecium
Paramecium sp. is a unicellular ciliated organism. They are single-celled, microscopic, free-living protozoans. They are categorized as ciliated organisms due to the presence of hairy structures, named cilia all over the organism. Their body is oblong or Slipper-shaped. Reproduction in Paramecium primarily occurs asexually by binary fission. Paramecia (Pleural) are found in freshwater, stagnant pond water, and marine environments. Although Paramecium can easily be cultured in laboratories. Paramecia are used widely as a biological model in laboratories to understand biological processes. Here we learn about Systematic position, Classification of Paramecium and their reproduction, and locomotion process.
What is Paramecium?
Paramecium is a genus of single-celled organisms belonging to the phylum Ciliophora. These microscopic organisms are commonly found in freshwater environments, such as ponds, lakes, and slow-moving streams. Paramecia are members of the protist kingdom, which includes a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms that do not fit into the categories of plants, animals, or fungi.
Paramecia are characterized by their slipper-like shape and their ability to move using hair-like structures called cilia. These cilia cover the surface of the cell and beat in coordinated waves, allowing the organism to move and propel itself through the water. Paramecia also use cilia to create water currents that sweep food particles into their oral groove.
Paramecium Kingdom
Kingdom- Protista
Phylum-Ciliophora
Class- Oligohymenophorea
Order- Peniculida
Family- Parameciidae
Genus- Paramecium
Classification of Paramecium Kingdom
Paramecium is a unicellular, eukaryotic protozoan kept in the Kingdom ‘Protista’ and came under the phylum Ciliophora.
The common species of Paramecium are-
Paramecium aurelia
Paramecium caudatum
Paramecium trichium
Paramecium woodruffi
Classification of Paramecium
Paramecium is a single-celled eukaryotic organism that belongs to the phylum Ciliophora. Within this phylum, Paramecium is further classified into the following taxonomic groups:
- Class: Oligohymenophorea
- Order: Peniculida
- Family: Parameciidae
- Genus: Paramecium
There are many different species of Paramecium, with the most commonly studied being Paramecium aurelia and Paramecium caudatum. These species are similar in their basic structure and behavior but have some differences in terms of their genetic makeup, morphology, and behavior.
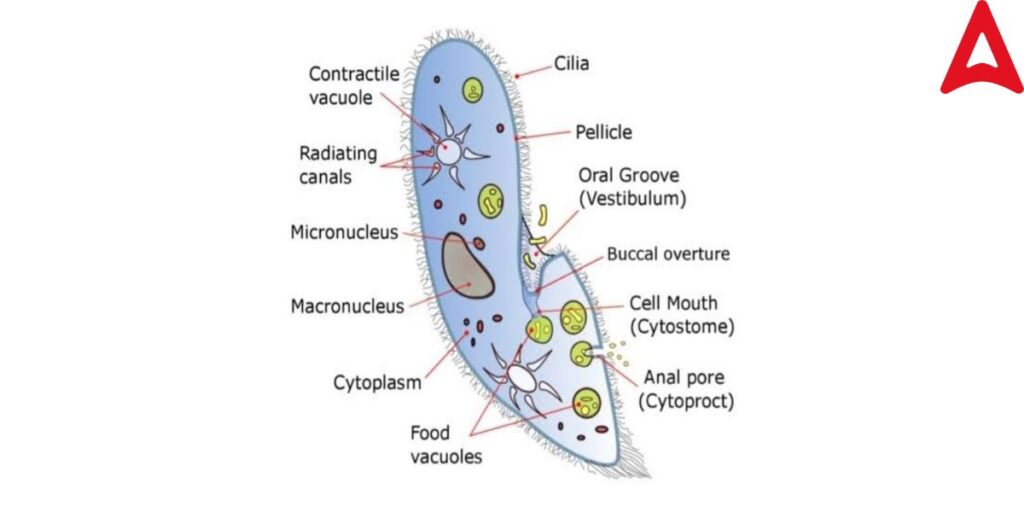
Paramecium Structure & Size
• Size & shape – Paramecium is known as a Slipper animalcule because of its slipper-like shape, it is 0.25 mm in length and microscopic. The anterior end is slender, the posterior end is thick and pointed. Grooved is oral or ventral surface.
• Pellicle- The cellular cytoplasm is surrounded by the pellicle. The pellicle is tough and flexible with hexagonal depressions. So, it gives the cell a changeable and definite shape.
• Cilia– cilia are made up of an axial filament (axoneme) and are surrounded by a protoplasmic sheath, arranged in longitudinal rows. It jas a buried part, called the root. Apart between the shaft and root is a plate-like that supports the cilia to hold in the pellicle, called the basal plate. A number of cilia are found large in Paramecium which is present all over the body and arranged in a spiral course. (Spiro arrangement)
• Protoplasm- Protoplasm is differentiated into 2 parts- outer ectoplasm which is nongranular that contains trichocyst and granular inner endoplasm, consisting of kidney-shaped macronucleus and a small micronucleus.
• Contractile vacuoles- In Paramecium, two star-shaped contractile vacuoles are found on either side of the body which serve as a reserver of excess water and metabolic waste in the body.
• Oral groove or cytostome- The Oral groove opens into funnel-shaped gullet or cytopharynx, present on the ventral side of the body called a cytostome.
• Food Vacuoles- A number of food vacuoles are present in the body of Paramecium, arranged in rows from anterior to posterior. Those food vacuoles help in the digestion of food.
• Cytopyge- Cytopyge is a pore by which undigested food is eliminated from the body, situated just posterior to the mouth.
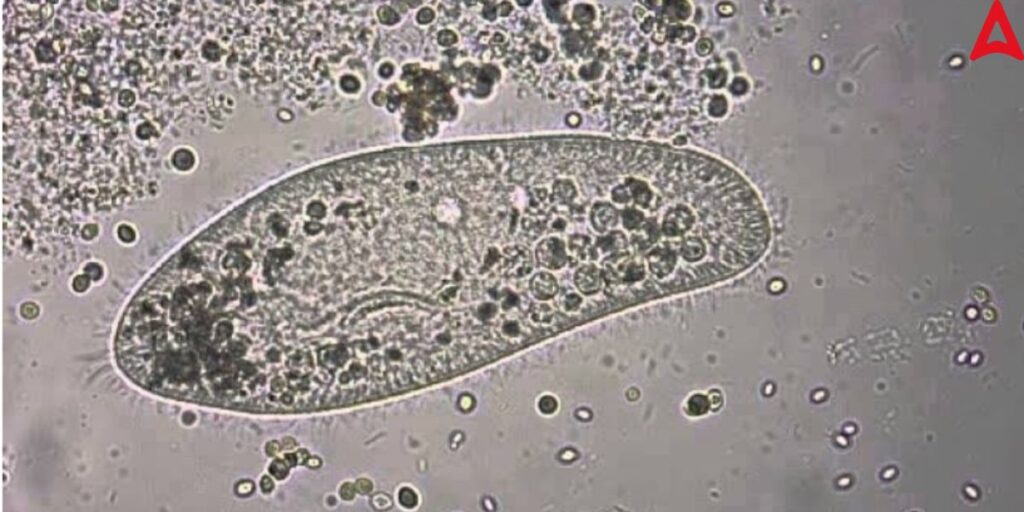
Paramecium Nutrition
Paramecia are found in freshwater, stagnant pond water. They are typically holozoic, feeds on protozoa, algae, bacteria, and small food particles, collected at the gullet, and undergo digestion in the food vacuoles. Then undigested food is eliminated through cytopyge from the body.
Paramecium Diagram (Paramecium ka chitra)
Paramecium is a single-cell Protista with a ciliary body. Paramecium is Classified under Kingdom-Protista and came under the phylum Ciliophora. Paramecium diagram is given below.
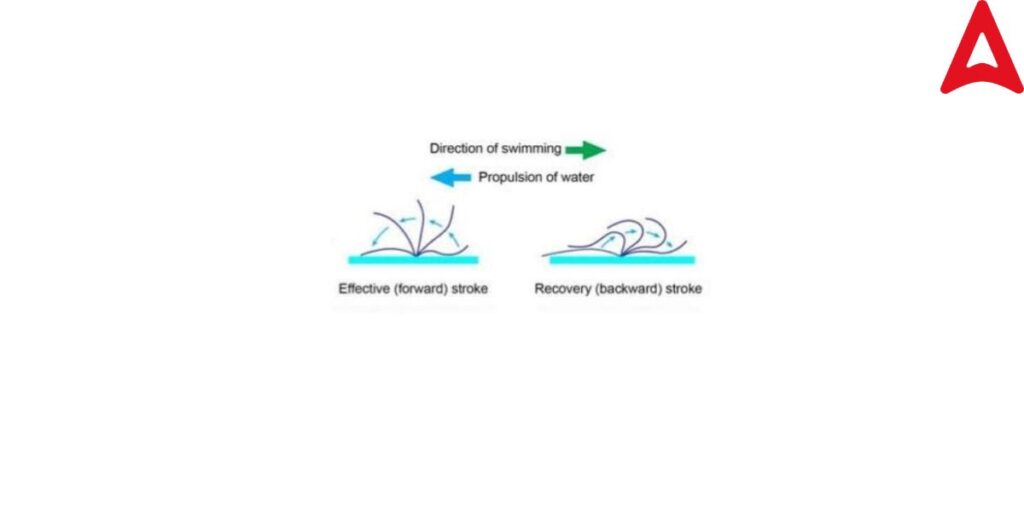
Paramecium Locomotion
Paramecium is a ciliate protozoan and moves by beating of cilia, called ciliary movement.
1. In ciliary movement, cilia show a typical dash-like movement having a powerful active stroke or power stroke followed by a recovery stroke.
3. Bending of the cilium is caused by topological movement of the dying arms along the central microtubules. This causes sliding of peripheral microtubules of one sight against the central microtubules.
4. All the cilia take part in the synchronous beating. This causes two kinds of movement-
• Isocronas movement- In this movement, the cilia beat independently. This is energy saving regular mode of movement.
• Metacronas movement – In this movement, beating is caused by the dependent movement of the cilia. This type of movement is mainly during feeding or searching for a suitable shelter.
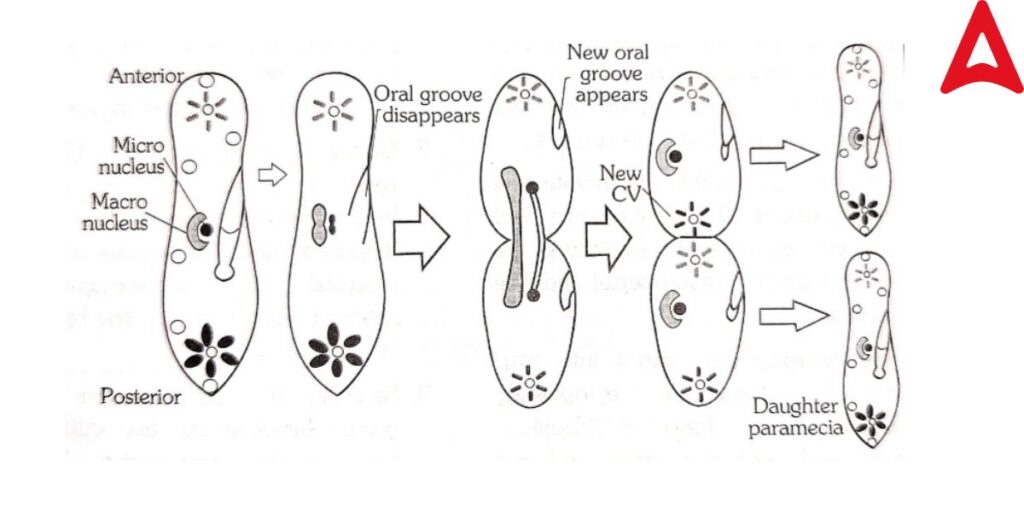
Paramecium Reproduction
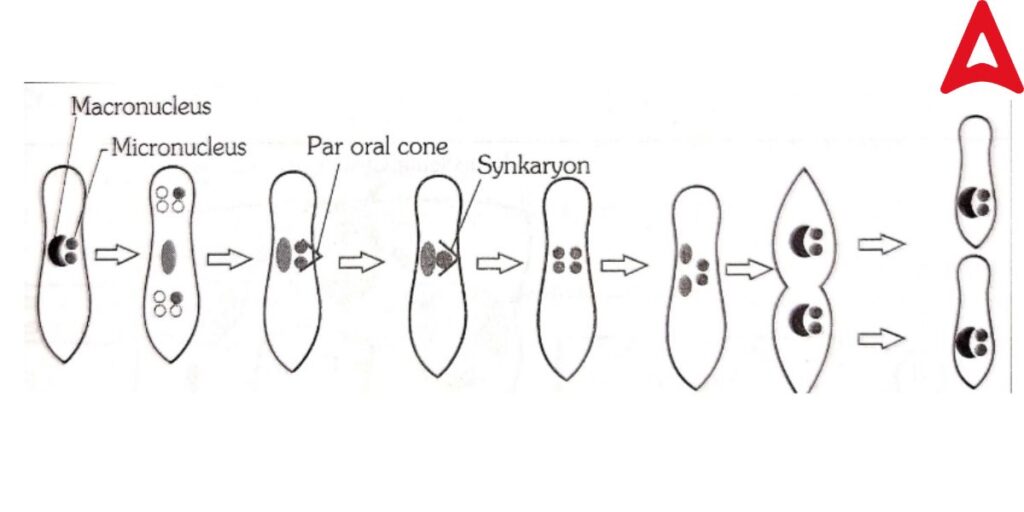
Paramecium reproduces offspring in both ways -(a) Asexual reproduction by Transverse binary fission and (b) Sexual reproduction by nuclear regeneration by Conjugation,
Endomyxis, Cytogamy and Autogamy .Let’s understand that one by one.
(a) Asexual reproduction by Transverse binary fission –
Transverse binary fission is the primary reproduction process in Paramecium. In this process, the animal divides into two distinct daughter organisms transversally. In this process, the Nuclear membrane remains intact only the micronucleus divides. It occurs in a suitable environment.
(b)Sexual reproduction by nuclear regeneration:
• Conjugation- When two individuals of the opposite sex of the same species form a temporary union to exchange their nuclear materials, this process is known as Conjugation.
Paramecium caudatum shows this type of Reproduction process.
In the Conjugation process, the conjugation bridge is formed between participating two individuals. These united Paramecia are called conjugants.
The macronucleus disappears and the micronucleus in each conjugant divides to form 4 micronuclei by meiosis, three of which degenerate. By cross-fertilization, the haploid nuclei of each conjugant fused and formed diploid micronuclei. After fusion conjugants separate from each other and become ex – conjugants. In each ex conjugants, transverse cytoplasmic division occurs and forms 4 daughter paramecia, each with one micro and one macronucleus.
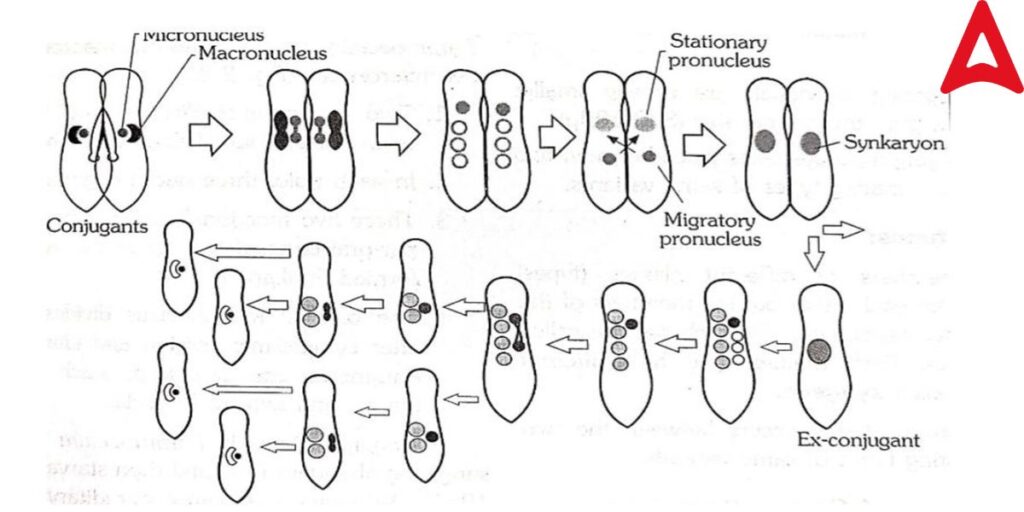
•Autogamy – Autogamy or self-fertilization occurs if the two nuclei undergo a complete in a single cell and form a new macronucleus. This process is found in Paramecium aurelia.
•Cytogamy- This process is less frequent in Paramecium. when two individuals fuse with their oral surface. But there is no nuclear exchange between them.
Structure of Paramecium
Paramecium: As we know that Paramecium is a single-celled organism that belongs to the phylum Ciliophora. It is widely distributed in freshwater environments and is commonly used as a model organism for studying cell biology and genetics. Paramecium exhibits unique features and characteristics, such as its complex ciliary structure, ability to reproduce sexually and asexually, and response to stimuli.
These features make Paramecium an interesting subject of study for researchers and students. In this article, we will going to know about the classification, features, characteristics, roles, advantages, and functions of Paramecium, and explore why it is such an important organism in the field of biology.
Paramecium is a single-celled eukaryotic organism that belongs to the phylum Ciliophora. It is a freshwater protist and is found in a wide range of aquatic environments. Paramecium is characterized by its ciliated structure, which is used for locomotion and feeding.
The body of Paramecium is elongated and has a characteristic slipper or cigar shape. It is covered in cilia, which are short hair-like structures that beat in coordinated waves to propel the organism through the water.
The cilia also serve to create a current that draws food into the oral groove, a specialized structure located on the surface of the cell. Once food particles are captured by the oral groove, they are engulfed and digested in specialized structures called vacuoles.
Paramecium has a complex genome that contains both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. It is capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction, with the latter being the more common method. During asexual reproduction, the organism divides by binary fission, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells. Sexual reproduction involves the exchange of genetic material between two individuals through a process called conjugation.
Features of Paramecium
These are the features of Paramecium
-
- Cilia: Paramecium is covered in thousands of tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which are used for locomotion and feeding.
- Nucleus: Paramecium has a large, complex nucleus that contains the organism’s genetic material.
- Contractile Vacuole: Paramecium possesses one or more contractile vacuoles that help to regulate the organism’s water balance.
- Oral Groove: Paramecium has a specialized structure called the oral groove, which is used to capture and ingest food particles.
- Macronucleus: Paramecium has a large macronucleus that is responsible for regulating gene expression and cell metabolism.
- Micronucleus: Paramecium has a small micronucleus that is involved in sexual reproduction.
- Pellicle: Paramecium has a stiff outer layer called the pellicle, which provides structural support to the organism.
- Cytoplasm: Paramecium’s cytoplasm contains various organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum, that are involved in cell metabolism and protein synthesis.
- Trichocysts: Paramecium has specialized organelles called trichocysts used to defend against predators.
- Binary Fission: Paramecium reproduces asexually by binary fission, a process in which the organism divides into two identical daughter cells.
Paramecium Characteristics
- Paramecium is a single-celled eukaryotic organism
- It has a characteristic slipper or cigar shape
- It is covered in cilia for locomotion and feeding
- It possesses one or more contractile vacuoles that help to regulate its water balance
- It has a complex genome that contains both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA
Paramecium Function
Paramecium plays an important role in aquatic ecosystems by serving as a food source for other organisms and by helping to recycle nutrients. It is also widely used as a model organism in scientific research and education. Being the major consumers in freshwater ecosystems, Paramecium feeds on bacteria and aids in the cycling of nutrients. A wide range of bigger species, including fish and aquatic insects, eat them as well. Because the bacteria that parasites consume are frequently found on decomposing plants, parasites are involved in the carbon cycle. In addition to the bacteria, Paramecium will consume the decomposing plant matter, accelerating the process of decomposition.
How do Paramecium reproduce?
Paramecium can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction occurs through a process called binary fission, in which the organism divides into two identical daughter cells. Sexual reproduction involves the exchange of genetic material between two individuals through a process called conjugation.
What are the advantages of Paramecium?
Paramecium is an important model organism for scientific research and education
- It is easy to culture in a laboratory setting
- It reproduces quickly, allowing for rapid experimentation
- It has a simple structure that is ideal for studying basic biological processes
- It is used in the study of genetics, cell biology, and evolutionary biology
- It has a complex genome that contains both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA
- It plays an important role in aquatic ecosystems by serving as a food source and helping to recycle nutrients.
What are the 7 functions of life in Paramecium?
The 7 functions of life in Paramecium are:
- Nutrition: Paramecium ingests food particles through its oral groove and digests them in specialized vacuoles.
- Respiration: Paramecium carries out respiration through its mitochondria, which generate ATP for energy.
- Growth: Paramecium grows through the process of cell division, either by binary fission or sexual reproduction.
- Response to stimuli: Paramecium responds to stimuli in its environment, such as changes in temperature or light.
- Reproduction: Paramecium reproduces through both sexual and asexual reproduction.
- Homeostasis: Paramecium maintains a stable internal environment through the regulation of its water balance.
- Excretion: Paramecium excretes waste products through its contractile vacuoles.
Paramecium Meaning in Hindi
पैरामीशियम सपा। एककोशिकीय सिलिअटेड जीव है। वे एकल-कोशिका वाले, सूक्ष्म, मुक्त-जीवित प्रोटोजोअन हैं। पूरे जीव में सिलिया नामक बालों वाली संरचनाओं की उपस्थिति के कारण उन्हें रोमक जीवों के रूप में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है। इनका शरीर तिरछा या चप्पल के आकार का होता है। Paramecium में प्रजनन मुख्य रूप से बाइनरी विखंडन द्वारा अलैंगिक रूप से होता है। Paramecia (फुफ्फुस) मीठे पानी, स्थिर तालाब के पानी और समुद्री वातावरण में पाए जाते हैं। हालांकि पैरामीशियम का संवर्धन प्रयोगशालाओं में आसानी से किया जा सकता है। Paramecia जैविक प्रक्रियाओं को समझने के लिए प्रयोगशालाओं में एक जैविक मॉडल के रूप में व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किया जाता है। यहां हम व्यवस्थित स्थिति, पैरामीशियम का वर्गीकरण और उनके प्रजनन, और हरकत प्रक्रिया के बारे में सीखते हैं।
पैरामीशियम किंगडम
किंगडम- प्रोटिस्टा
फाइलम-सिलियोफोरा
वर्ग- ओलिगोहाइमेनोफोरिया
आदेश- पेनिकुलिडा
परिवार- Parameciidae
जीनस- पैरामीशियम
पैरामीशियम किंगडम वर्गीकरण
Paramecium एक एककोशिकीय, यूकेरियोटिक प्रोटोजोआ है जिसे प्रोटिस्टा साम्राज्य में रखा गया है और यह फाइलम सिलियोफोरा के अंतर्गत आता है।
Paramecium की सामान्य प्रजातियाँ हैं-
पैरामीशियम ऑरेलिया
Paramecium caudatum
पैरामीशियम ट्राइकियम
पैरामीशियम वुड्रूफी
Paramecium संरचना और आकार
• आकार और आकार – पैरामीशियम को स्लीपर एनिमलक्यूल के रूप में जाना जाता है क्योंकि इसकी चप्पल जैसी आकृति के कारण इसकी लंबाई 0.25 मिमी और सूक्ष्म होती है। आगे का सिरा पतला, पिछला सिरा मोटा और नुकीला होता है। अंडाकार मौखिक या उदर सतह है।
• पेलिकल- कोशिकीय कोशिका द्रव्य पेलिकल से घिरा होता है। षट्कोणीय अवसादों के साथ पेलिकल सख्त और लचीला होता है। तो, यह कोशिका को एक परिवर्तनशील और निश्चित आकार देता है।
• सिलिया-सिलिया एक अक्षीय तंतु (अक्षतंतु) से बनी होती है और एक प्रोटोप्लाज्मिक म्यान से घिरी होती है, जो अनुदैर्ध्य पंक्तियों में व्यवस्थित होती है। यह एक दबे हुए हिस्से को जड़ देता है, जिसे जड़ कहा जाता है। शाफ्ट और जड़ के बीच एक प्लेट जैसी होती है जो सिलिया को पेलिकल में धारण करने के लिए सहारा देती है, जिसे बेसल प्लेट कहा जाता है। Paramecium में बड़ी संख्या में सिलिया पाए जाते हैं जो पूरे शरीर में मौजूद होते हैं और एक सर्पिल पाठ्यक्रम में व्यवस्थित होते हैं। (स्पाइरो व्यवस्था)
• प्रोटोप्लाज्म- प्रोटोप्लाज्म को 2 भागों में विभेदित किया जाता है- बाहरी एक्टोप्लाज्म जो नॉनग्रेनुलर होता है जिसमें ट्राइकोसिस्ट और दानेदार आंतरिक एंडोप्लाज्म होता है, जिसमें गुर्दे के आकार का मैक्रोन्यूक्लियस और एक छोटा माइक्रोन्यूक्लियस होता है।
• सिकुड़ा हुआ रिक्तिकाएं- पैरामीशियम में, शरीर के दोनों ओर दो तारे के आकार की सिकुड़ी हुई रिक्तिकाएं पाई जाती हैं जो शरीर में अतिरिक्त पानी और चयापचय अपशिष्ट के भंडार के रूप में काम करती हैं।
• ओरल ग्रूव या साइटोस्टोम- ओरल ग्रूव फ़नल के आकार के गुलेट या साइटोफैरिनक्स में खुलता है, जो शरीर के उदर भाग पर मौजूद होता है जिसे साइटोस्टोम कहा जाता है।
• खाद्य रिक्तिकाएं- पैरामीशियम के शरीर में कई खाद्य रिक्तिकाएं मौजूद होती हैं, जो पूर्वकाल से पीछे की ओर पंक्तियों में व्यवस्थित होती हैं। वे भोजन रिक्तिकाएँ भोजन के पाचन में सहायता करती हैं।
• साइटोपायज- साइटोपीज एक छिद्र है जिसके द्वारा मुंह के ठीक पीछे स्थित शरीर से अपाच्य भोजन को हटा दिया जाता है।
Paramecium Meaning in Tamil
“பராமேசியம்” என்ற சொல், புரோட்டோசோவான்களின், குறிப்பாக சிலியட்டுகளின் குழுவிற்குச் சொந்தமான ஒற்றை உயிரணு வகைகளைக் குறிக்கிறது. இது அதன் தனித்துவமான வடிவம் மற்றும் சிலியாவின் இருப்பு ஆகியவற்றால் வகைப்படுத்தப்படுகிறது, அவை இயக்கம் மற்றும் உணவளிக்க பயன்படுத்தும் முடி போன்ற அமைப்புகளாகும்.
தமிழில் “பரமீசியம்” என்பதை “பரமீசியம்” (பிரமீசியம்) என்று மொழிபெயர்க்கலாம். அறிவியல் சொற்கள் எப்போதும் மொழிகளில் நேரடி மொழிபெயர்ப்புகளைக் கொண்டிருக்காமல் இருக்கலாம், எனவே வழங்கப்பட்ட தமிழ்ச் சொல் தோராயமானதாகும்.
Related Post:










 CLAT Result 2026 Out, Download Scorecard...
CLAT Result 2026 Out, Download Scorecard...
 CLAT Topper List 2026 Released with Rank...
CLAT Topper List 2026 Released with Rank...
 When Will NEET 2026 Registration Start? ...
When Will NEET 2026 Registration Start? ...














