Parenchyma Meaning
A basic permanent tissue known as Parenchyma or parenchyma makes up a large portion of the ground tissues of plants, where vascular tissues and other tissues are attached. They are non-vascular and made up of undifferentiated, primitive living cells that have undergone modifications to carry out distinct tasks.
Parenchyma Cells
Parenchyma cells are a type of simple plant cells that are essential for various functions within a plant. They are a fundamental component of plant tissues and are found throughout the plant body, primarily in the ground tissue system. Parenchyma cells have several important roles, including photosynthesis, storage, secretion, and providing structural support.
Key characteristics of parenchyma cells include:
Shape and Structure: Parenchyma cells are usually isodiametric (roughly spherical) in shape, but they can also be elongated or irregular in some cases. They have thin cell walls made of cellulose, which allows for flexibility and efficient exchange of substances.
Cell Wall: The cell walls of parenchyma cells are relatively thin compared to other plant cell types, such as collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells. This thinness facilitates various functions, including rapid diffusion of gases and movement of water and nutrients.
Vacuoles: Parenchyma cells often contain large central vacuoles that store water, nutrients, and waste products. These vacuoles help maintain turgor pressure and play a role in regulating water balance within the plant.
Photosynthesis: Many parenchyma cells are capable of photosynthesis, as they contain chloroplasts. These cells are involved in producing energy-rich compounds, such as glucose, through the process of photosynthesis. They are found in leaves and other green parts of plants.
Storage: Parenchyma cells can store various substances, including starch, oils, and proteins. These stored materials can be used by the plant when needed, such as during periods of growth or when energy reserves are required.
Regeneration and Healing: Parenchyma cells are often involved in tissue regeneration and wound healing. They can divide and differentiate into other cell types to repair damaged plant tissues.
Function in Gas Exchange: Parenchyma cells are involved in gaseous exchange within the plant, allowing for the movement of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases between the plant and its environment.
Structural Support: In some cases, parenchyma cells can provide support to plant tissues. For example, collenchyma cells have thickened cell walls and are a specialized type of parenchyma cells that provide flexible support to growing parts of plants.
parenchyma cells are versatile and perform essential roles that contribute to the growth, development, and overall functioning of plants. Their diversity in function and location makes them a crucial component of plant biology.
Parenchyma Tissue
In plants, parenchyma or Parenchyma is a tissue that is often made up of live cells with thin walls, an unspecialized structure, and the ability to adapt to varied functions through differentiation. Since they are alive, the cells are actively involved in photosynthesis, secretion, food storage, and other functions of plant life. Parenchymatous can be found in several locations throughout plant bodies. Along with sclerenchyma (dead support tissues with thick walls) and collenchyma, parenchyma is one of the three primary forms of ground, or foundational, tissue in plants (living support tissues with irregular walls).
Parenchyma Tissue Diagram
The parenchyma tissue diagram is given below.
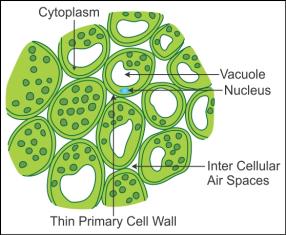
Human Eye Definition, Diagram, Structure
Parenchymatous
“Parenchymatous” refers to the tissue structure found in plants, animals, and some other organisms. It is characterized by having cells that are loosely arranged, often with thin cell walls and relatively large intercellular spaces. Parenchyma cells are typically involved in various functions such as storage, photosynthesis, and gas exchange.
In plants, parenchyma cells are found in various organs and tissues, including leaves, stems, roots, and fruits. They play a crucial role in tasks like photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, and wound healing. In animals, parenchymal tissue is also present in certain organs and glands, where it carries out specialized functions.
Overall, the term “parenchymatous” describes the structural and functional characteristics of tissues composed of parenchyma cells.
Parenchyma Algae Function
Parenchymatous seaweeds are defined as having cells that resemble higher plants and have a boxy shape. Others have a parenchymatous look in cross-section but are actually formed of interwoven filaments, giving them this appearance. Pseudoparenchymatous is the word for them.
- Parenchymatous algae are primarily macroscopic, have undifferentiated cells, and arise from meristems that have three-dimensional cell division.
- In the case of parenchymatous algae, primary filament cells divide in any direction, eliminating any necessary filamentous structure.
- Many of the brown algae and Ulva (Chlorophyta), as well as this tissue organisation.
- Pseudoparenchymatous algae, particularly red algae, are composed of a loose or compact assemblage of many, tangled, branching filaments that collectively constitute the thallus and are kept together by mucilages.
Parenchyma Organs Function
Parenchyma or Parenchyma and connective tissue stroma make up this solid organ, and the stroma divides the parenchyma into lobes, segments, lobules, acini, or cortex, and medulla. The kidneys, adrenal glands, liver, spleen, and pancreas are among the parenchymal or Parenchymatous organs.
Parenchyma in Nature
- As reproductive cells (spores, gametes) are parenchymatous in nature, parenchyma cells serve as the building blocks of plants.
- A zygote’s single parenchyma cell has the capacity to grow into a complete plant. “Totipotent” cells are what these cells are.
- In homogeneous parenchyma tissues, such as the mesophyll of leaves, the flesh of succulent fruits, and the endosperm of seeds, parenchyma cells are found in continuous masses.
- Xylem and phloem parenchyma are examples of heterogeneous complex tissues that can be created when parenchyma or Parenchymatous cells are combined with other types of cells.
- The functions of parenchyma or Parenchymatous cells include photosynthesis, water and solute storage, secretion, assimilation, respiration, excretion, and radial transport.
Scientific Names Of The Common Animals And Plants
Parenchyma Diagram
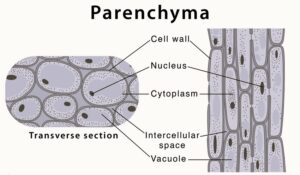
Structure of Parenchymatous or Parenchyma
Parenchyma Meaning in Hindi
पैरेन्काइमा या पैरेन्काइमा के रूप में जाना जाने वाला एक मूल स्थायी ऊतक पौधों के जमीन के ऊतकों का एक बड़ा हिस्सा बनाता है, जहां संवहनी ऊतक और अन्य ऊतक जुड़े होते हैं। वे गैर-संवहनी हैं और अविभाजित, आदिम जीवित कोशिकाओं से बने हैं जिनमें अलग-अलग कार्य करने के लिए संशोधन किए गए हैं।
पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएँ
पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएँ एक प्रकार की सरल पादप कोशिकाएँ हैं जो पौधे के भीतर विभिन्न कार्यों के लिए आवश्यक होती हैं। वे पौधों के ऊतकों का एक मूलभूत घटक हैं और पूरे पौधे के शरीर में पाए जाते हैं, मुख्य रूप से जमीनी ऊतक प्रणाली में। पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं की कई महत्वपूर्ण भूमिकाएँ होती हैं, जिनमें प्रकाश संश्लेषण, भंडारण, स्राव और संरचनात्मक सहायता प्रदान करना शामिल है।
पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं की प्रमुख विशेषताओं में शामिल हैं:
आकार और संरचना: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं आमतौर पर आकार में आइसोडायमेट्रिक (लगभग गोलाकार) होती हैं, लेकिन कुछ मामलों में वे लम्बी या अनियमित भी हो सकती हैं। इनमें सेलूलोज़ से बनी पतली कोशिका दीवारें होती हैं, जो लचीलेपन और पदार्थों के कुशल आदान-प्रदान की अनुमति देती हैं।
कोशिका भित्ति: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं की कोशिका दीवारें अन्य पादप कोशिका प्रकारों, जैसे कोलेन्काइमा और स्क्लेरेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं की तुलना में अपेक्षाकृत पतली होती हैं। यह पतलापन विभिन्न कार्यों को सुविधाजनक बनाता है, जिसमें गैसों का तेजी से प्रसार और पानी और पोषक तत्वों की आवाजाही शामिल है।
रिक्तिकाएँ: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं में अक्सर बड़ी केंद्रीय रिक्तिकाएँ होती हैं जो पानी, पोषक तत्व और अपशिष्ट उत्पादों को संग्रहित करती हैं। ये रिक्तिकाएँ स्फीति दबाव बनाए रखने में मदद करती हैं और पौधे के भीतर जल संतुलन को विनियमित करने में भूमिका निभाती हैं।
प्रकाश संश्लेषण: कई पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं प्रकाश संश्लेषण में सक्षम होती हैं, क्योंकि उनमें क्लोरोप्लास्ट होते हैं। ये कोशिकाएं प्रकाश संश्लेषण की प्रक्रिया के माध्यम से ग्लूकोज जैसे ऊर्जा-समृद्ध यौगिकों का उत्पादन करने में शामिल होती हैं। वे पत्तियों और पौधों के अन्य हरे भागों में पाए जाते हैं।
भंडारण: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं स्टार्च, तेल और प्रोटीन सहित विभिन्न पदार्थों को संग्रहीत कर सकती हैं। इन संग्रहीत सामग्रियों का उपयोग पौधे द्वारा आवश्यकता पड़ने पर किया जा सकता है, जैसे कि विकास की अवधि के दौरान या जब ऊर्जा भंडार की आवश्यकता होती है।
पुनर्जनन और उपचार: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं अक्सर ऊतक पुनर्जनन और घाव भरने में शामिल होती हैं। वे क्षतिग्रस्त पौधों के ऊतकों की मरम्मत के लिए अन्य प्रकार की कोशिकाओं में विभाजित और विभेदित हो सकते हैं।
गैस विनिमय में कार्य: पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं पौधे के भीतर गैसीय विनिमय में शामिल होती हैं, जिससे पौधे और उसके पर्यावरण के बीच ऑक्सीजन, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और अन्य गैसों के आवागमन की अनुमति मिलती है।
संरचनात्मक सहायता: कुछ मामलों में, पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएं पौधों के ऊतकों को सहायता प्रदान कर सकती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, कोलेन्काइमा कोशिकाओं की कोशिका दीवारें मोटी होती हैं और ये एक विशेष प्रकार की पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएँ होती हैं जो पौधों के बढ़ते भागों को लचीला समर्थन प्रदान करती हैं।
पैरेन्काइमा कोशिकाएँ बहुमुखी हैं और आवश्यक भूमिकाएँ निभाती हैं जो पौधों की वृद्धि, विकास और समग्र कामकाज में योगदान करती हैं। कार्य और स्थान में उनकी विविधता उन्हें पादप जीव विज्ञान का एक महत्वपूर्ण घटक बनाती है।
पैरेन्काइमा ऊतक
पौधों में, पैरेन्काइमा या पैरेन्काइमा एक ऊतक है जो अक्सर पतली दीवारों, एक अविशिष्ट संरचना और विभेदन के माध्यम से विभिन्न कार्यों को अनुकूलित करने की क्षमता वाली जीवित कोशिकाओं से बना होता है। चूँकि वे जीवित हैं, कोशिकाएँ प्रकाश संश्लेषण, स्राव, भोजन भंडारण और पौधों के जीवन के अन्य कार्यों में सक्रिय रूप से शामिल होती हैं। पैरेन्काइमेटस पूरे पौधे के शरीर में कई स्थानों पर पाया जा सकता है। स्क्लेरेन्काइमा (मोटी दीवारों वाले मृत सहायक ऊतक) और कोलेन्काइमा के साथ, पैरेन्काइमा पौधों में जमीन, या मूलभूत, ऊतक (अनियमित दीवारों वाले जीवित सहायक ऊतक) के तीन प्राथमिक रूपों में से एक है।
Also Read:
- What Is Hybridization?- Sp3, Sp2, Examples And Formula
- What Is A Stethoscope?- Its Parts, Uses, & Diagram
- Parallel Axis Theorem, Proof, Definition, Formula, Examples
- Oscillatory Motion, Meaning, Definition, Example, Diagram
- Planets Name In English And Hindi
- What Is The Unit Of Current, Resistance And Voltage?
- All About Father Of Genetics- Gregor Mendel
- States And Union Territories Capitals Of India 2023
- 7 Rainbow Colours Name In Order, Drawing, Vibgyor Meaning








 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














