Present Continuous tense: The Present Continuous Tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that are happening now or that are in progress. It is also used to describe actions that are happening repeatedly or habitually. It is one of the twelve tenses present in the English grammar. It is one of the four tenses in the Present form other than the Simple Present Tense, Present Perfect Tense, and Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Present Continuous Tense (Progressive Tense)
The present continuous form tense, as the name suggests, is a form of tense used to express actions that are ongoing or taking place at this moment. It is also known as the present progressive tense because it represents an action going on in the present tense. Now let’s look at the definitions provided in various dictionaries for the present tense.
This continuous Tense is formed by adding the -ing ending to the base form of the verb. For example, the verb “to eat” becomes “eating” in this Continuous Tense. That means this tense takes 4th form of the verb. The subject of the sentence determines the form of the verb in this Tense. For singular subjects, the verb is am/is/are + verb-ing. For plural subjects, the verb is are + verb-ing.
Present Continuous Tense Definition
The Cambridge Dictionary defines “present tense” as “a verb tense used for an action or event that is ongoing or developing”. The present tense is followed by the present participle and is specifically used to indicate that a present action or event is ongoing, recurring, temporary, or expresses the future. “A tense used to talk about an action or action that is in progress or planned in the future”.
Present Continuous Tense Formula
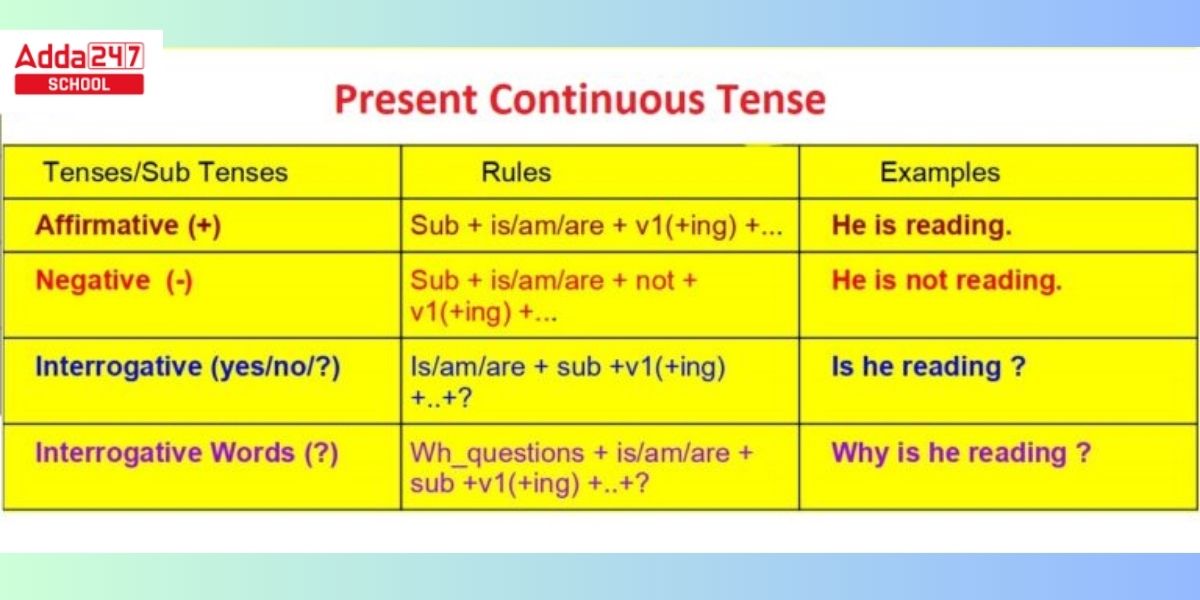
| Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence |
However, there are other things to be aware of. You should also learn how sentences are constructed using the present tense of verbs when the verbs are positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative.
Look at the table below to get a better understanding of the structure of the present tense.
| Positive | Negative | Interrogative | Negative Interrogative |
| Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence | Subject + am/is/are +not+present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence | Am/is/are + subject + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence? | Am/is/are + subject + not+ present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence?
(or) Ain’t + subject + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence? |
Examples
|
Examples
|
Examples
|
Examples
|
Note:- Ain’t is a contraction used for is not, are not, am not, has not, have not
Present Continuous Tense Uses
The Present Continuous form of Tense also called present progressive tense, is used to describe actions that are currently ongoing or that may occur in the future.
The present tense is usually used in four general cases:
- To describe an event that is currently occurring.
For examples:
- I am watching television.
- She is currently completing her work.
- Children are playing in the park.
2. List upcoming events.
For examples:
- What are you going to wear tomorrow?
- I heard that you are coming to the evening party.
- So, you are moving to the Paris next month.
3. For lengthy actions that may be taking place for a temporary period only.
For examples:
- He is learning to drive a car.
- Salima is taking a spoken English course.
- The teacher is learning a new language at the moment.
4. To discuss a new pattern or habit.
For examples:
- These days almost people are using mobile phones.
- She is always running late with deadlines.
- Nowadays people are using email rather than letters.
Present Continuous Tense Rules
Just like other Tense forms, this tense is also governed by certain rules. Rules to be used while writing this tense are given below.
- Use the helping verb appropriately. With third person singular ‘is’ will be used, with a plural noun or pronoun ‘are’ will be used and with only ‘I’, ‘am’ will be used.
- Add ‘-ing’ in the main action verb.
- Note that like other pronouns in interrogative sentences, the pronoun ‘am’ cannot be used in the negative form. “aren`t” is used instead of “ain`t”.
For examples:
Ain’t I reading the book? (wrong)
Ain’t/ aren’t I reading the book? (correct)
Present Continuous Tense Examples Sentences
Here are some examples of of this tense for the better understanding of students. These examples will hel students understand this tense in a better way.
- Children are going to school. (Positive)
- Children are not going to school. (Negative)
- Are children going to school? (Interrogative)
- Ain’t children going to school? (Negative interrogative)
- The boys are playing in the park. (Positive)
- The boys are not playing in the park. (Negative)
- Are the boys playing in the park? (Interrogative)
- Ain’t the boys playing in the park? (Negative interrogative)
- The baby is crying out loud. (Positive)
- The baby is not crying out loud. (Negative)
- Is the baby crying out loud? (Interrogative)
- Ain’t the baby crying out loud? (Negative interrogative)
- It is raining now. (Positive)
- It isn’t raining now. (Negative)
- Is it raining now? (Interrogative)
- Isn’t it raining now? (Negative interrogative)
- I am cooking pasta for lunch. (Positive)
- I ain’t cooking pasta for lunch. (Negative)
- Am I cooking pasta for lunch? (Interrogative)
- Ain’t I cooking pasta for lunch? (Negative interrogative)
- Miss Peters is teaching in the class. (Positive)
- Miss Peters isn’t teaching in the class. (Negative)
- Is Miss Peters teaching in the class? (Interrogative)
- Isn’t Miss Peters teaching in the class? (Negative interrogative)
Present Continuous Tense in Hindi
वर्तमान विन्यासी काल, जिसे हिंदी में “वर्तमान सतत काल” कहा जाता है, वह वाक्यांश है जिसमें किसी कार्य को वर्तमान के समय में व्यक्त किया जाता है, जो कि अभी चल रहा है और समय के साथ परिवर्तित हो सकता है। यह काल सामान्यतया किसी कार्य की स्थिति, प्रगति, या तत्परता को व्यक्त करने के लिए प्रयोग किया जाता है।
इस काल का उपयोग करते समय क्रिया के लिए “रह रहा है”, “रह रही है”, या “रह रहे हैं” जैसे शब्दों का उपयोग किया जाता है।
यहां कुछ उदाहरण हैं जो वर्तमान सतत काल में हैं:
- मैं अभी पढ़ाई कर रहा हूँ।
- वह फ़ोन पर बात कर रही है।
- हम अपनी टीम के साथ योजना बना रहे हैं।
- वे खेल के मैदान में दौड़ रहे हैं।
- तुम अपनी कहानी लिख रहे हो।
वर्तमान सतत काल का प्रयोग करते समय वाक्य में कार्य की अस्थिरता और प्रगति का अहसास होता है। यह काल किसी कार्य के चल रहे होने को दर्शाता है जो समय के साथ परिवर्तित हो सकता है या जिसकी अवधि सीमित होती है। इस काल के प्रयोग से किसी क्रिया का आधिकारिकता और दुर्मिलता प्रकट होती है, और यह व्यक्तिगत और व्यापारिक संदर्भों में प्रयोग किया जा सकता है।
Present Continuous Tense Exercises
After looking at all the examples given, you should have a really good idea of the continuous tense in the present form. Here is the exercise given below for a better understanding of the concepts:
Q. Fill in the blanks using the correct form of the verb given in the bracket:
- Janet …………………….. a special dish for her family. (cook)
2. I …………………………… them to complete the work on time. (expect)
3. The students ………………………… a poem on the stage. (recite)
4. The old man ……………………………. on his bed. (sleep)
5. The children ……………………………… sand castles on the beach. (make)
6. The birds ………………………………. on the trees.(sing)
7. The children ……………………………… mangoes. (pick)
8. I …………………………….. a portrait of a lady. (draw)
9. She ……………………….. French. (learn)
10. The kids …………………………. fruits. (eat)
Check your answers
1. Janet is cooking a special dish for her family. (cook)
2. I am expecting them to complete the work on time. (expect)
3. The students are reciting a poem on the stage. (recite)
4. The old man is sleeping on his bed. (sleep)
5. The children are making sand castles on the beach. (make)
6. The birds are singing on the trees. (sing)
7. The children are picking mangoes. (pick)
8. I am drawing a portrait of a lady. (draw)
9. She is learning French. (learn)
10. The kids are eating fruits. (eat)
Present Continuous Tense in Hindi
वर्तमान निरंतर काल, जैसा कि नाम से पता चलता है, इस समय चल रही या हो रही क्रियाओं को व्यक्त करने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले काल का एक रूप है। इसे वर्तमान प्रगतिशील काल के रूप में भी जाना जाता है क्योंकि यह वर्तमान काल में चल रही एक क्रिया का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। अब आइए वर्तमान काल के लिए विभिन्न शब्दकोशों में दी गई परिभाषाओं को देखें।
वर्तमान सतत काल – परिभाषा
कैम्ब्रिज डिक्शनरी “वर्तमान काल” को “एक क्रिया या घटना के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला क्रिया काल” के रूप में परिभाषित करता है जो चल रहा है या विकसित हो रहा है। वर्तमान काल के बाद वर्तमान कृदंत होता है और विशेष रूप से यह इंगित करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है कि एक वर्तमान क्रिया या घटना चल रही है, आवर्ती, अस्थायी, या भविष्य को व्यक्त करती है। “किसी क्रिया या क्रिया के बारे में बात करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला काल जो प्रगति पर है या भविष्य में नियोजित है”।
Related Post:
- Personal Pronouns: Definition, Examples, Exercise, And Chart
- Relative Pronoun: Definition And Examples, Exercise
- Reflexive Pronoun: Definition, Examples, Exercise
- Letter Writing Examples In English & Hindi
- Present Perfect Tense-Formula, Examples, Exercise, Rules, Sentences
- Types Of Sentences With Examples, Definition, Exercises, Chart, PDF
- Opposite Words In English And Hindi
- Transitive And Intransitive Verb: Definition, Examples, Exercise
- Possessive Pronoun: Definition, Examples, Exercise Sentences










 Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
 Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
 Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...
Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...














