The present tense is a verb tense that is used to describe actions that are occurring right now, actions that occur on a regular basis, or actions that are always true. There are three types of present tense: simple present tense, continuous present tense, and perfect present tense.
Present Tense
The present tense is used to describe actions that occur now or on a regular basis. For instance, “I eat breakfast every morning.”The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are taking place or are currently taking place. For example, “I’m eating breakfast right now.”The present perfect tense is used to express activities that occurred in the past but have present-day relevance. “I’ve already eaten breakfast,” for example. The present tense is a versatile tense that can depict a wide range of acts. You may enhance your English grammar and communication skills by studying the many varieties of present tense and how to apply them.
Present tense refers to an action or event that is or is taking place in the present tense. Present Tense represents the subject’s current activity or state in a particular context. The present tense is used to talk about what is happening in the present time.
This article will teach you Present tense definitions, structures, usage rules, and examples.
Present Tense Definition
According to the Oxford Learners’ Dictionary, the present tense is “the action verb form that describes what is happening now or at the time of speaking”. The Cambridge Dictionary defines the present tense as “a verb form used to indicate that something is happening or existing”.
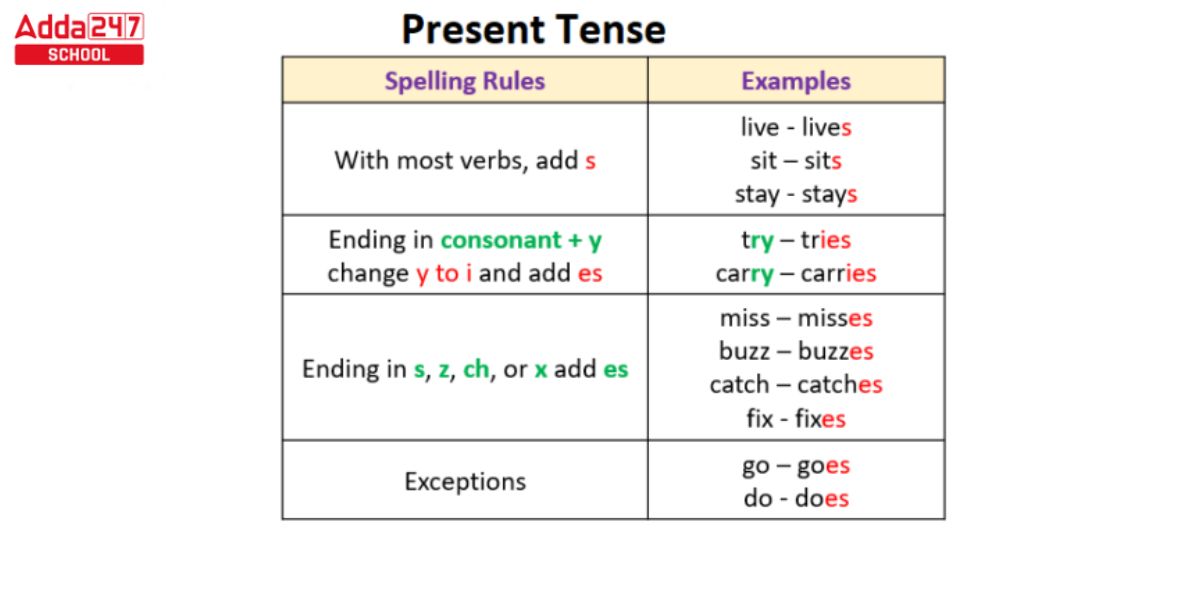
Present Tense Formula
The simple present tense is used to describe actions or situations that are regular, routine, or generally true. It is one of the basic tenses in English and is formed using a simple formula:
Subject + Base Form of Verb (+s/es for third person singular)
Here’s how it works:
- For most verbs (those not ending in -s, -x, -z, -sh, or -ch):
- I/You/We/They eat breakfast every morning. (no change in the base form)
- He/She/It eats breakfast every morning. (add ‘s’ or ‘es’ for third person singular)
- For verbs ending in -s, -x, -z, -sh, or -ch:
- I/You/We/They wash the dishes every evening. (no change in the base form)
- He/She/It washes the dishes every evening. (add ‘es’ for third person singular)
Examples:
- I play soccer on weekends. (base form)
- She loves to read books. (add ‘s’ for third person singular)
- They speak English fluently. (base form)
- He teaches mathematics at the school. (add ‘es’ for third person singular)
The simple present tense is also used for general truths, habits, and facts that are always true.
Examples:
- The Earth revolves around the Sun. (general truth)
- I usually go for a run in the morning. (habit)
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius. (fact)
Remember that there are some irregular verbs in English that do not follow this regular pattern. For these verbs, you need to memorize their specific forms.
Present Tense Types
There are four different types of Present tenses in the English language.
Simple present tense – used to indicate current or regularly occurring actions.
Present continuous tense – used to express an action in progress in the present moment.
Present perfect tense – used to indicate an action, used to indicate an action that is finished but affects the subject or object of a sentence.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense – used to describe an action that started in the recent past and is still ongoing.
Present Tense Structure
The structure of Present Tense is as follows:
| Structure of Present Tense | |||
| Simple present tense | Present continuous tense | Present perfect tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Subject + base form of the verb/verb+s/es(if needed) + rest of the sentence. | Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence | Subject + have/has + past participle (third form of the verb) + rest of the sentence. | Subject + have/has + been + present participle (verb+ing) + since/for (if needed) + the rest of the sentence. |
Present Tense Chart with Examples
The table below consists of Present tense chart with example.
| Tense | Subject | Verb | Example |
| Simple Present | I, you, we, they | The base form of the verb |
I eat breakfast every morning.
|
| Simple Present | He/she/it | -s or -es |
He eats breakfast every morning.
|
| Present Continuous | I, you, we, they | Am/are/is + -ing |
I am eating breakfast right now.
|
| Present Continuous | He/she/it | Is/are + -ing |
He is eating breakfast right now.
|
| Present Perfect | I, you, we, they | Have/has + past participle |
I have eaten breakfast already.
|
| Present Perfect | He/she/it | Has/have + past participle |
He has eaten breakfast already.
|
Present Tense Examples
Examples of Present Tense are given below:
- She doesn’t go to school daily.
- You read this chapter.
- I listen to songs every morning.
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
- Do cats drink milk?
Examples of Present Continuous Tense are given below:
- She is learning the chapter.
- The teacher is teaching in the class.
- Are birds chirping on trees?
- They aren’t going anywhere.
- Some people are following her.
Examples of Present Perfect Tense are given below:
- She has watched this movie.
- I have never gone there.
- Has he completed his work?
- Have they taken their lunch?
- We have learned this lesson.
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense are given below:
- We have been living here since 1992.
- It has been raining since morning.
- Children have been studying for two hours.
- Jack has been doing this work for five hours.
- Ben has not been playing a video game since 6 p.m.
Present Tense Exercise
Fill in the blanks using the correct form of the verb given in the bracket according to the present tense:
- Janet …………………….. a special dish for her family. (cook)
- I …………………………… them to complete the work on time. (expect)
- The students ………………………… a poem on the stage. (recite)
- The old man ……………………………. on his bed. (sleep)
- He (work)…………..in the same school since 2011.
- I (wait) …………for you since four o’clock.
- Curie (live) …………. in Brazil since 2000.
- He ______ to the office every day. (go)
- When ____ you go to school? (does)
- She _______ she is so intelligent. (think)
- Does he _____ in India? (lives)
- The dust __________ everywhere in the kitchen. (blow)
- She ___________ anything yet for the party wearing. (not/ choose)
- _____ she ______ this task completely? (do)
- He _______ most of the time playing video games. (spend)
Check your answers
- Janet is cooking a special dish for her family. (cook)
- I expect them to complete the work on time. (expect)
- The students are reciting a poem on the stage. (recite)
- The old man is sleeping on his bed. (sleep)
- He has been working in the same school since 2011.
- I have been waiting for you since four o’clock.
- Curie has been living in Brazil since 2000.
- He goes to the office every day. (go)
- When do you go to school? (does)
- She thinks she is so intelligent. (think)
- Does he live in India? (lives)
- The dust has blown everywhere in the kitchen. (blow)
- She has not chosen anything yet for the party wearing. (not/ choose)
- Has she done this task completely? (do)
- He has spent most of his time playing video games. (spend)
Related Post:










 Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
 Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
 Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...
Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...














