Satyendra Nath Bose
Satyendra Nath Bose was an Indian mathematician and physicist, an expert in theoretical physics. The Bose statistics and the theory of the Bose condensate were developed as a result of his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s. He is most known for his early 1920s work on quantum mechanics, his collaboration with Albert Einstein on the development of the theory of the Bose-Einstein condensate, and the foundation for Bose-Einstein statistics. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society and received the Padma Vibhushan, the country of India’s second-highest civilian honour, bestowed by the Government of India, in 1954 for his work in theoretical physics.
Satyendranath Bose Images

Satyendra Nath Bose Biography and Education
Satyendra Nath Bose was a well-known Bengali-Indian physicist and brilliant mathematician best known for developing the Bose-Einstein condensate alongside Albert Einstein and serving as the inspiration for the boson particle.
• S.N. Bose was born in Kolkata on January 1, 1894. He was the eldest of a family of seven children of Surendranath Bose, his father who was a member of the East Indian Railway Company’s technical staff.
• Bose was a very intelligent student in both high school and college. He passed the matriculation exam in 1909 and secured fifth place on the merit list. He then enrolled in the intermediate science programme at Presidency College in Calcutta, where he was taught by Prafulla Chandra Ray, Sarada Prasanna Das, and Jagadish Chandra Bose.
• Bose graduated first in his class from Presidency College with a Bachelor of Science in combined mathematics in 1913. He then enrolled in Sir Ashutosh Mukherjee’s newly founded Science College, where in 1915 he once again won the MSc combined mathematics test. In the University of Calcutta’s records, his performance on the MSc examination set a new mark that hasn’t been surpassed.
• In 1916, Bose began studying the theory of relativity at the Science College of Calcutta University as a research scholar after receiving his MSc.
• In 1916, Bose joined as a lecturer in the Rajabazar Science College’s physics department of the University of Calcutta.
• In 1921, He joined the newly established University of Dhaka’s Department of Physics as a Reader.
• In 1924, Bose finally published a paper in which he had derived Planck’s “quantum radiation law,” it was the biggest and most significant accomplishment of his career. Without referring to any traditional physics ideas, he simply counted the number of identical states to achieve this.
• Bose sent his paper to Albert Einstein in Germany. Albert Einstein Realizing the significance of this research, he translated into German and published in a major German journal on Bose’s behalf. “Planck’s Law and Hypothesis of Light Quanta” was the title of the study. Later, Albert Einstein and Bose worked together to expand the concept.
• As a result, Bose was allowed to work for two years at European X-ray and crystallography laboratories, during which time he collaborated with Louis de Broglie, Marie Curie, and Einstein.
• Bose’s theory was adopted by Einstein and applied to atoms in the paper. Because of this, the Bose-Einstein Condensate phenomenon was predicted to occur. One of the many bosons is the Higgs boson particle, also referred to as the God particle or Higgs boson.
• His discovery is still regarded as one of the greatest accomplishments of the 20th century, and S N Bose is one of the most illustrious figures in theoretical physics.
• He was a Fellow of the Royal Society and was awarded the Padma Vibhushan in 1954 for his contributions to theoretical physics, the second-highest civilian honour in India.
• He conducted research in literature (Bengali and English) and biotechnology in addition to physics. He conducted extensive research in the areas of chemistry, geology, zoology, anthropology, engineering, and others.
• On February 4, 1974, Satyendra Nath Bose passed away. Salt Lake City, which bears Calcutta’s name in his honour, is home to the S.N. Bose National Centre for the Basic Sciences.
Satyendra Nath Bose Invention- Contribution to Physics and Mathematics
Satyendra Nath Bose is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for Bose statistics and the theory of the Bose condensate.
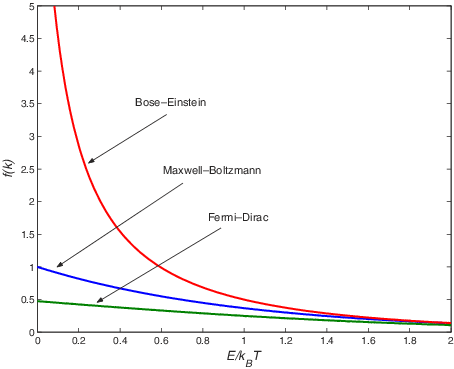
Bose-Einstein statistics
Satyendra Nath Bose created this hypothesis in 1924 after realising that a group of identical and indistinguishable particles may be distributed in this fashion. Later, Albert Einstein and Bose worked together to expand the concept.
A group of non-interacting, indistinguishable particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states in thermodynamic equilibrium in one of two ways, according to Bose-Einstein statistics. The cohesive streaming of laser light and the frictionless creep of superfluid helium are both explained by the aggregation of particles in the same state, a property of particles following Bose-Einstein statistics.
Only particles that are not constrained to single occupancy of the same state—i.e., particles that do not adhere to the Pauli exclusion principle restrictions—are subject to the Bose-Einstein statistics. Such particles are known as bosons particles because they have integer spin values. Paul Dirac first used the name boson to honour Satyendra Nath Bose’s contribution.
Satyendra Nath Bose Achievements Information
• Visva Parichay, Rabindranath Tagore’s sole work of science, was dedicated to Satyendra Nath Bose in 1937.
•The Indian government awarded Bose the Padma Vibhushan title in 1954.
•He received the nation’s highest honour for a scholar in 1959 when he was named the National Professor, a post he maintained for 15 years.
•The S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences was established in Salt Lake, Calcutta, in 1986 by a law passed by the Indian government’s parliament in honour of Satendranath bose
•Bose became a consultant for the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
•He served as the National Institute of Science’s and the Indian Physical Society’s president. Also he was elected as the Indian Science Congress’ general president.
• He was Vice President and then President of the Indian Statistical Institute.. He was admitted as a Fellow of the British Royal Society in 1958.
Satyendra Nath Bose in Hindi
सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस एक भारतीय गणितज्ञ और भौतिक विज्ञानी, सैद्धांतिक भौतिकी के विशेषज्ञ थे। बोस के आंकड़े और बोस कंडेनसेट के सिद्धांत को 1920 के दशक की शुरुआत में क्वांटम यांत्रिकी पर उनके काम के परिणामस्वरूप विकसित किया गया था। उन्हें क्वांटम यांत्रिकी पर 1920 के दशक के शुरुआती काम, बोस-आइंस्टीन कंडेनसेट के सिद्धांत के विकास पर अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन के साथ उनके सहयोग और बोस-आइंस्टीन सांख्यिकी की नींव के लिए जाना जाता है। वह रॉयल सोसाइटी के फेलो थे और उन्हें सैद्धांतिक भौतिकी में उनके काम के लिए 1954 में भारत सरकार द्वारा दिया गया भारत का दूसरा सर्वोच्च नागरिक सम्मान पद्म विभूषण मिला।
Satyendra Nath Bose Biography and Education in Hindi
सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस एक प्रसिद्ध बंगाली-भारतीय भौतिक विज्ञानी और शानदार गणितज्ञ थे, जिन्हें अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन के साथ बोस-आइंस्टीन कंडेनसेट विकसित करने और बोसॉन कण के लिए प्रेरणा के रूप में सेवा करने के लिए जाना जाता था।
• एस.एन. बोस का जन्म 1 जनवरी, 1894 को कोलकाता में हुआ था। वे अपने पिता सुरेंद्रनाथ बोस के सात बच्चों के परिवार में सबसे बड़े थे, जो ईस्ट इंडियन रेलवे कंपनी के तकनीकी स्टाफ के सदस्य थे।
• बोस हाई स्कूल और कॉलेज दोनों में बहुत होशियार छात्र थे। उन्होंने 1909 में मैट्रिक की परीक्षा पास की और मेरिट लिस्ट में पांचवां स्थान हासिल किया। इसके बाद उन्होंने कलकत्ता के प्रेसीडेंसी कॉलेज में इंटरमीडिएट विज्ञान कार्यक्रम में दाखिला लिया, जहाँ उन्हें प्रफुल्ल चंद्र रे, शारदा प्रसन्न दास और जगदीश चंद्र बोस ने पढ़ाया।
• बोस ने 1913 में संयुक्त गणित में विज्ञान स्नातक के साथ प्रेसीडेंसी कॉलेज से अपनी कक्षा में प्रथम स्नातक की उपाधि प्राप्त की। इसके बाद उन्होंने सर आशुतोष मुखर्जी के नव स्थापित साइंस कॉलेज में दाखिला लिया, जहाँ 1915 में उन्होंने एक बार फिर एमएससी की संयुक्त गणित की परीक्षा जीती। कलकत्ता विश्वविद्यालय के रिकॉर्ड में, एमएससी परीक्षा में उनके प्रदर्शन ने एक नया अंक स्थापित किया जिसे पार नहीं किया गया है।
• 1916 में, बोस ने एमएससी प्राप्त करने के बाद एक शोध विद्वान के रूप में कलकत्ता विश्वविद्यालय के साइंस कॉलेज में सापेक्षता के सिद्धांत का अध्ययन शुरू किया।
• 1916 में, बोस कलकत्ता विश्वविद्यालय के राजाबाजार साइंस कॉलेज के भौतिकी विभाग में एक व्याख्याता के रूप में शामिल हुए।
• 1921 में, वे ढाका के भौतिकी विभाग के नव स्थापित विश्वविद्यालय में एक पाठक के रूप में शामिल हुए।
• 1924 में, बोस ने अंततः एक पेपर प्रकाशित किया जिसमें उन्होंने प्लैंक के “क्वांटम विकिरण कानून” को व्युत्पन्न किया था, यह उनके करियर की सबसे बड़ी और सबसे महत्वपूर्ण उपलब्धि थी। किसी भी पारंपरिक भौतिकी विचारों का उल्लेख किए बिना, उन्होंने इसे प्राप्त करने के लिए समान राज्यों की संख्या की गणना की।
• बोस ने जर्मनी में अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन को अपना पेपर भेजा। अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन ने इस शोध के महत्व को समझते हुए, उन्होंने जर्मन में अनुवाद किया और बोस की ओर से एक प्रमुख जर्मन पत्रिका में प्रकाशित किया। “प्लैंक का नियम और प्रकाश क्वांटा की परिकल्पना” अध्ययन का शीर्षक था। बाद में, अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन और बोस ने अवधारणा का विस्तार करने के लिए मिलकर काम किया।
• परिणामस्वरूप, बोस को यूरोपीय एक्स रे और क्रिस्टलोग्राफी प्रयोगशालाओं में दो साल तक काम करने की अनुमति दी गई, इस दौरान उन्होंने लुई डी ब्रोगली, मैरी क्यूरी और आइंस्टीन के साथ सहयोग किया।
• बोस के सिद्धांत को आइंस्टीन ने अपनाया और कागज में परमाणुओं पर लागू किया। इस वजह से, बोस-आइंस्टीन कंडेनसेट घटना होने की भविष्यवाणी की गई थी। कई बोसॉन में से एक हिग्स बोसॉन कण है, जिसे गॉड पार्टिकल या हिग्स बोसॉन भी कहा जाता है।
• उनकी खोज को अभी भी 20वीं सदी की सबसे बड़ी उपलब्धियों में से एक माना जाता है, और एस एन बोस सैद्धांतिक भौतिकी में सबसे शानदार शख्सियतों में से एक हैं।
• वे रॉयल सोसाइटी के फेलो थे और सैद्धांतिक भौतिकी में उनके योगदान के लिए 1954 में पद्म विभूषण से सम्मानित किया गया था, जो भारत में दूसरा सर्वोच्च नागरिक सम्मान है।
• उन्होंने भौतिकी के अलावा साहित्य (बंगाली और अंग्रेजी) और जैव प्रौद्योगिकी में शोध किया। उन्होंने रसायन विज्ञान, भूविज्ञान, प्राणीशास्त्र, नृविज्ञान, इंजीनियरिंग, और अन्य के क्षेत्रों में व्यापक शोध किया।
• 4 फरवरी 1974 को सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस का निधन हो गया। साल्ट लेक सिटी, जो उनके सम्मान में कलकत्ता का नाम रखता है, एस.एन. बोस नेशनल सेंटर फॉर द बेसिक साइंसेज।
Satyendra Nath Bose Contributions in Physics and Mathematics [Hindi]
सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस को 1920 के दशक की शुरुआत में बोस सांख्यिकी की नींव और बोस कंडेनसेट के सिद्धांत के विकास में क्वांटम यांत्रिकी पर उनके काम के लिए जाना जाता है।
बोस-आइंस्टीन सांख्यिकी
सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस ने यह परिकल्पना 1924 में यह महसूस करने के बाद की थी कि समान और अप्रभेद्य कणों का एक समूह इस तरह से वितरित किया जा सकता है। बाद में, अल्बर्ट आइंस्टीन और बोस ने अवधारणा का विस्तार करने के लिए मिलकर काम किया।
बोस-आइंस्टीन के आंकड़ों के अनुसार, गैर-अंतःक्रियात्मक, अप्रभेद्य कणों का एक समूह थर्मोडायनामिक संतुलन में उपलब्ध असतत ऊर्जा राज्यों के एक सेट पर दो तरीकों में से एक पर कब्जा कर सकता है। लेज़र प्रकाश की कोसिव स्ट्रीमिंग और सुपरफ्लुइड हीलियम के घर्षण रहित रेंगना दोनों को एक ही अवस्था में कणों के एकत्रीकरण द्वारा समझाया गया है, जो बोस-आइंस्टीन आंकड़े के बाद कणों की एक संपत्ति है।
केवल वे कण जो एक ही राज्य के एकल अधिभोग के लिए विवश नहीं हैं – यानी, वे कण जो पाउली अपवर्जन सिद्धांत प्रतिबंधों का पालन नहीं करते हैं – बोस-आइंस्टीन के आंकड़ों के अधीन हैं। ऐसे कणों को बोसॉन कण के रूप में जाना जाता है क्योंकि उनके पास पूर्णांक स्पिन मान होते हैं। पॉल डिराक ने सबसे पहले सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस के योगदान का सम्मान करने के लिए बोसॉन नाम का इस्तेमाल किया।
सतेंद्रनाथ बोस उपलब्धियां
• विश्व परिचय, रवींद्रनाथ टैगोर का विज्ञान का एकमात्र काम, 1937 में सत्येंद्र नाथ बोस को समर्पित किया गया था।
•भारत सरकार ने 1954 में बोस को पद्म विभूषण की उपाधि से सम्मानित किया।
• उन्हें 1959 में एक विद्वान के लिए देश का सर्वोच्च सम्मान मिला जब उन्हें राष्ट्रीय प्रोफेसर नामित किया गया, इस पद पर उन्होंने 15 वर्षों तक काम किया।
•एस.एन. बोस नेशनल सेंटर फॉर बेसिक साइंसेज की स्थापना साल्ट लेक, कलकत्ता में 1986 में सतेंद्रनाथ बोस के सम्मान में भारत सरकार की संसद द्वारा पारित एक कानून द्वारा की गई थी।
बोस वैज्ञानिक और औद्योगिक अनुसंधान परिषद के सलाहकार बने।
• उन्होंने राष्ट्रीय विज्ञान संस्थान और भारतीय भौतिक समाज के अध्यक्ष के रूप में कार्य किया। इसके अलावा उन्हें भारतीय विज्ञान कांग्रेस के महासचिव के रूप में चुना गया था।
• वे भारतीय सांख्यिकी संस्थान के उपाध्यक्ष और तत्कालीन अध्यक्ष थे। उन्हें 1958 में ब्रिटिश रॉयल सोसाइटी के फेलो के रूप में भर्ती कराया गया था।
Satyendra Nath Bose- FAQs
Q. Why Satyendra Nath Bose is famous?
Satyendra Nath Bose was a well-known Bengali-Indian physicist and brilliant mathematician best known for developing the Bose-Einstein condensate alongside Albert Einstein and serving as the inspiration for the boson particle.
Q. What are the greatest achievements of S.N.Bose?
•He served as the National Institute of Science’s and the Indian Physical Society’s president. Also, he was elected as the Indian Science Congress’ general president.
• He was Vice President and then President of the Indian Statistical Institute. He was admitted as a Fellow of the British Royal Society in 1958.
• He received the Padma Vibhushan, the country of India’s second-highest civilian honour, bestowed by the Government of India, in 1954 for his work in theoretical physics.
Q. In which year was S.N. Bose National Centre established?
The S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences was established in Salt Lake, Calcutta, in 1986 by a law passed by the Indian government’s parliament in honour of Satendranath bose
Q. Were bosons named after Bose?
Yes. The word “boson” is named after S.N. Not because we discovered bosons. Nobel Prize-winning physicist Paul Dirac named it to honour Bose’s contribution to his Einsteinian statistics.









 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














