What is Semiconductor?
Semiconductors are an essential component of electronic devices. Semiconductors are used extensively everywhere, from tiny watches to mobile phones and smartphones, digital cameras, televisions, washing machines, refrigerators, and LED lights. A semiconductor is a substance that conducts electricity more than an insulator but less than a pure conductor. As a result, Semiconductors are the perfect medium for controlling electrical current. In this article we are going to discover more about semiconductors, its definition, examples, Uses, Types, and Devices, Let’s Start Learning
Check: What is Cryogenic Engine
Semiconductor Definition
A semiconductor is a material product typically made of silicon that conducts electricity more than an insulator like glass but less than a pure conductor like copper or aluminum. Semiconductors belong to a class of crystalline solids that have a conductivity between conductors (primarily metals) and non-conductors or insulators (such as ceramics). With the addition of impurities, a process known as doping, their conductivity and other properties can be changed to suit the unique requirements of the electronic component in which they are found.
Semiconductor Examples
Semiconductors are substances with unique electronic properties that fall between insulators and conductors in terms of electrical conductivity. Silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide are three of the most popular semiconductors. Gallium arsenide is utilized in solar cells, laser diodes, and other electronic components, whereas silicon is created into electrical circuits.
Semiconductor Material
solid-state materials can be classified into three categories—insulators, semiconductors, and conductors The properties of Semiconductors can be found in a wide variety of elements and compounds, including:
- Crystalline solids are the most typical semiconducting materials, These include combinations of arsenic, selenium, and tellurium in various ratios, as well as hydrogenated amorphous silicon. These substances have intermediate conductivity, a rapid change in conductivity with temperature, sporadic negative resistance,with more well-known semiconductors.
- Group 14 of the periodic table contains a few pure elements, the two most significant in terms of commerce being silicon and germanium. Due to their capacity to gain or lose electrons simultaneously and having four valence electrons in their outermost shell, silicon and germanium are used efficiently in this application.
- Binary compounds, especially between elements in groups 13 and 15, like gallium arsenide, groups 12 and 16, groups 14 and 16, and between other group-14 elements, such as silicon carbide.
Semiconductor working principle
Semiconductors are substances with conductivity intermediate between that of conductors (often metals) and that of nonconductors or insulators (such as most ceramics). We need to comprehend how electrons arrange themselves within the atom in order to properly comprehend how semiconductors function. Inside an atom, electrons organize themselves into layers known as shells. Among the atom’s shells, the valence shell is the outermost.
These valence shell electrons are responsible for forming bonds with nearby atoms. These bonds are known as covalent bonds. One electron occupies the valence shell in the majority of conductors. On the other hand, semiconductors normally have four electrons in their valence shell.
Therefore, electrons may bond with the valence electrons of neighboring atoms if they share the same valence. Atoms arrange themselves into crystal formations whenever that occurs. These crystals are used to produce the majority of semiconductors.
Types of Semiconductor
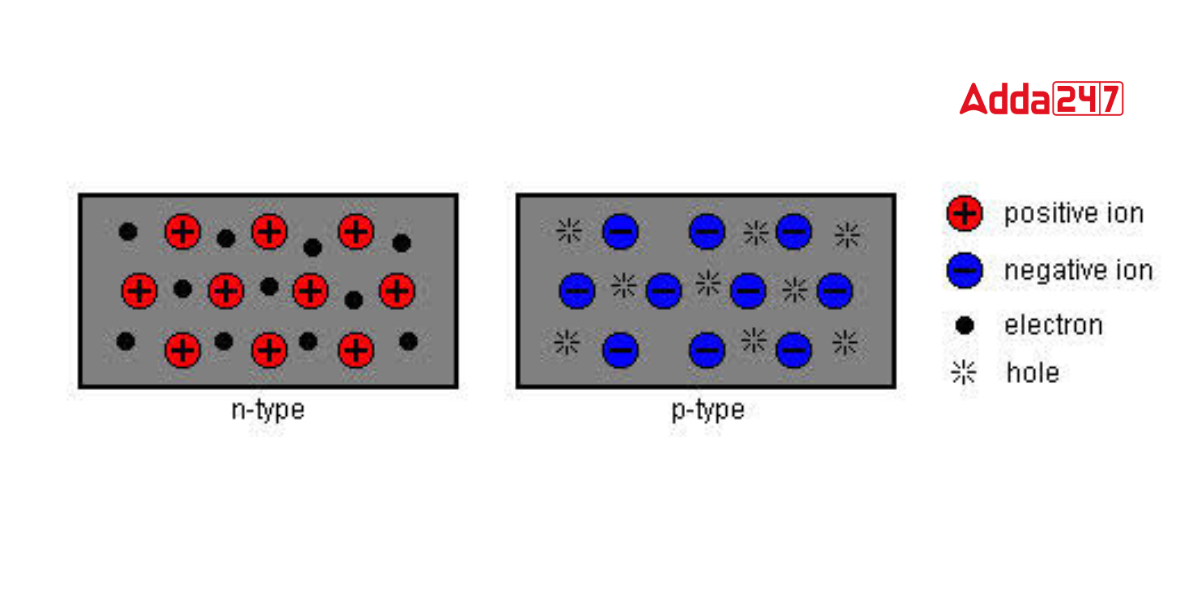
Based on the components that are incorporated with silicon during the “doping” process, semiconductors can be divided into two basic categories.Such as N-type and P-type. To change the characteristics of the final semiconductor, certain “impurities” are added to the crystalline silicon:
Similar to how current flows via a wire, an N-type semiconductor mostly transports current in the form of negatively charged electrons. One or more pentavalent atom-based impurities, such as phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, can be found in an n-type semiconductor.
In a P-type semiconductor, holes are the most common form of current transport. A hole has an electric charge that is positive, the exact opposite of what an electron has. The direction of the flow of holes in a semiconductor material is the exact opposite of the direction of the flow of electrons. The valence layer of a p-type semiconductor contains dopants with five electrons. For this reason, phosphorus, antimony, or arsenic are frequently utilized.
Semiconductor chip
A semiconductor regulates and manages the electric current flow in electronic devices and equipment. As a result, it is a widely used part of electronic chips used in many electrical devices and computing components. All modern electronics and information and communications technology products depend on semiconductor chips to operate properly. They can be thought of as the fundamental components that make up modern cars, household appliances, and necessary medical equipment.
Semiconductor Uses
The use of semiconductors is steadily rising as we utilize digital devices more and more every day. Seconcutors play a key role in every electronic device.The uses of semiconductors are as follows
- Memory chips, which act as temporary data storage and transfer information to and from the brains of computer machines, are made of semiconductors.
- The core logic needed to carry out tasks is included in semiconductors, which act as central processing units.
- Semiconductors are sed in microchips and autonomous vehicles
- utilized in computers, solar panels, calculators, and other electronics.
- The semiconductors are utilised to create the transistors and MOSFETs that operate as switches in electrical circuits.
- Semiconductors are used to create transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs).
- Semiconductors are a component of numerous items, including computers, smartphones, appliances, gaming devices, and medical supplies.
Semiconductor Devices
An electronic component that depends on the electronic characteristics of a semiconductor material is known as a semiconductor device.
Numerous electronic devices now depend on semiconductors, which makes our daily lives possible. Semiconductors play an important role in equipment control in a variety of fields,The development of communications, computing, healthcare, military systems, transportation, clean energy, operating air conditioners at a comfortable room temperature, improving automobile safety, providing laser treatment in cutting-edge medical care, and many more.
Semiconductor -FAQs
Q. Which is a semiconductor?
Semiconductors are substances with conductivity intermediate between that of conductors (often metals) and that of nonconductors or insulators (such as most ceramics). Semiconductors can be made of compounds like gallium arsenide or cadmium selenide or pure elements like silicon or germanium.
Q.Why are semiconductors used?
Semiconductors are used in many electrical circuits. Due to their ability to control the flow of electrons, for instance through the use of a controlling current, In addition, semiconductors have other unique features that are exploited. A solar cell is really constructed of light-sensitive semiconductors.
Q.What are the Examples of Semiconductors?
Silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide are three of the most popular semiconductors. Gallium arsenide is utilized in solar cells, laser diodes, and other electronic components, whereas silicon is created into electrical circuits.








 CBSE Admit Card 2026 Out for Regular, Pr...
CBSE Admit Card 2026 Out for Regular, Pr...
 UP Board 10th Admit Card 2026 Release Da...
UP Board 10th Admit Card 2026 Release Da...
 When Will NEET 2026 Registration Start? ...
When Will NEET 2026 Registration Start? ...














