Stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical tool used for auscultation, or listening to an animal’s or person’s body’s internal sounds. One or two tubes connected to two earpieces and a small disc-shaped resonator that rests against the skin are typical components. The heart, lungs, or intestines can all be heard with a stethoscope, as can the blood flowing through the arteries and veins. It is frequently utilised in conjunction with a manual sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure.
Stethoscope Parts
Following are the parts of a stethoscope:
CHESTPIECE
The device’s core component is a circular piece called the chestpiece, which is also referred to as the head. This is the component of the device that is pressed up against the patient’s body. It is the crucial component of a stethoscope.
DIAPHRAGM
The diaphragm is the chestpiece’s rounded and circular end. You can listen to a larger portion of the patient’s body thanks to its size. It can pick up higher-frequency noises in a sizable portion of the patient.
BELL
The bell refers to the chestpiece’s oblong end. It is perfect for little body parts because, while being smaller than the diaphragm, it can detect lower frequency sounds.
STEM
The component known as the stem joins the stethoscope tubing to the chestpiece. It ensures a secure connection for the best performance and is composed of steel or metal. You can also choose between the bell and the diaphragm.
TUBING
The flexible PVC or rubber pipe that joins the chestpiece to the headset is known as the stethoscope tubing. This stethoscope component is in charge of efficiently transmitting the sound waves captured by the diaphragm and bell to the headset.
HEADSET
The headset is located on the top portion of the stethoscope. It is made of of ear tips, tension springs, and two ear tubes. It makes sure that sound enters the ear canal effectively, causing the least amount of disruption possible.
Stethoscope Types
Acoustic Stethoscope
Acoustic stethoscopes work by transmitting sound from the chest piece to the listener’s ears through hollow tubes filled with air. The chestpiece often has two sides that can be put against the patient to detect sound, such as a bell or a diaphragm (plastic disc) (hollow cup).
Electronic Stethoscope
The low sound levels are overcome with an electronic stethoscope (or stethophone), which electronically amplifies bodily noises. Electronically amplified stethoscopes have a limited range of applications due to the amplification of stethoscope contact artefacts and component cutoffs (frequency response thresholds of electronic stethoscope microphones, pre-amps, amps, and speakers), which amplify mid-range sounds while simultaneously attenuating high- and low-frequency range sounds.
Recording Stethoscope
Some electronic stethoscopes have a direct audio output that can be utilised with an MP3 player or other external recording device. Through the same link, the previously recorded auscultation can be listened to through the stethoscope headphones, enabling additional in-depth study for general research as well as evaluation and consultation for a specific patient’s condition and telemedicine, or remote diagnosis.
Fetal Stethoscope
An acoustic stethoscope shaped like a listening trumpet is known as a foetal stethoscope or fetoscope. To hear the foetus’ heartbeat, it is put against the pregnant woman’s abdomen.
Doppler Stethoscope
The Doppler effect of ultrasound waves reflected from inside organs is measured with a Doppler stethoscope, an electronic instrument. The Doppler effect causes the frequency of the reflected waves to shift, which allows us to perceive motion. The Doppler stethoscope is therefore especially well equipped to deal with moving items like a beating heart.
EAR TUBES
Acoustic tubes and ear tips are joined by ear tubes, which are hollow metal tubes. They offer sound waves the left and right channels to go through. You may modify how tightly your stethoscope is resting on your ears by adjusting the tension spring, which is located between the ear tubes.
EAR TIPS
The components that fit into the ears are the ear tips, which are constructed of silicone or rubber. They sit on the ends of the ear tubes and feature a hole in the centre for sound release. To seal your ears and block out all external noise, ear tips should be both soft and solid.
Stethoscope Uses
- Stethoscope, a medical device used to hear noises made by the body, primarily in the heart or lungs.
- The liver’s size can be determined using a Stethoscope. It can achieve this by calculating the liver’s vertical length starting from the nipple line.
- Doctors may permit patients to use the stethoscope if their hearing is compromised. Doctors can also speak through the chest piece to act as a temporary hearing aid.
- This is another another common application for stethoscopes. In order to hear the heartbeat at the brachial artery, doctors position the stethoscope below the blood pressure cuff that is attached to the upper arm.
- Heart sounds can also be heard with stethoscopes. Doctors are able to determine if a heartbeat “murmurs” or “gallops.”
- It is simple to listen for abnormal bowel sounds, but in cases of paralytic ileus or bowel obstructions, it is essential.
- Congestive heart failure may be present if the heart and the lungs are producing abnormal sounds.
Stethoscope Diagram
Stethoscope
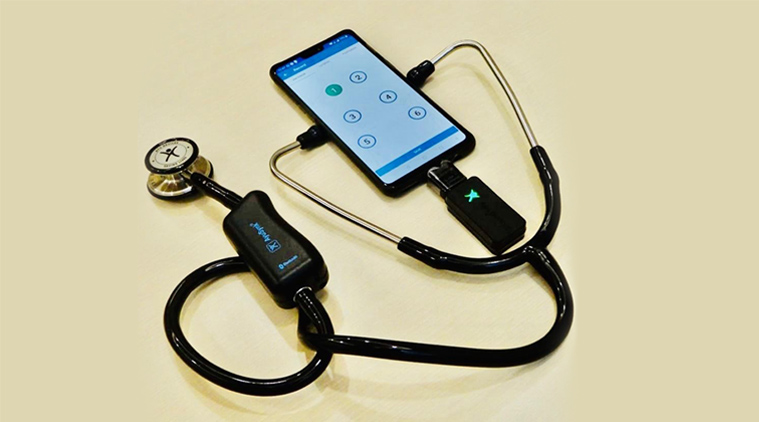
Electronic Stethoscope
Stethoscope: FAQs
What is a stethoscope used for?
In essence, the stethoscope amplifies noises made by the heart, lungs, and bowls inside the body. Doctors listen for interior sounds within certain “normal” frequency ranges. The stethoscope has undergone technological advancements since it was initially used in the medical field, as have the things that doctors listen for.
What are the 3 parts of stethoscope?
It is obvious from the name that this is the portion of the stethoscope that is pressed on the patient’s chest. The diaphragm, the bell, and the stem make up this object. The diaphragm can be one-sided and tunable, two-sided, or two-sided and tunable.
Do 1st year MBBS students get stethoscope?
One of the tools you need to get through and excel in medical school is a stethoscope. Selecting the right stethoscope is essential because you will likely be obliged to acquire one starting in your first or second year.
What are the two types of stethoscope?
Stethoscopes that use sound. By directing more sound waves toward your ears than would otherwise get there, an acoustic stethoscope works. Electronic stethoscopes and Acoustic stethoscopes both are incredible, but Electronic stethoscopes have a certain amount of sound amplification power.
Also Read:
- Parallel Axis Theorem, Proof, Definition, Formula, Examples
- Oscillatory Motion, Meaning, Definition, Example, Diagram
- Planets Name In English And Hindi
- Human Eye Definition, Diagram, Structure
- What Is The Unit Of Current, Resistance And Voltage?
- All About Father Of Genetics- Gregor Mendel
- 7 Rainbow Colours Name In Order, Drawing, Vibgyor Meaning
- What Is The Value Of Root 3?
- Which Is The Ugliest Language In India?









 CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...














