Verbs are frequently employed in English grammar to signify the activity or the moment at which an event occurred. These verbs, known as tenses, occasionally alter their forms to indicate the time of an action, an occurrence, or a situation. There are three basic kinds of tenses: past, present, and future. Each type is further divided into four subcategories: Perfect, Continuous, Simple, and Perfect Continuous. Thus, we shall go into great detail about tense charts with rules and examples in this article.
Tense Chart
A Tense chart is a visual representation of the numerous English tenses. Tense Charts can be used to assist students in learning and understanding the various uses of tenses, as well as in creating accurate and grammatically acceptable phrases. In English, there are three basic tenses: present, past, and future. Each type is further broken down into four tenses: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. The simple tenses are used to express acts that occur on a regular or repetitive basis, or that are generally true. Continuous tenses are used to represent acts that are currently taking place or have taken place over some time. Perfect tenses are used to express acts that have already occurred or that occurred before a specific moment in time. The perfect continuous tenses are used to depict acts that have occurred over time and continue to occur. Tense can be an effective aid for pupils studying English grammar. Tense Charts can assist pupils in seeing the various applications of tenses and understanding how to apply them effectively.
What is Tense?
Tense- The word “tense” in the English language refers to a characteristic of the verb in a sentence. A verb’s tense can be used to describe the exact moment that an event is occurring.
Definition Of Tense
Definition of Tense is according to The Merriam-Webster Dictionary gives a somewhat different definition of the term “tense,” which it defines as “any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb.” It states that “a distinction of form in a verb to represent distinctions of time or duration of the action or state it denotes” is what the word “tense” means.
The Collins Dictionary defines “tense” as “any of the forms of a verb which reveal the time at which an action happened,” while the Cambridge Dictionary defines “tense” as “any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
Tense Chart in English
A Tense Chart is very useful for students. Verbs are frequently used in English grammar to indicate or denote the action or the moment at which an event occurred. These verbs, also known as tenses, may change their forms to indicate the timing of an action, an event, or a situation.
There are three basic kinds of tenses: present, past, and future. The four subtypes of each kind are Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous. As a result, we will go into great length on tense charts with rules and examples in this post.
Tense Chart Importance
The tense chart with rules has very important among the students. The English language’s tenses are frequently regarded as fundamental and essential concepts. Everything seems silly without tenses. You can describe actions that occur at various periods by using multiple tenses. Tense Chart helps you make your context and the facts you’re trying to get across clear. You may also create complex sentence constructions using it. Therefore, you should be familiar with all twelve tenses and their usage if you want to be able to communicate information properly and quickly.
Different Tenses in English
In English grammar, there are three main tenses and they are each further classified into four different forms which sum up to twelve tenses in total. The three tenses in English are:

The four different forms of tense are:
- Simple Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples PDF
Tense Chart PDF with Rules and examples are given below.
Click here to Download Tense Chart PDF
Tenses Chart with Rules and Examples in English
Here is a Tenses Chart with rules, and examples, Formulas are given in the form of a table for a better understanding of tenses.
| TENSE CHART | ||
| TENSE | FORMULA & RULES | EXAMPLE |
| SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE | Subject + base form of the verb/verb+s/es(if needed) + rest of the sentence. | He takes oats for breakfast. |
| SIMPLE PAST TENSE | Subject + past form of the verb (verb 2) + rest of the sentence. | She went for a walk early in the morning. |
| SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE | Subject + helping verb(will) + base form of the verb+ rest of the sentence. | Jeffry will travel around the country in December. |
| PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence | I am watching television. |
| PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + was/were + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence | She was completing her work when her mother came back. |
| FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + will +be + base form of the verb + the rest of the sentence | Children will be going to school. |
| PRESENT PERFECT TENSE | Subject + have/has + past participle (third form of the verb) + rest of the sentence. | I have worked as an educator for two years. |
| PAST PERFECT TENSE | Subject + had + past participle (third form of the verb) + rest of the sentence. | You had worked as a clerk for five years. |
| FUTURE PERFECT TENSE | Subject + Helping verbs (will + have) + third form of the verb + object. | I will have done this work before she comes. |
| PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + have/has + been + present participle (verb+ing) + since/for (if needed) + the rest of the sentence. | You have been telling the truth. |
| PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + had + been + present participle (verb+ing) + since/for (if needed) + the rest of the sentence. | I had been living at my uncle’s place. |
| FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE | Subject + will have + been + present participle (verb+ing) + since/for (if needed) + object. | She will have been waiting here for three hours by seven o’clock. |
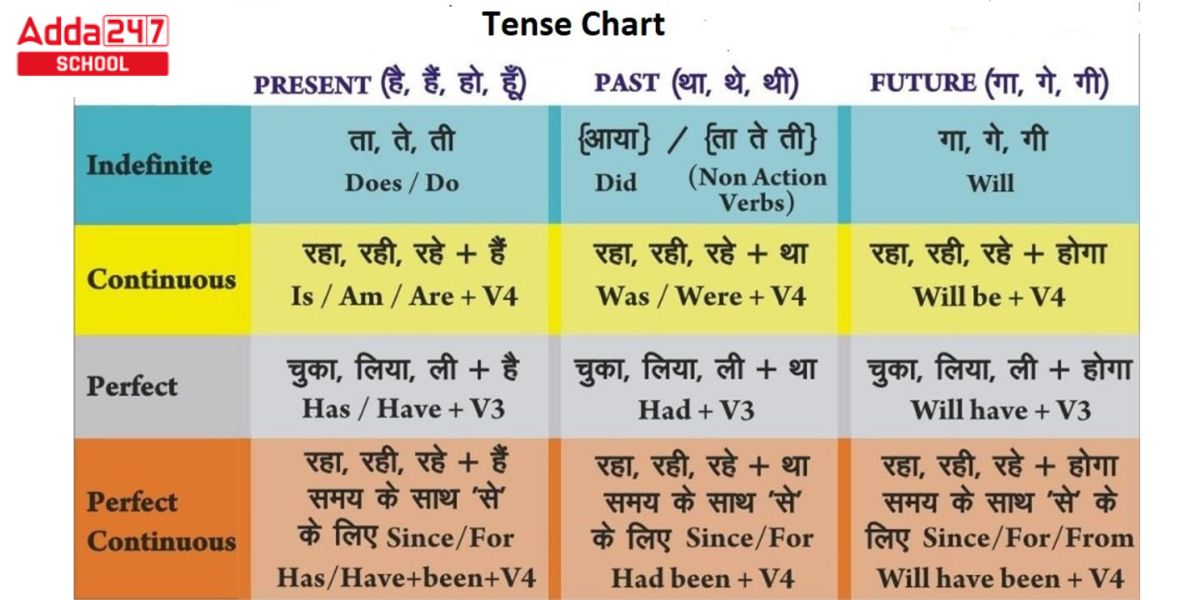
Tenses Chart in Hindi
The tenses Chart in Hindi is given below in this image chart.
Tenses Table
Here in the table below a tense table is given with the three forms of the verb.
|
Tense Table – Different Forms of Verbs
|
||
| Base Form /V1 | Past Simple/ V2 |
Past Participle /V3
|
| be (is, am, are) | was, were | been |
| begin | began | begun |
| bend | bent | bent |
| bet | bet | bet |
| bid | bid | bid |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| blow | blew | blown |
| break | broke | broken |
| burn | burned/burnt | burned/burnt |
| buy | bought | bought |
| catch | caught | caught |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| cut | cut | cut |
| dig | dug | dug |
| dive | dove | dived |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feel | felt | felt |
| fight | fought | fought |
| find | found | found |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven |
| freeze | froze | frozen |
| get | got | gotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| grow | grew | grown |
| hang | hung | hung |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hold | held | held |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| keep | kept | kept |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| leave | left | left |
| lend | lent | lent |
| let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| mean | meant | meant |
| meet | met | met |
| pay | paid | paid |
| put | put | put |
| read | read | read |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| rise | rose | risen |
| see | saw | seen |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sit | sat | sat |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| spend | spent | spent |
| stand | stood | stood |
| swim | swam | swum |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| understand | understood | understood |
| wake | woke | woken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| win | won | won |
| write | wrote | written |
How to learn English Tense Chart?
There are only a few things you need to remember to increase your tenses knowledge and usage. Look at the following details.
- Remain focused. Prepare to relearn and unlearn things.
- Understand the various tenses and how to use them.
- Every tense is constructed according to specific rules. If you make an effort to identify the patterns and understand them, the entire procedure will become much simpler. The continuous tense, for example, requires a supporting verb and the verb in the present participle form (verb+ing’).
- Study as many examples as you can. Practice as much as possible to become familiar with how each tense functions in various situations.
- Naturally, there are some exceptions. You only need to read them carefully and put them into practice. It will take some time, but with your hard work and persistence, you will be able to perfect it.
- One thing in particular should be included in your list of things to do. Watch movies, videos, or even series, read books (anything that interests you and is educational), or both. You will be able to increase your vocabulary and acquire many new sentence patterns that make use of the various tense forms without even knowing of them.
Tenses Chart Project
A tense chart project is a type of project that is used to help students learn about the different tenses in English grammar. The project typically involves creating a chart that shows the different tenses, their uses, and their forms. Students may also be asked to provide examples of sentences in each tense.
There are many different ways to create a tense chart project. Some students may create a simple chart that lists the different tenses and their uses. Others may choose to create a more complex chart that includes examples of sentences in each tense. Some students may even create a creative chart that uses images or symbols to represent the different tenses.
The purpose of a tenses charts project is to help students learn about the different tenses in English grammar. By creating a chart, students can see the different tenses visually. This can help them to understand the uses of the different tenses and to remember their forms.
Here are some tips for creating a tenses chart project:
- Start by brainstorming a list of the different tenses in English grammar.
- Decide on the format of your chart. Will it be a simple list or a more complex chart with examples?
- Gather information about the different tenses. This information can be found in grammar books, online resources, or by asking your teacher.
- Create your chart. Be sure to include the name of the tense, its use, and its form.
- Add examples of sentences in each tense.
- Proofread your chart carefully before you turn it in.
Chart of Tenses Rules
Tenses are an essential aspect of grammar that helps convey the timing of actions and events in a sentence. English has several tenses, and understanding the rules for using them correctly is important for effective communication. Here are some basic rules for using tenses in English:
- Simple Present Tense:
- Used for actions that are habitual, general truths, or regular occurrences.
- Formed with the base form of the verb (e.g., “I eat pizza every Friday”).
- Present Continuous Tense:
- Used for actions happening right now or in the current period.
- Formed with the present tense of “to be” (am, is, are) and the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “I am eating lunch”).
- Simple Past Tense:
- Used for actions that happened and ended in the past.
- Typically formed by adding -ed to regular verbs or using the past form of irregular verbs (e.g., “She walked to school”).
- Past Continuous Tense:
- Used to describe actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past.
- Formed with the past tense of “to be” (was, were) and the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “They were studying all night”).
- Simple Future Tense:
- Used to express actions or events that will happen in the future.
- Often formed using “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb (e.g., “I will call you tomorrow”).
- Future Continuous Tense:
- Used to describe actions that will be ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the future.
- Formed with “will be” or “shall be” followed by the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “They will be working late tonight”).
- Present Perfect Tense:
- Used to describe actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past but have relevance to the present.
- Formed with “have” or “has” and the past participle of the verb (e.g., “She has visited Paris”).
- Past Perfect Tense:
- Used to indicate an action that occurred before another action in the past.
- Formed with “had” and the past participle of the verb (e.g., “He had already finished when I arrived”).
- Future Perfect Tense:
- Used to describe an action that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
- Formed with “will have” or “shall have” and the past participle of the verb (e.g., “By next year, they will have graduated”).
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Used to emphasize the duration or continuity of an action that started in the past and continues into the present.
- Formed with “have been” or “has been” and the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “I have been reading for hours”).
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Used to emphasize the duration of an action that occurred before another action in the past.
- Formed with “had been” and the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “She had been studying for hours before the exam”).
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Used to describe the duration of an action that will continue up to a specific point in the future.
- Formed with “will have been” or “shall have been” and the base form of the verb with -ing (e.g., “By 5 PM, I will have been working for eight hours”).
Remember that these rules provide a general framework for understanding tenses, but there can be exceptions and variations in usage. Mastery of tenses comes with practice and exposure to various contexts in which these tenses are used. Additionally, understanding the time relationships between different actions in a narrative is crucial for choosing the appropriate tense.









 English Poems for Kids of Class 1 to 5, ...
English Poems for Kids of Class 1 to 5, ...
 Most Repeated Questions from Class 10 En...
Most Repeated Questions from Class 10 En...
 Republic Day Speech In English 2025, 26 ...
Republic Day Speech In English 2025, 26 ...














