Theoretical Yield Formula: Our nature constantly performs chemical reactions without our knowledge and whenever a chemical reaction takes place, the concept of theoretical yield formula comes in. When you go for a walk, you are literally walking through a natural lab where hundreds of chemical reactions are happening without you even noticing. The formation of methane gas from cow dung or the formation and degradation of ozone gas in the upper stratosphere, all these are chemical reactions that are constantly taking place. These chemical reactions play an important role in the equilibrium of the world and our universe as a whole. As you now know the ubiquitous nature of chemical reactions, let us now dive deep into the importance of the Theoretical Yield Formula
Theoretical Yield Formula
Theoretical yield formula is used to determine the yield of a particular chemical reaction. Whenever a chemical reaction takes place, some substances are broken down or converted into another substance. A chemical reaction is shown by substance → substance, which is also known as a chemical equation. The left side represents the substances before the chemical reaction while the right side of the arrow are the substances formed after the chemical reaction. Let us understand the technical terms for these substances.
What is a Reactant?
Reactant are those substances that are present before the chemical reaction takes place. It is shown on the left hand side of the chemical equation.
What is a Product?
The substances formed after the chemical reaction takes place are known as products. The product formed is shown on the right hand side of the chemical equation.
Reagent: A reagent, also known by the name analytical reagent, is a compound supplied to a reaction to trigger a chemical reaction or check to see whether one happens.
Limiting Reagent: The reactant that is totally consumed during a reaction is known as the limiting reagent. In other words, the limiting reagent decides when the chemical process comes to an end. So, the amount of produce heavily depends on the quantity of the limiting reagent.
Theoretical Yield Formula is used to find the quantity of the Product, that is present on the right hand side of the chemical equation.
What is Theoretical Yield?
Theoretical Yield is the quantity of product formed by the given quantity of reactants. In other words, the highest amount of product you anticipate a chemical reaction could produce is referred to as the theoretical yield. It must be noted that the theoretical yield gives the ideal maximum quantity of product that a chemical reaction can produce, which differs from the actual yield produced in the real/laboratory conditions. The theoretical yield formula gives the ideal maximum quantity of product that a chemical reaction can produce. It is always better to know how much product can be formed by the given reactant, especially for important chemical reactions. Theoretical yield formula plays a greater role at industrial scale where an essential component of cost control is examining the quantity of a product produced in every given reaction.
Theoretical Yield Formula
In chemistry, the amount of product that can be produced by the given quantity of reactants in an ideal condition is called the theoretical yield formula.
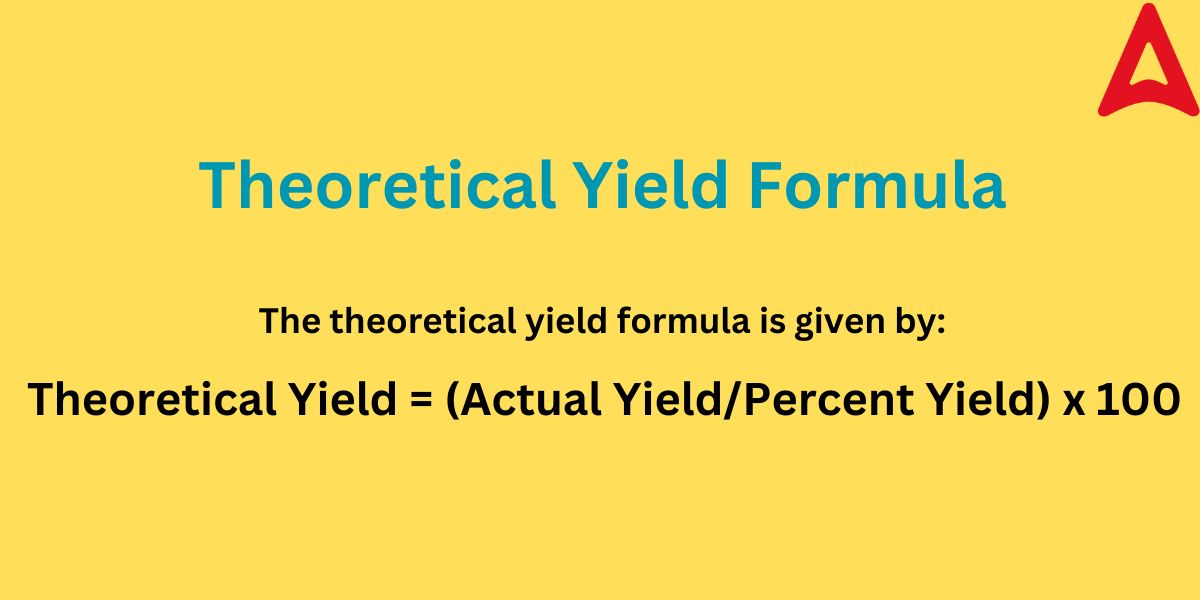
The Theoretical Yield Formula is given by:
Theoretical Yield = (Actual Yield/Percent Yield) x 100
where, Actual Yield = It is the actual amount of product formed in a chemical reaction
The theoretical yield formula can be used to find the yield of the product both in grams and moles.
How to Calculate Theoretical Yield using Theoretical Yield Formula
The theoretical yield formula is used to determine the theoretical yield of the product in a particular reaction. To calculate the theoretical yield, first you will have to balance the equation and find the limiting reagent. The steps to calculate the theoretical yield using the theoretical yield formula is given below:
Step 1: Balance the given chemical equation
Balancing a chemical equation means the number of atoms of elements involved in a chemical reaction must be equal on both sides of the chemical equation. In other words, the number of atoms of elements in the reactant and product side must be same.
For example: H2 + O2 → H2O is an unbalanced reaction
After balancing, we get
2H2 + O2 → H2O
Step 2: Find the Limiting Reagent of the Reaction
As discussed above, a limiting reagent is the reactant that limits or halts the chemical reaction. The limiting reactant can be found by converting the molar mass of each reactant into moles. After that, you must find the molar ratio to find the limiting reagent. The molar ratio will give the idea about which reactant is the limiting reagent.
Step 3: Find out and Compare the ratio of molecules
After finding the limiting reagent, compare the ratio of molecules in product and reactant. Convert into the ideal ratio as per the limiting reagent moles. This will help you to obtain the quantity of product that will be formed.
Step 4: Multiply the limiting reagent’s quantity
In this last step, you will have to multiply the moles ratio by the limiting reagent’s quantity. It must be noted that the limiting reagent’s quantity here must be in the form of moles as calculated in the 2nd step. This will give you the theoretical yield in moles.
Theoretical Yield from Limiting Reagent
The theoretical yield is found using the theoretical yield formula using the moles of the limiting reagent. We can find the theoretical yield by finding out the limiting reagent in the reaction. By converting the masses of all the molecules in moles, one can then form mole ratio. By comparing the mole ration with the limiting reagent, one can find the number of moles that the product will form. Hence, by multiplying the limiting reagent’s mole quantity to the product, one can find the theoretical yield in moles from the limiting reagent.
Theoretical Yield in Grams using Theoretical Yield Formula
The theoretical yield of a product can be found in grams too. In the theoretical yield calculation step, we got the theoretical yield in moles. After that step, if we multiply the obtained moles of product with their molar mass, then we obtain the theoretical yield in grams. The molar mass is defined as the mass of 1 mole of that particular compound.
For example, the molar mass of H2O = 18 gram
So let us say we obtain 1.5 moles of H2O from the equation H2 + O2 → H2O
So the theoretical yield in grams will be 1.5 x 18 = 27 grams
Theoretical Yield Formula in Organic Chemistry
The theoretical yield formula to calculate the theoretical yield remains same in the organic chemistry. Just observe the products that can be formed from the given chemical reactions. After that, one should follow the same step of balancing the equation, and converting the given weight into moles to find the limiting reagent. After than, multiply all the product with the given moles of the limiting reagent. One can then convert the theoretical yield in grams using the molar mass concept. Thus, the theoretical yield formula can be used to find the theoretical yield of a product in the organic chemistry just like in any other branch of chemistry.
Theoretical Yield Formula Solved Examples
Some of the solved questions on the theoretical yield formula is given below. These solved examples will help students understand this topic in a better way. This topic is essential for those students who have opted for the chemistry subject in Class 11 and Class 12.
Example 1: According to the given chemical equation: Mg + O2→ MgO2, magnesium and oxygen react to produce magnesium oxide. if the reaction uses 1.3 g of magnesium. What is the magnesium oxide theoretical yield in grammes? Mg has a molecular weight of 24.3 g/mol, and MgO has a molecular weight of 40.3 g/mol.
Solution: As we have been given the equation: Mg + O2 →MgO2
First of all, we will balance the equation
2Mg + 2O2 → 2MgO2
Given the weight of Mg = 1.3 gram
Molar weight of Mg = 24.3
Molar weight of MgO = 40.3
Determining the quantity of the limiting reactant in the given chemical equation by calculating the number of moles.
As, number of moles = given mass/molar mass
Number of moles of Mg = 1.3/24.3
Number of moles of MgO = produced weight of MgO/40.3
or, Number of moles of MgO = Theoretical yield of MgO/40.3
Using the limiting reactant (Mg) mole ratio, we get
1.3/24.3 = Theoretical yield of MgO/40.3
or, Theoretical yield of MgO = (1.3 x 40.3)/24.3
Theoretical yield of MgO = 2.16 gram
Example 2: Determine the theoretical yield for producing sodium chloride from 375 g of reactants. A lab uses 417g of refined product and 375g of raw material to manufacture 375g of sodium chloride. It is stated that the yield percentage is 94.1%.
Solution: We have been given the actual yield = 417 gram
yield percentage = 94.1%
we have to find the theoretical yield
As we known, Theoretical Yield = (Actual Yield/Percent Yield) x 100
So, Theoretical yield = (417/94.1) x 100
Hence, Theoretical yield = 443 gram









 CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26...
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26...
 CLAT Exam Pattern 2026 – Updated Paper...
CLAT Exam Pattern 2026 – Updated Paper...
 CBSE Class 11 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 PDF...
CBSE Class 11 Maths Syllabus 2025-26 PDF...












