Valency of Carbon
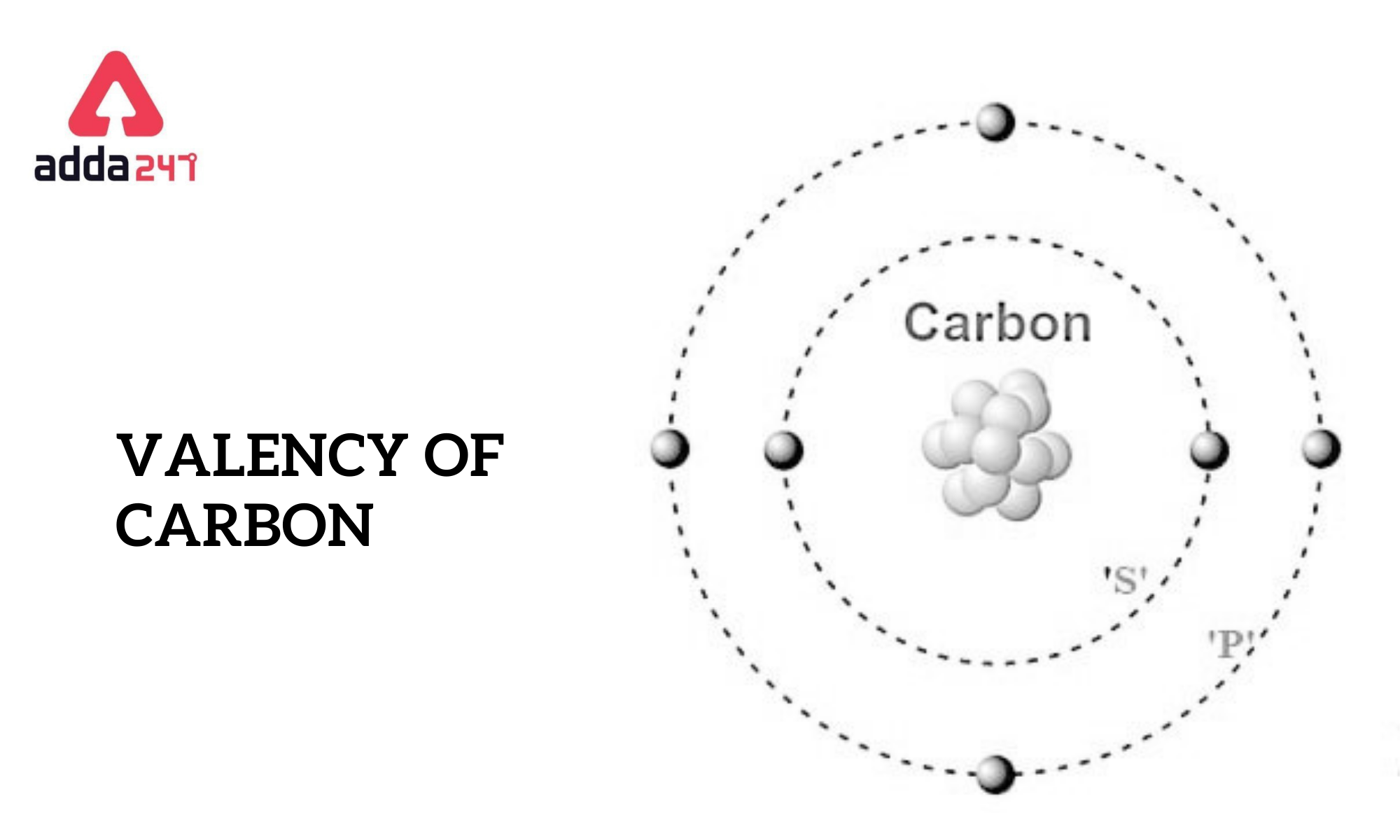
Valency of carbon is 4. The valency of an element refers to how well it can combine with other atoms to form chemical compounds or molecules. Carbon contains four valence electrons and has a valence of four in this situation. Carbon forms four covalent bonds and shares its valence electrons to achieve the noble gas configuration. The valency of Carbon is four. A carbon’s exterior electronic configuration is 2S2 and 2P2.
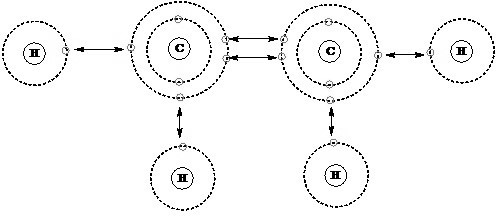
Carbon Valency
The valency of carbon (C) is typically four. Valency refers to the combined capacity of an element, specifically the number of electrons an atom can gain, lose, or share to form chemical bonds with other atoms. Carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost shell, and it strives to achieve a stable electron configuration by sharing these electrons with other atoms. Carbon commonly forms covalent bonds, where carbon valency shares its four valence electrons with other atoms, allowing it to form stable compounds.
The ability of carbon to form strong covalent bonds and its valency of four make it a versatile element, enabling it to form a wide variety of compounds, including organic compounds found in living organisms.
Carbon Valence Electrons
Carbon (C) has four valence electrons.
The valence electrons of an atom are the electrons in the outermost energy level, also known as the valence shell. In the case of carbon, it is located in Group 14 of the periodic table, which means it has four electrons in its outermost shell. These valence electrons are the ones involved in forming chemical bonds with other atoms.
Carbon has the electron configuration 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2. The 2s and 2p orbitals together hold four valence electrons. Carbon can form four covalent bonds by sharing these four valence electrons with other atoms, allowing it to form a wide range of stable compounds.
The ability of carbon to form multiple bonds and its four valence electrons make it a key element in the chemistry of life and the formation of organic compounds.
Valency of C
Valency of C is 4. This means that in most organic compounds, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other carbon atoms.
Valency of CO
The valency of carbon monoxide (CO) is two.
Valency refers to the combining capacity of an element or compound, specifically the number of electrons it can gain, lose, or share to form chemical bonds with other atoms or molecules.
In the case of carbon monoxide (CO), carbon has a valency of four as it contributes four valence electrons. Oxygen, on the other hand, has a valency of two as it needs to gain two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
When carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon monoxide (CO), carbon shares two electrons with oxygen, and oxygen gains two electrons from carbon to complete its valence shell. This sharing of electrons results in a double bond between carbon and oxygen and satisfies the valency requirements of both elements.
So, in the compound carbon monoxide (CO), the valency of carbon is two, and the valency of oxygen is also two.
What is the Valency of Carbon by Hybridisation?
Hybridization is the process of mixing atomic orbitals to create new hybrid orbitals that are suitable for representing bonding qualities. Apart from being an important aspect of valence bond theory, hybridized orbitals are useful in characterizing the form of molecular orbitals. The atomic orbitals that contribute to hybridization are referred to as hybrid. For example, one s-orbital and three p-orbitals on the carbon atom form a set of sp3 orbitals in methane, whose chemical formula is CH4. The four hydrogen atoms at the vertices of a typical tetrahedron are targeted by these orbitals.
A double bond exists between the carbon atoms in ethene(C2H4). sp2 hybridizes the carbon here. The 2s orbital mingles with two of the three 2p orbitals available in sp2 hybridization, resulting in a total of 3sp2 orbitals with one remaining p-orbital. Two carbon atoms form a sigma bond by overlaying two sp2 orbitals in ethane, and each carbon atom forms two covalent connections with hydrogen by overlapping all s-sp2 with 120o angles. A 2p-2p overlap forms the pi connection between the carbon atoms. The hydrogen-carbon bonds are of similar length and strength, which is supported by experimental evidence.
Valency of Carbon and its Compounds Alkane
Single bonds exist between the carbon atoms of an alkane. Ethane C2H6 is the simplest alkane with more than one carbon atom. Each carbon is coupled with three hydrogens and is held together by a single bond. As a result, each carbon in the alkane has one carbon bond and three hydrogen bonds, giving it a total valency of four.
Valency of Carbon In Alkyne
The carbon atoms in an alkyne have three bonds between them. Ethyne or acetylene C2H2 is an alkyne molecule with more than one carbon atom. The carbons are joined in a triple bond, with one hydrogen linked to each carbon. As a result, each carbon in the alkyne has three carbon bonds and one hydrogen bond, giving it a total valency of four.
Valency of Carbon and its Compounds Alkene
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with the chemical formula CnH2n that contain carbon-carbon double bonds. Cycloalkanes have the same molecular formula as this. Alkenes are named in the same way that alkanes are, with the exception that the suffix is now -ene. The carbons are double bonded, with two hydrogens bound to each of them. As a result, each carbon in the alkyne has two bonds with carbon and two bonds with hydrogen, giving it a total valency of four.
Related Post:
- Moment Of Inertia- Definition, Formula, Factors, Example, Unit
- Magnetic Flux- Definition, Density, Formula, SI Unit
- RRB NTPC Full Form In Railways
- Kolbe Electrolysis Reaction- Definition, Mechanism








 CUET UG 2026 Online Registration Started...
CUET UG 2026 Online Registration Started...
 CUET 2026 Free Batches Launched by CUET ...
CUET 2026 Free Batches Launched by CUET ...
 CBSE Date Sheet 2026 for Class 10 & ...
CBSE Date Sheet 2026 for Class 10 & ...














