Vegetative Propagation Meaning
Vegetative propagation meaning is, Vegetative Propagation, also known as vegetative reproduction, is any asexual mode of plant reproduction in which a new plant develops from a cutting, fragment, or other reproductive organs of the parent plant. For example, bud, tuber, corm, etc. are the organ units of plants. In this article, we go through vegetative propagation in plants, their types, and examples in detail.
Define Vegetative Propagation for Class 10
The process of asexual reproduction in which a part or part of the plant body is separated from the parent plant and produces a new plant is called Vegetative propagation. The reproductive units are called propagules. Many clones are created in a very short period of time in the process of organ reproduction. Purity, resistance, good race, variety, etc. are preserved in this type of breeding. Crops tend to multiply and grow quickly.
Vegetative Propagation Meaning in Hindi
Vegetative propagation in hindi: अलैंगिक प्रजनन की वह प्रक्रिया जिसमें पौधे के शरीर का एक भाग या भाग मूल पौधे से अलग हो जाता है और एक नया पौधा पैदा करता है, वनस्पति प्रसार कहलाता है। प्रजनन इकाइयों को प्रोपेगुल्स कहा जाता है। अंग प्रजनन की प्रक्रिया में बहुत कम समय में कई क्लोन बनाए जाते हैं। पवित्रता, प्रतिरोध, अच्छी जाति और विविधता आदि। इस प्रकार के प्रजनन में संरक्षित हैं। फसलें तेजी से बढ़ती और बढ़ती हैं।
Vegetative Propagation in Plants
3 This might occur as a result of specific vegetative plant components fragmenting and regenerating. Vegetative propagation occurs in plants in two methods – Natural Vegetative propagation and Artificial Vegetative propagation. Let’s learn about those types with detailed explanations.
Natural Vegetative propagation
Asexual reproduction in which a part or part of the plant body is separated from the parent plant and produces a new plant in a natural way without any external interference is known as Natural Vegetative propagation.
Rhizomes, stems, bulbs, runners, and tubers are the units of the parent plant from which a new plant grows by natural vegetative propagation.
Natural vegetative reproduction is of the following types—
Vegetative propagation by Roots
The main root and adventitious roots of the plant participate in the Vegetative propagation. The main root of some plants produces adventitious buds, from which new plants grow, eg Dalbergia (Sheesham), Guava, Albizia, etc. Some new plant grows from the ectopic bud arising from the fleshy root, such as Sweet potato, Tapioca, Dahlia, Asparagus, etc.
Vegetative propagation by stem
Different types of different plants are participating in Vegetative propagation as follows
Aerial stem
The stems of Opuntia plants are thick and succulent and form phylloclades. Each segment of such a stem separates from the mother body to give rise to a new plant. Acacia (sugar cane) roots are formed from the plant phases. A new plant will emerge from the plant when the plant is planted in the soil with the adventitious root. Each part of such a stem helps in the creation of a new plant.
Underground stems
There are different kinds of underground stems that are responsible for vegetative propagation as follows.
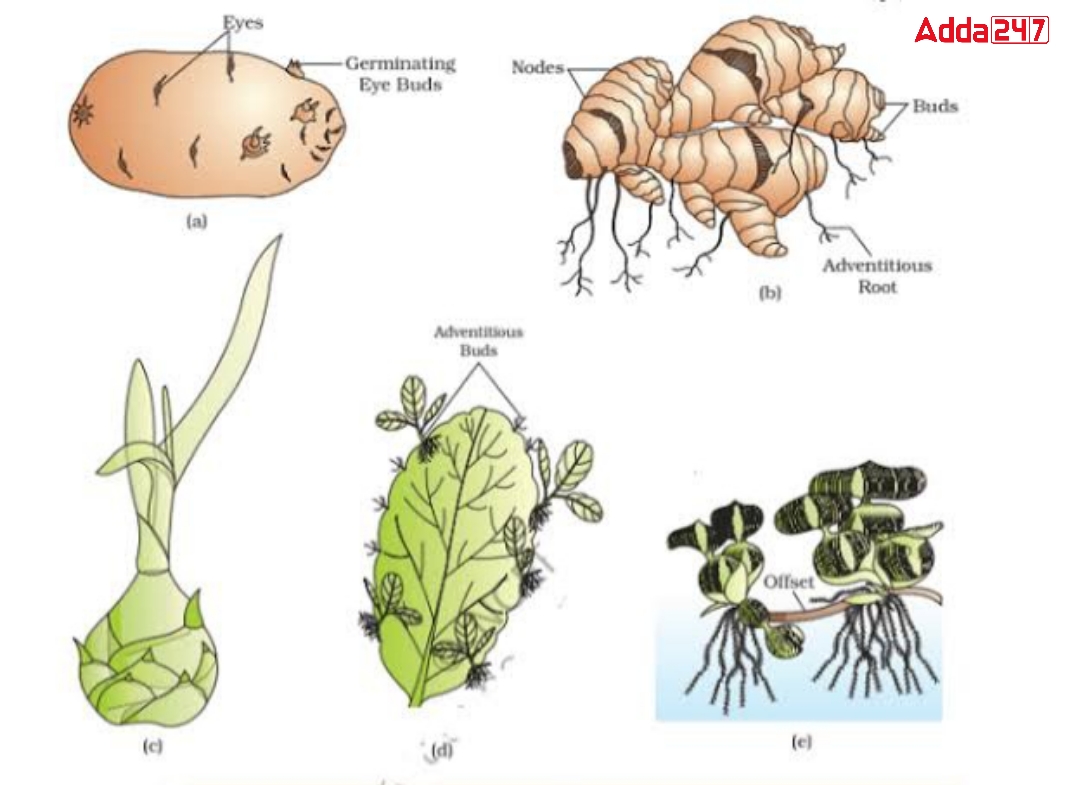
1. Tuber: A new plant is formed from the bud located in the round potato. If the potato bud is cut and planted in the ground, a new plant is born.
2. Bulbs: Bulbs of garlic, onion, etc. have small disk-like compressed pods. The stem has one or more buds. New plants grow from these buds.
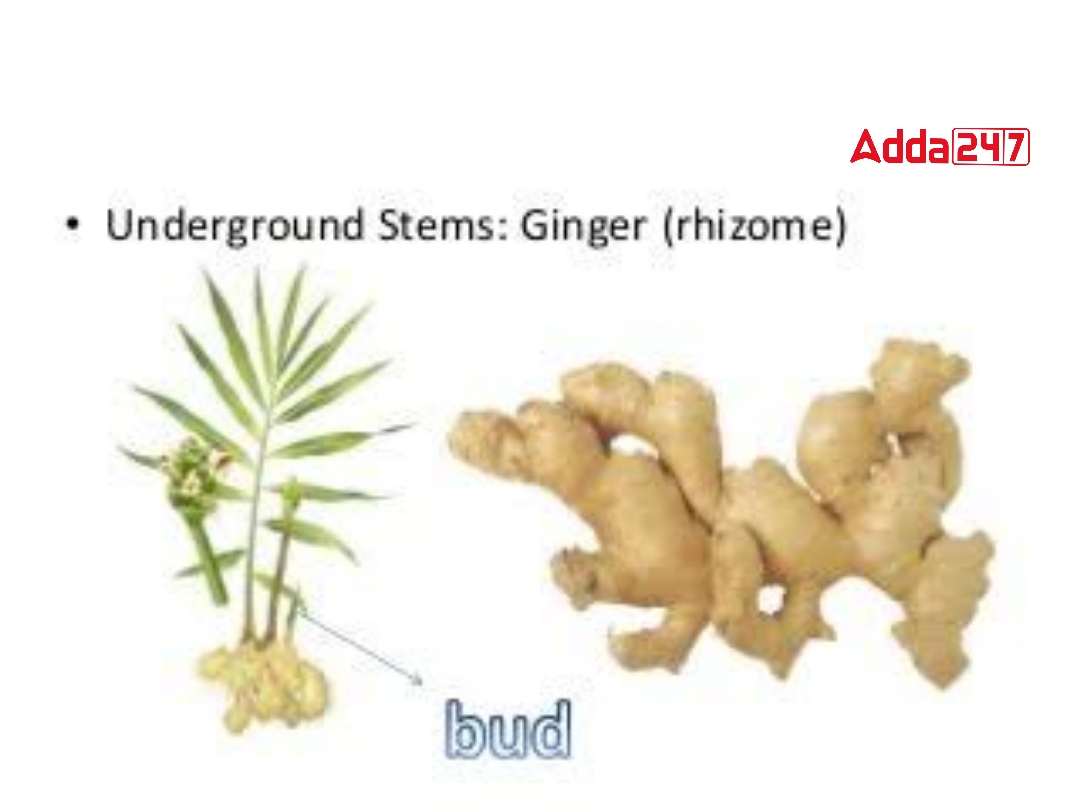

3. Corms: It is a type of underground stem. Orbital buds are formed in their cyclic phase. From these axillary buds, the shoot is formed. Amorphophallus, Colocasia, etc. are produced from axillary buds.
4. Rhizome: Rhizome is a type of underground stem. In such trunks the tree stores food for the future. In the tip there are buds and in the bract cells are the orbital buds. New plants grow from these buds. This type of organ growth is seen in plants like ginger, turmeric, banana, etc.
5. Suckers: From the base of the aerial stem grow a kind of narrow and long underground branch. After this branch grows some distance it separates from the parent body and forms a new trunk. Durbaghas, chandramallikas, are such plants where Vegetative reproduction is found.
Leaves
Some plant leaves leave the parent plant and grow into a new plant. Begonia (Begonia), petioles form axillary buds on the edges of the leaves.

Bulbil
It is a kind of multicellular thick bud called bulbil. Isolated from bulbs (Dioscorea), Globba, Agave, etc. The flower buds play a role in vegetative reproduction.
Artificial Vegetative propagation
Artificial vegetative reproduction is an asexual reproduction method in which a portion of the parent plant’s body is removed to create a new plant that can be used to meet human needs. Artificial Vegetative propagation can be performed by following methods
Cutting
Cutting the root, trunk, leaves, and other parts of some plant species from the main plant body. The cuttings will take root and sprout when placed in the soil. For rooting in the cutting procedure, chemicals like IBA (Indol butyric acid) and NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid) are used.
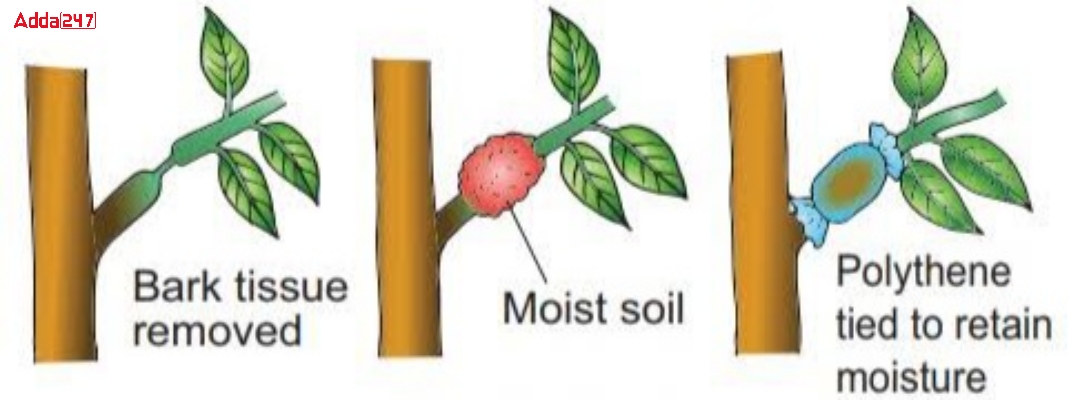
Layering
In this instance, a plant branch has been bent and bound with sand. At the same time, the water must occasionally be emptied. The stage of the branch that is in the soil at a particular period is where abdominal roots are created. After that, the branch with the root is cut off and firmly planted in the ground.
Grafting
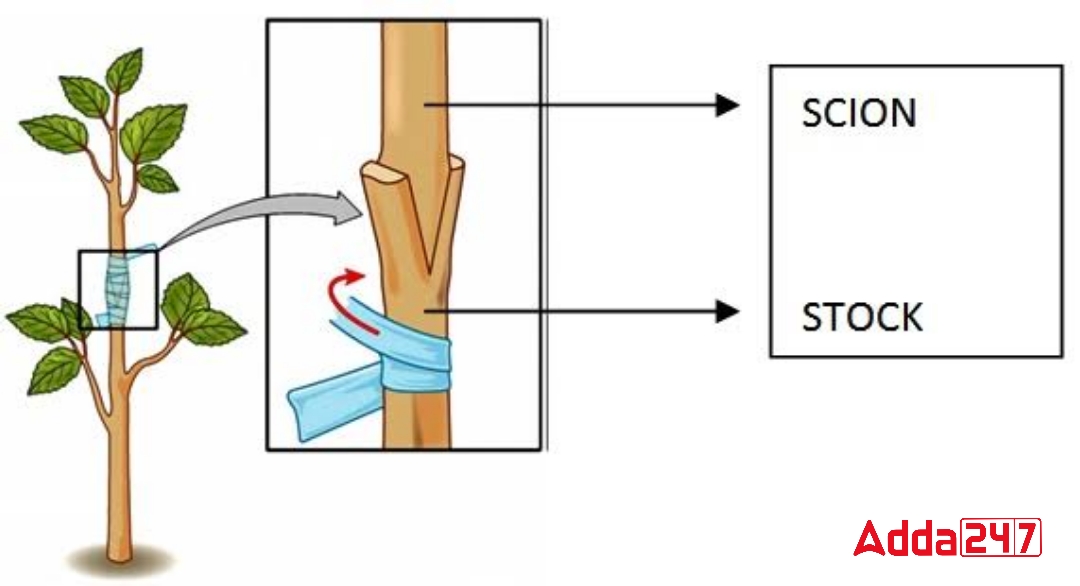
Grafting is the process of fusing the branches of two distinct plants belonging to the same species. In gardening, calculations of this kind are common. Plants like guava, mango, lemon, apple, etc. are grafted. grafting is the joining of a branch from one species of a plant to a branch from another species of that same genus. the tree’s root that the bundle is linked to. It is known as the stock, and the branch of the neighboring tree that is connected to the stock is known as the scion. The cambium is pressed up against the banana at the joint of the two branches. The two branches are then firmly linked together using a rope. Both of the branches are joined after a few days. Pairing the two branches will allow you to sprinkle auxin propensity on the section that was previously clipped.
Tissue culture
Tissue culture is the most advanced vegetative reproduction. In order to create a new plant, parts of plants are cultivated in a lab environment. This Tissue culture method aids in boosting the number of rare and endangered plant species that cannot flourish in their natural habitats.
Vegetative Propagation Examples
Here are some examples of plants that show vegetative propagation –
| Methods | Examples |
| Vegetative Propagation By Root | Dalbergia (Sheesham), Guava, Albizia,sweet potato etc |
| Vegetative Propagation By stem | Acacia (sugar cane),Amorphophallus |
| Vegetative Propagation By leaves | Begonia and Bryophyllum |
| Vegetative Propagation By Bulbs | garlic, onion, etc. |
| Vegatative Propagation By Ribozome | ginger, turmeric, banana, etc. |
Advantages of Vegetative propagation
The advantages of Vegetative reproduction are pointed below
1. The process of vegetative propagation is simpler, quicker, and less expensive.
2. In this process, The purity and the characteristics are intact in the new plant.
3. Seedless plants can be grown using this method.
4. The plants created using this technique are exact replicas of the parent plant and have no variations.
The disadvantage of Vegetative propagation
There are certain disadvantages of Vegetative reproduction those are-
1. In this process, no new characters are introduced to the new plants.
2. Very skilled professionals are required for artificial Vegetative propagation.
3.Compared to seed-propagated plants, vegetative propagated plants have a shorter lifespan and are smaller.
Vegetative Propagation for Class 10 Students
Vegetative propagation is a method of reproducing plants in which new plants are produced from parts of the parent plant, such as roots, stems, or leaves. Some of the key facts about vegetative propagation include:
- It is a natural process: Vegetative propagation is a natural process that occurs in many plants, including trees, shrubs, and herbaceous plants.
- No involvement of seeds: Vegetative propagation does not involve seeds, and therefore the new plants will be genetically identical to the parent plant.
- Types: There are several different types of vegetative propagation, including rooting stem cuttings, layering, and dividing rhizomes or bulbs.
- Advantages: Vegetative propagation has several advantages over seed propagation, including the ability to reproduce plants that do not produce viable seeds, the ability to reproduce plants quickly and easily, and the ability to maintain specific genetic characteristics.
- Disadvantages: Some of the disadvantages of vegetative propagation include the lack of genetic diversity, increased vulnerability to disease, and the need for specialized equipment or techniques.
- Applications: Vegetative propagation is widely used in horticulture and agriculture for the production of plants such as fruit trees, ornamental plants, and lawn grasses.
- Commercial use: Vegetative propagation is also used commercially for the production of clones of plants that are desirable for their disease resistance, hardiness, or other desirable characteristics.
- Methods: Different methods are used for vegetative propagation such as grafting, layering, cutting, and tissue culture.









 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














