What are isobars?- Alfred Walter Stewart proposed the word “isobars” for nuclides in 1918. It comes from the Greek words. Isos means “equal,” and baros means “weight.”
Isobars are elements with different chemical properties but the same physical properties. As a result, we can define isobars as elements with various atomic numbers but the same mass number. Because of the difference in the number of electrons, their chemical properties are different. The atomic mass is the same, but the atomic number is different. This is because the discrepancy in the number of nucleons is compensated by an increased number of neutrons.
Read About: Largest Solar Floating plant in India.
What are Isotopes and Isobars?
If two neighboring elements on the periodic table have isotopes with the same mass number, at least one of these isobars must be a radionuclide, according to the Mattauch isobar rule. When three isobars with sequential elements are present, branching decay of the middle isobar can occur if the first and last remain stable.
There are no observationally stable isobars for mass numbers 5, 8, 147, 151, or 209 and above. However, there are two observationally stable isobars for 36, 40, 46, 50, 54, 58, 64, 70, 74, 80, 84, 86, 92, 94, 96, 98, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 120, 122, 123, 124, 126, 132, 134, 136, 138, 142, 154, 156, 158, 160, 16.
There are no stable nuclides with the same mass number as each other, and no stable nuclides with the mass numbers 5, 8, 143–155, 160–162, or 165 exist. The beta-decay stable nuclides for these mass numbers can, theoretically, undergo alpha decay.
Electrons, protons, and neutrons make up atoms. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, with electrons revolving around it. Atomic mass is equal to the number of protons multiplied by the number of neutrons, while the atomic number is equal to the number of protons multiplied by the number of neutrons multiplied by the number of protons in an element remains constant, whereas the number of neutrons varies.
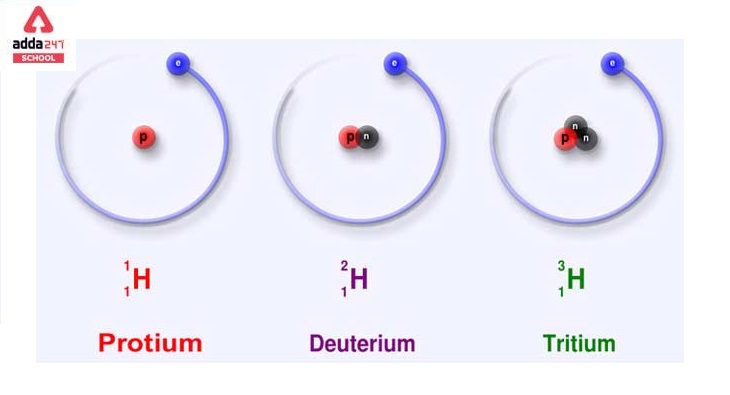
Isotopes are atoms that have different numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons. We can deduce from the foregoing definitions of atomic mass and atomic number that isotopes are elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Read About: Permanent Tissue
What is Isobars in Hindi?
अल्फ्रेड वाल्टर स्टीवर्ट ने 1918 में न्यूक्लाइड्स के लिए “आइसोबार्स” शब्द का प्रस्ताव रखा। यह ग्रीक शब्द आइसोस से आया है, जिसका अर्थ है “बराबर,” और बारोस, जिसका अर्थ है “वजन।”
आइसोबार ऐसे तत्व होते हैं जिनमें विभिन्न रासायनिक गुण होते हैं लेकिन भौतिक गुण समान होते हैं। नतीजतन, हम आइसोबार को विभिन्न परमाणु संख्या वाले तत्वों के रूप में परिभाषित कर सकते हैं लेकिन समान द्रव्यमान संख्या। इलेक्ट्रॉनों की संख्या में अंतर के कारण, उनके रासायनिक गुण भिन्न होते हैं। परमाणु द्रव्यमान समान है, लेकिन परमाणु क्रमांक भिन्न है। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि न्यूक्लियंस की संख्या में विसंगति की भरपाई न्यूट्रॉन की बढ़ी हुई संख्या से होती है।
यदि आवर्त सारणी पर दो पड़ोसी तत्वों में समान द्रव्यमान संख्या वाले समस्थानिक हैं, तो मैटौच आइसोबार नियम के अनुसार, इनमें से कम से कम एक आइसोबार रेडियोन्यूक्लाइड होना चाहिए। जब अनुक्रमिक तत्वों के साथ तीन आइसोबार मौजूद होते हैं, तो मध्य समस्थानिक का शाखा क्षय हो सकता है यदि पहला और अंतिम स्थिर रहता है।
द्रव्यमान संख्या 5, 8, 147, 151 या 209 और उससे अधिक के लिए कोई अवलोकनीय रूप से स्थिर आइसोबार नहीं हैं। हालांकि, 36, 40, 46, 50, 54, 58, 64, 70, 74, 80, 84, 86, 92, 94, 96, 98, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 120, 122, 123, 124, 126, 132, 134, 136, 138, 142, 154, 156, 158, 160, 16 के लिए दो अवलोकनीय रूप से स्थिर आइसोबार हैं।
एक दूसरे के समान द्रव्यमान संख्या वाले कोई स्थिर न्यूक्लाइड नहीं हैं, और द्रव्यमान संख्या 5, 8, 143–155, 160–162, या 165 के साथ कोई स्थिर न्यूक्लाइड मौजूद नहीं है। इन द्रव्यमान संख्याओं के लिए बीटा-क्षय स्थिर न्यूक्लाइड, सैद्धांतिक रूप से, अल्फा क्षय से गुजर सकते हैं।
इलेक्ट्रॉन, प्रोटॉन और न्यूट्रॉन परमाणु बनाते हैं। नाभिक प्रोटॉन और न्यूट्रॉन से बना होता है, जिसके चारों ओर इलेक्ट्रॉन घूमते हैं। परमाणु द्रव्यमान न्यूट्रॉन की संख्या से गुणा किए गए प्रोटॉन की संख्या के बराबर होता है, जबकि परमाणु संख्या एक तत्व में प्रोटॉन की संख्या से गुणा किए गए प्रोटॉन की संख्या के बराबर होती है, जबकि एक तत्व में प्रोटॉन की संख्या स्थिर रहती है, जबकि न्यूट्रॉन की संख्या भिन्न होता है।
आइसोटोप ऐसे परमाणु होते हैं जिनमें न्यूट्रॉन की संख्या अलग-अलग होती है लेकिन प्रोटॉन की संख्या समान होती है। हम परमाणु द्रव्यमान और परमाणु संख्या की पूर्वगामी परिभाषाओं से यह निष्कर्ष निकाल सकते हैं कि समस्थानिक एक ही परमाणु संख्या वाले तत्व हैं लेकिन विभिन्न द्रव्यमान संख्याएँ हैं।








 CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
CBSE Admit Card 2026 for Private & R...
 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...














