Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: The Zeroth law of thermodynamics is one of the four laws of thermodynamics. Ralph H. Fowler is credited with developing the law. Surprisingly, the Zeroth law of thermodynamics was formulated considerably later than the first three laws. However, there was some debate about whether it should be called the Fourth Law or something else. The problem occurred because the new legislation provided a much better definition of temperature and effectively substituted what the previous three laws had to declare. Finally, Fowler came up with a name to stop this conflict.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
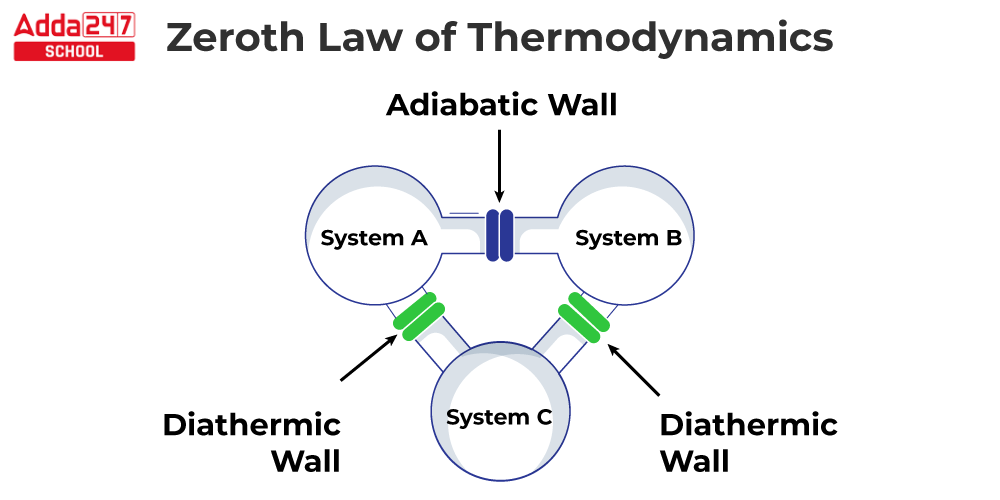
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is a fundamental law of thermodynamics that states that if two systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they must also be in thermal equilibrium with each other. Temperature, in other words, is a feature that may be used to compare two systems, according to the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. When two systems have the same temperature, they are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Ralph H. Fowler proposed the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics in 1931. The “zeroth” law was so named because it was introduced after the first three laws of thermodynamics had already been established. The first three laws of thermodynamics deal with energy conservation, the direction of spontaneous processes, and system entropy. Temperature is a property that can be used to compare two systems, according to the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics PDF
Read Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics by clicking on the below link.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics PDF
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Equation
The Zeroth law of thermodynamics equation is very similar to the transitive property of equality in mathematics:
If a = b and b = c, then a = c.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Formula
The Zeroth law of thermodynamics is highly similar to the mathematical transitive property of equality: if a = b and b = c, then a = c.
What is Thermal Equilibrium ?
Temperature is a feature that distinguishes thermodynamics from other sciences. This characteristic can discriminate between hot and cold. When two or more bodies of differing temperatures come into touch, they eventually reach a common temperature and are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium if there is no heat transfer, even if they are capable of doing so based on other considerations. For example, if we place food in the refrigerator overnight, the food is in thermal equilibrium with the refrigerator’s air. Thermal equilibrium occurs when heat no longer transfers from food to air or from air to food.
Application of Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
Here are some examples of Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics applications:
- Thermometers measure the temperature of a system by comparing it to the temperature of a known reference point. Typically, the reference point is a liquid, such as mercury or alcohol. The liquid expands when the temperature of the system exceeds the temperature of the reference point. When the temperature of the system falls below that of the reference point, the liquid contracts. The quantity of liquid expansion or contraction is proportional to the temperature difference between the system and the reference point.
- Cooking involves the transmission of thermal energy from a heat source to the food. When the meal achieves the same temperature as the heat source, it is cooked. For example, if you’re grilling a steak, it’ll be done when it reaches the same temperature as the grill.
- Air conditioners work by extracting thermal energy from a room in order to chill it down. The air conditioner will continue to run until the temperature of the room matches that of the outside air.
- Refrigerators also work by extracting thermal energy from a place in order to cool it down. The refrigerator will keep running until the temperature of the space matches that of the air outside.
- The human body maintains a steady internal temperature of approximately 37 degrees Celsius. This is accomplished through a mechanism known as thermoregulation. Thermoregulation is the process through which the body generates and loses heat in order to maintain a consistent internal temperature. When you exercise, for example, your body produces more heat. Your body will sweat in order to maintain a consistent internal temperature. Sweat will evaporate, aiding in the cooling of your body.
- The progressive increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s climate system is known as global warming. The fundamental source of global warming is the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide. Greenhouse gases capture solar heat, causing the Earth’s temperature to rise.
- Thermal energy transfer is defined as the passage of energy from a warmer to a cooler object. This can happen by conduction, convection, or radiation. The transfer of thermal energy via direct contact is known as conduction. Convection is the movement of fluids that transfers thermal energy. The transfer of heat energy by electromagnetic waves is known as radiation.
- Heat engines are machines that transform thermal energy into mechanical energy. The internal combustion engine is the most frequent type of heat engine. Internal combustion engines utilise the heat generated by the combustion of fuel to power a piston or turbine. The piston or turbine then rotates a crankshaft, which powers a car’s or other vehicle’s wheels.
- Power plants are enormous structures that generate electricity. Power plants create electricity using a range of technologies, including coal, natural gas, nuclear power, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
- The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics is employed in a variety of medical applications, including:
- Thermometers are devices that measure the temperature of the human body and other things.
- Diathermy is a medical practice in which heat is used to relieve pain and inflammation. Diathermy is performed by passing a high-frequency electric current through the body. The electric current heats up the tissues, which can assist to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Cryotherapy is a medical practice that uses cold temperatures to treat a variety of ailments, including warts, acne, and discomfort. Cryotherapy works by freezing the cells in the affected location, which can kill or damage the cells to the point that they can no longer create problems.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics in Hindi
थर्मोडायनामिक्स का शून्य विधि (Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics) थर्मोडायनामिक्स विज्ञान में एक महत्वपूर्ण सिद्धांत है, जो वस्तुओं के तापमान के मध्य संबंध स्थापित करता है। यह नियम विद्यमान तीसरे नियम के बाद प्रस्तुत किया गया था, लेकिन इसे “शून्य विधि” के नाम से जाना जाता है क्योंकि यह थर्मोडायनामिक्स के अन्य दो नियमों को स्थापित करने से पहले ही प्रारंभिक रूप से अपनाया जा रहा था।
शून्य विधि के अनुसार, यदि दो वस्तुएँ एक तृतीय वस्तु के साथ अलग-अलग समयों में आपस में तापमान की समानता दिखाती हैं, तो वे दोनों वस्तुएँ एक-दूसरे से तापीय संतुलन में हैं। इससे हम यह निष्कर्ष निकाल सकते हैं कि वे दोनों वस्तुएँ एक दूसरे के साथ ताप विनिमय करती हैं और एक दूसरे के साथ समान तापमान पर पहुंचती हैं।
इसे समझने के लिए, हम एक उदाहरण ले सकते हैं। मान लीजिए आपके पास एक गर्म चाय का प्याला है और एक समान तापमान पर ठंडी सेब का सेब है। यदि आप इन दोनों वस्तुओं को एक साथ रखते हैं, तो वे धीरे-धीरे एक-दूसरे के साथ ताप विनिमय करेंगी और अंत में दोनों का तापमान समान हो जाएगा। यही शून्य विधि का सिद्धांत है, जिससे हम वस्तुओं के तापमान के संबंध को समझ सकते हैं और थर्मोडायनामिक्स के विज्ञान में इसका बड़ा महत्व होता है।
Thermodynamics Class 11 Notes PDF for NEET
The chapter on thermodynamics features in both class 11 Chemistry NCERT textbook and class 11 Physics text book. This chapter features at chapter number 6 in chemistry and chapter number 11 in physics class 11 NCERT text books. Due to its high significance and its comprehensive application, we study this chapter in both subjects. So, it is highly important to master this chapter seeing its high significance. In order to facilitate students’ comprehension of all subsequent related ideas as they prepare for the competitive exam, the topic was taught in the eleventh grade. The major objective of this chapter is to help you understand the ideas surrounding the conservation of energy and flow of heat energy. Every year, the NEET chemistry section bears at least 1 question from this topic. To help students prepare the chapter from the NEET exam perspective, we have compiled the detailed Notes PDF as per the chemistry syllabus.
Download Thermodynamics Chemistry Notes for NEET
Thermodynamics Video Lecture for NEET
The detailed lecture by one of the top faculty for chemistry in the country has been made on the chapter of thermodynamics. By going through the video lecture and revising the above-given notes, students will be able to solve any question related to thermodynamics.









 AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
AILET 2026 AIR 1: Check Full Toppers Lis...
 AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
AILET Result 2026 OUT, How to Download S...
 CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...
CUET PG Crash Course 2026: Subject-Wise ...














