Table of Contents
Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB) has officially released the Bihar DElEd Notification 2025 on 10 January 2025 on their official website. Candidates interested in applying for the Bihar DElEd Entrance Exam 2025 must submit their complete online application to secure admission for the 2-year Diploma in Elementary Education (D.El.Ed) Course. As the application process is underway, aspiring candidates must prepare thoroughly, leaving no stone unturned in their pursuit of this opportunity.
While preparing for the exam, it is essential for candidates to stay well-informed about the selection process. One important aspect of the Bihar DElEd exam that every candidate must be aware of is the normalization process. The Bihar DElEd Normalization process plays a vital role in ensuring fairness and accuracy in the evaluation of candidates’ performance across different exam shifts. In this article, we will delve deeper into how this process works and why it is integral to the exam.
How Does the Bihar DElEd Normalization Process Work?
The Bihar DElEd exam is held across multiple shifts, and each shift can have question papers of varying difficulty levels. To ensure fairness and eliminate any bias in scoring, the normalization process is applied. This method compares the performance of candidates from different shifts, taking into account the difficulty level of each set of questions. The scores are then adjusted to reflect a level playing field, ensuring that no candidate is unfairly impacted by the shift they appeared in. Through this process, the Bihar DElEd exam ensures that all candidates are assessed on an equal basis, regardless of when or in which shift they take the exam.
Step-by-Step Bihar DElEd Normalization Process
The normalization process is crucial in ensuring that all candidates are evaluated fairly, especially when there are variations in the difficulty levels of exam shifts. Since exams are often held in multiple shifts, one shift might have easier questions compared to another, which could unfairly advantage or disadvantage candidates. To address this, the normalization process adjusts the raw scores of candidates, making sure that differences in difficulty don’t affect the fairness of the results. Here’s how the calculation works:
- Raw Scores Collection: Initially, the raw scores, which are the number of correct answers a candidate provided, are collected for each shift.
- Difficulty Index: Each shift’s exam difficulty is assessed based on how well candidates performed in that shift. For example, if candidates in one shift perform significantly better than those in another shift, it suggests the first shift was easier.
- Formula Application: A formula is applied to adjust the raw scores. The formula looks like this:
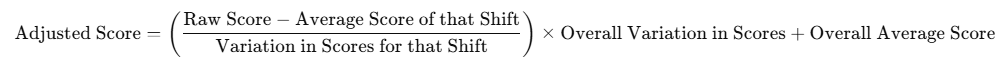
-
- Average Score of that Shift: This is the average score of all candidates in that particular shift.
- Variation in Scores for that Shift: This measures how much the scores in that shift differ from the average score. If most candidates scored similarly, the variation is low. If the scores were spread out, the variation would be higher.
- Overall Average Score: This is the average score of all candidates across all shifts.
- Overall Variation in Scores: This shows how much the scores vary overall, across all shifts.
- Adjusted Scores: The formula adjusts each candidate’s raw score by considering the difficulty of the shift they appeared for. The result is an adjusted score that provides a fair comparison between candidates from different shifts.
- Final Outcome: The final adjusted scores are used to rank candidates and determine their eligibility for selection, ensuring fairness across all shifts.




 MP TET Varg 3 Exam Date 2026 Out, Check ...
MP TET Varg 3 Exam Date 2026 Out, Check ...
 Odisha OTET Question Paper 2025, Direct ...
Odisha OTET Question Paper 2025, Direct ...
 MPESB Exam Calendar 2026 Out, Check Exam...
MPESB Exam Calendar 2026 Out, Check Exam...












