In English Grammar, Part of Speech serves as the most basic thing. Students can identify every word in a Sentence if they have a clear idea about parts of the Speech chapter in the English Language. Read the full article to know all the 8 Types Parts of Speech Definition and Examples.
Parts of Speech
The “parts of speech” refers to the grammatical category that a word belongs to based on its function and role within a sentence. It helps us understand how words are used about other words in a sentence and contributes to the overall meaning.
English Grammar has 8 types of parts of speech namely noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech describes how the word acts both meaning-wise and grammatically within the phrase.
Parts of Speech Definition
In classical English grammar, a part of speech, sometimes known as a part of speech, is a group of words with comparable grammatical features. Words belonging to the same part of speech have similar syntax, morphology (in that they undergo inflection for similar properties), and even semantic behavior.
What is Parts of Speech?
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, numbers, articles, or determiners are common English parts of speech, as with other terminologies such as word class, lexical class, and lexical category.
Other Facts about Part of Speech
Some scholars limit the word lexical category to a specific form of syntactic category, and they claim that it excludes parts of speech that are deemed functional, such as pronouns. The word form class is also used, and it can be classed as open or closed, despite contradicting meanings. Whereas open ones regularly get new members, closed classes gain new members seldom, if at all. Nouns, verbs, and adjectives are found in open classes, while pronouns and conjunctions are found in closed classes.
Parts of Speech Examples
Parts of speech are categories that we use to classify words based on their function and role in a sentence. Here are some simple definitions and examples of the main components of it.
- Noun: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. Example: dog, city, happiness
- Verb: A verb is a word that describes an action, occurrence, or state of being. Example: run, eat, is
- Adjective: An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. Example: happy, tall, blue
- Adverb: An adverb is a word that describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Example: quickly, very, happily
- Pronoun: A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun to avoid repetition. Example: he, she, they
- Preposition: A preposition is a word that shows a relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Example: in, on, at
- Conjunction: A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses. Example: and, but, or
- Interjection: An interjection is a word or phrase used to express strong emotion or surprise. Example: wow, oh, ouch
These are the 8 basic parts of speech, and understanding them can help us analyze and construct sentences correctly.
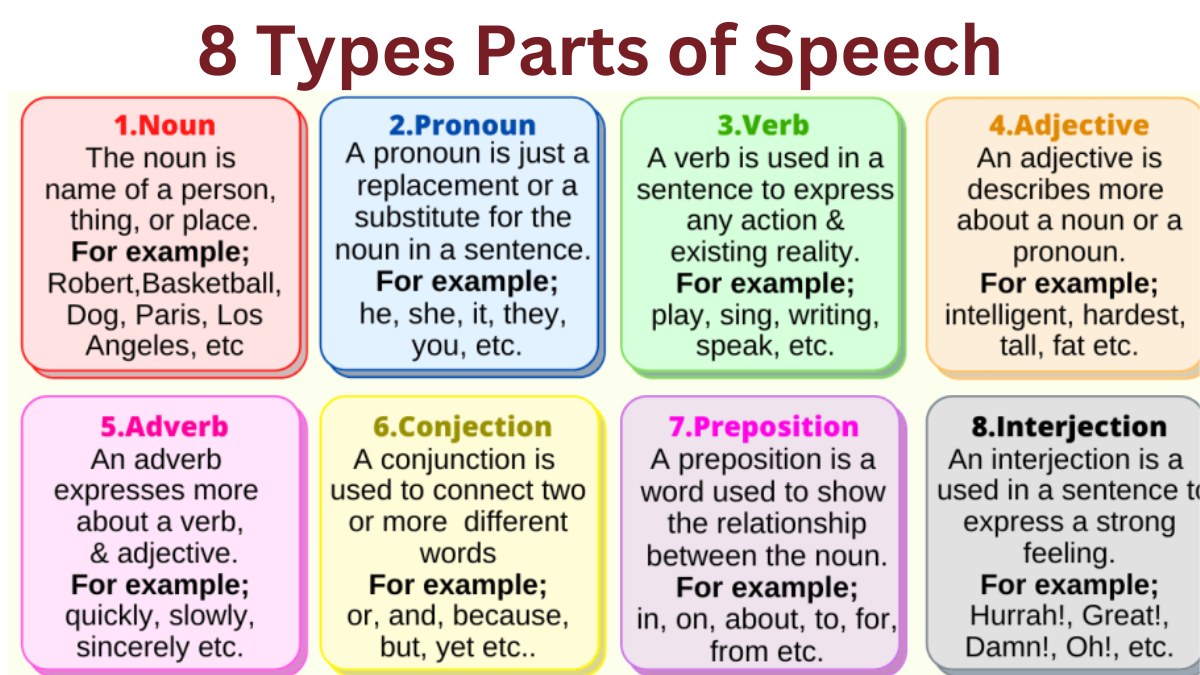
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples Chart
For better understanding, we have shared the compare chart of the 8 Parts of speech definitions with examples in brief.
8 Parts of Speach in a Single Sentence
For a better understanding, we have put a sentence that has all parts of speech in itself.
Hurray! My best friend and I will go on a yearly vacation to Zurich which is in Switzerland and we will visit all the beautiful places there.
- Best friend – Noun
- Hurray – Interjection
- beautiful – adjective
- Go – verb
- Yearly – adverb
- we – pronoun
- to – preposition
- and – conjunction
The various parts of speech and their definitions are discussed next part of the article.
First Part of Speech: Noun
A noun is a term that serves as the name for a single thing or group of objects. Living creatures, places, acts, attributes, states of existence, and concepts are all examples of objects. However, because a noun is not a semantic category, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs can all be used to represent activities and states of being.
A noun is a member of a wide, open part of speech that can appear as the main word in a clause’s subject, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition. There are many distinct sorts of nouns, including proper and common nouns, collective nouns, mass nouns, and so on. The syntactic rules for nouns change between languages, and parts of speech are defined in terms of how their members mix with other kinds of expressions.
Noun Examples
- We live in India.
India = Country, place
Second Part of Speech: Pronoun
Pronouns have been considered one of the parts of speech for a long time. Personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns are examples of pronouns in both plural and singular forms.
Pronoun Examples
- I met him yesterday.
I = first person singular number, Him = Third Person Singular Number
Third Part of Speech: Verb
A verb is a part of speech that expresses an action through grammar. An activity that can refer to anything that happens or a state of being. Verbs are inflected to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice in many languages, and a verb may also agree with the person, gender, or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject or object. Tenses are used to show that an activity is being carried out, that an action has been completed, or that an action will be completed.
Verb Examples
- Did you enter the house?
Did = past form of Do, Enter = Present form of Enter.
Fourth Part of Speech: Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or noun phrase in linguistics. Adjectives were once thought to be one of the most important components of speech in the English language. Historically, they were grouped with nouns, but today they are separated, and even words that were once categorized as adjectives, such as the, this, and my, are now classified as determiners.
Adjective Examples
- You are a good student.
Good = It is telling about the noun.
Fifth Part of Speech: Adverb
An adverb is a word that tells more information about a Verb. It expresses manner, location, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty that modifies a verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence. Adverbs usually respond to questions like how, when, where, and to what extent.
Adverbs are traditionally considered one of the parts of speech, although current linguists observe that the term “adverb” has become a type of “catch-all” category. Adverbs are used to categorize words based on their syntactic behavior.
Adverb Examples
- Why did you come so late to school?
Late – It lets us know more information about the verb.
Sixth Part of Speech: Conjunction
We use conjunction to connect two or more phases or clauses. Some of the examples of Conjunction are – and, or, because, or, yet, though, etc.
Conjunction Examples
- Shtal and Abhira are going on the trip together.
And = we used ‘and’ to tell about two friends in one sentence.
Seventh Part of Speech: Preposition
Prepositions are a group of words that are used to convey spatial or temporal links, as well as to denote different semantic responsibilities. Prepositions, rather than postpositions, are used to combine a noun phrase or, in some cases, an object.
Words like in, under, and of come before their objects. Postpositions are used instead of prepositions in some languages that have a different word order, and a prepositional phrase is created by a preposition or postposition and its complement. In a sentence, such prepositional phrases are frequently used as adverbs.
Preposition Examples
- My brother put the book on the table.
On = this word is telling about the position of the book.
Eight Parts of Speech: Interjection
An interjection is a word or statement indicates a spontaneous feeling or reaction. It is a broad category that encompasses a wide range of speech elements. Interjections intersect with a few other categories, such as profanities, discourse markers, and fillers, due to their various characteristics, and the use and linguistic study of interjections may be traced back to the Greek and Latin Modistae.
Interjection Examples
- Wow! The view of the hills is amazing.
Wow = we use the interjection to show our amusement after seeing a beautiful hill.
Parts of Speech: Article
Any member of a class of devoted words used with noun phrases is referred to as an article. They are used to indicate the identifiability of the noun phrases’ referents.
Article Examples
- This is the last ball of the match.
The = this article is saying about a specific thing.
Part of Speech: Prefix and Suffix
Prefix and Suffix are the small syllables generally added before and after a word. A prefix is an affix that goes before the stem of a word and transforms it into another word and a Suffix is attached last of a word. A prefix is sometimes referred to as a preformative in the study of languages.
Prefixes change the form of the words they are attached to, and like other affixes, they can be inflectional (creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and lexical category) or derivational (creating a new word with a new semantic meaning and, in some cases, a different lexical category). The word prefix is made up of ‘fix’, which in this context means “attach” and the prefix ‘pre-‘, meaning “before”.
Prefix and Suffix Examples
- Understand = Misunderstand (Mis – prefix added)
- Truth = Truthful (full – suffix added)









 Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
Vocabulary Words with Meaning and Senten...
 Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Formula,...
 Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...
Hyperbole- Explanation, Definition, Exam...














