Pronoun
While learning English and Grammar, we have to learn about the Parts of Speech and Pronouns as important Parts of Speech. Pronouns are used to counter the repetitiveness of nouns in the sentences. A pronoun is a term that replaces a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence as using too many times of nouns makes the sentence absurd. Pronouns refer to either a previously specified noun or a noun that does not need to be named expressly.
Pronouns
Pronouns are a word or a collection of words that can be used to replace a noun or a noun phrase in linguistics and grammar and has traditionally been considered one of the components of speech. However, because of the range of functions they fulfill cross-linguistically, several current theorists do not believe them to be a single class.
Read: Figure of Speech
Pronoun Definition
A pronoun is a word category and a pro-form is a type of function word or expression that stands in for another word, phrase, clause, or sentence, the meaning of which can be deduced from the context. Pronouns are typically used as pro-forms in English, however, there are certain pronouns that aren’t pro-forms and pro-forms that aren’t pronouns.
The usage of pronouns frequently involves anaphora, in which the pronoun’s meaning is determined by the antecedent. The adjective “pronominal” is used to describe “pronoun.” A pronominal is a term or phrase that serves as a substitute for a pronoun.
In this article, we will be talking about Pronouns and their types.
Read: Part of Speech
Pronoun Types List
The different types of pronouns are mentioned below:
1. Personal Pronouns
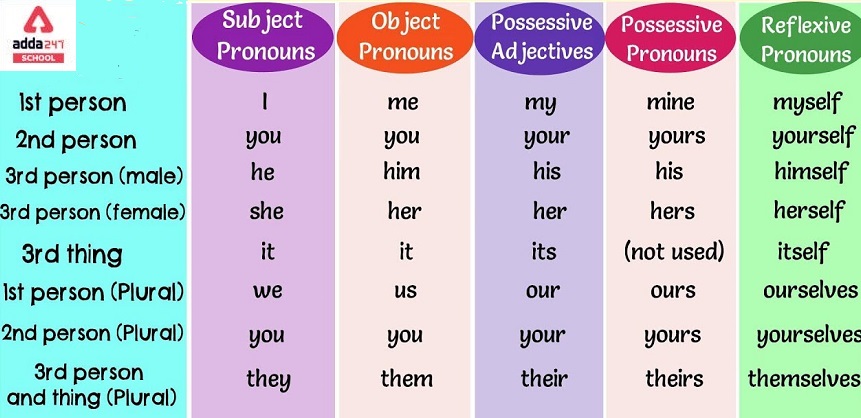
Personal pronouns, which refer to the person or persons speaking or writing (first person), the person or people being spoken to (second person), or other people or objects, are the most common pronouns (third person). There are separate pronoun forms for male, female, and neuter gender in the third person singular.
Subject and object are the two cases of English personal pronouns. Object pronouns are used for the object of a verb or preposition, while subject pronouns are used in the subject position.
2. Possessive pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to refer to things or persons that someone owns. Some appear as standalone noun phrases, such as mine, yours, hers, ours, and theirs, while others operate as a determiner and must be used in conjunction with a noun, such as my, your, her, our, your, and their, as in: I misplaced my wallet. Those of the second category have been called possessive adjectives in the past, and possessive determiners in more recent nomenclature. The phrase “possessive pronoun” is occasionally applied just to the first form of the possessive pronoun. Both sorts of possessive noun phrases are replaced. Their crusade to catch our attention, for example, may take the place of the advertisers’ crusade to capture our attention.
Read: Women Empowerment
3. Relative pronouns
Relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause, which is a component of a sentence that has a subject and verb but does not stand alone. That, which, who, whom, what, and whose are the most common relative pronouns.
They rely on an antecedent and refer to individuals or things that have been addressed previously. In relative clauses, they are utilised. Complementizers can also be used with relative pronouns.
4. Reflexive pronouns
Reflexive pronouns, such as myself, herself, ourselves, and itself, refer back to the subject of a sentence or clause and are produced by adding -self or -selves to a personal pronoun or possessive adjective.
5. Indefinite pronouns
Everybody, either, none, and anything is Indefinite pronouns that do not refer to a specific person or thing, but rather to something unidentified or unfamiliar.
Read: Air Pollution
Pronoun ki Definition in Hindi
एक सर्वनाम एक शब्द श्रेणी है और एक प्रो-फॉर्म एक प्रकार का फ़ंक्शन शब्द या अभिव्यक्ति है जो किसी अन्य शब्द, वाक्यांश, खंड या वाक्य के लिए खड़ा होता है, जिसका अर्थ संदर्भ से निकाला जा सकता है। सर्वनाम आमतौर पर अंग्रेजी में प्रो-फॉर्म के रूप में उपयोग किए जाते हैं, हालांकि, कुछ ऐसे सर्वनाम हैं जो प्रो-फॉर्म और प्रो-फॉर्म नहीं हैं जो सर्वनाम नहीं हैं।
सर्वनाम के उपयोग में अक्सर अनाफोरा शामिल होता है, जिसमें सर्वनाम का अर्थ पूर्ववर्ती द्वारा निर्धारित किया जाता है। विशेषण “सर्वनाम” का उपयोग “सर्वनाम” का वर्णन करने के लिए किया जाता है। एक सर्वनाम एक शब्द या वाक्यांश है जो एक सर्वनाम के विकल्प के रूप में कार्य करता है।
इस लेख में हम सर्वनाम और उनके प्रकारों के बारे में बात करेंगे।
सर्वनाम प्रकार सूची
विभिन्न प्रकार के सर्वनामों का उल्लेख नीचे किया गया है:
1. व्यक्तिगत सर्वनाम
व्यक्तिगत सर्वनाम, जो व्यक्ति या व्यक्ति बोलने या लिखने (प्रथम व्यक्ति), व्यक्ति या लोगों से बात की जा रही है (दूसरा व्यक्ति), या अन्य लोगों या वस्तुओं को संदर्भित करते हैं, सबसे आम सर्वनाम (तीसरे व्यक्ति) हैं। तीसरे व्यक्ति एकवचन में पुरुष, महिला और नपुंसक लिंग के लिए अलग-अलग सर्वनाम रूप हैं।
विषय और वस्तु अंग्रेजी व्यक्तिगत सर्वनाम के दो मामले हैं। वस्तु सर्वनाम का उपयोग क्रिया या पूर्वसर्ग की वस्तु के लिए किया जाता है, जबकि विषय सर्वनाम का उपयोग विषय स्थिति में किया जाता है।
2. अधिकारवाचक सर्वनाम
possessive pronouns का प्रयोग उन चीज़ों या व्यक्तियों के लिए किया जाता है जो किसी के पास होती हैं। कुछ स्टैंडअलोन संज्ञा वाक्यांशों के रूप में प्रकट होते हैं, जैसे कि मेरा, तुम्हारा, उसका, हमारा, और उनका, जबकि अन्य एक निर्धारक के रूप में काम करते हैं और संज्ञा के साथ संयोजन के रूप में उपयोग किया जाना चाहिए, जैसे कि मेरा, आपका, उसका, हमारा, आपका, और उनका , जैसे: मैंने अपना बटुआ खो दिया। दूसरी श्रेणी के उन लोगों को अतीत में स्वामित्व विशेषण कहा जाता है, और हाल ही के नामकरण में स्वामित्व निर्धारक कहा जाता है। वाक्यांश “अधिकारी सर्वनाम” कभी-कभी केवल स्वामित्व वाले सर्वनाम के पहले रूप में लागू होता है। दोनों प्रकार के अधिकारवाचक संज्ञा वाक्यांशों को प्रतिस्थापित किया जाता है। हमारा ध्यान आकर्षित करने के लिए उनका धर्मयुद्ध, उदाहरण के लिए, हमारा ध्यान आकर्षित करने के लिए विज्ञापनदाताओं के धर्मयुद्ध की जगह ले सकता है।
3. सापेक्ष सर्वनाम
सापेक्ष सर्वनाम एक अधीनस्थ उपवाक्य का परिचय देते हैं, जो एक वाक्य का एक घटक है जिसमें एक विषय और क्रिया है लेकिन अकेले खड़े नहीं होते हैं। वह, कौन, कौन, क्या, और किसके सबसे सामान्य सापेक्ष सर्वनाम हैं।
वे एक पूर्ववृत्त पर भरोसा करते हैं और उन व्यक्तियों या चीजों को संदर्भित करते हैं जिन्हें पहले संबोधित किया गया है। सापेक्ष उपवाक्य में इनका प्रयोग होता है। पूरक सर्वनामों का उपयोग सापेक्ष सर्वनामों के साथ भी किया जा सकता है।
4. रिफ्लेक्टिव सर्वनाम
रिफ्लेक्सिव सर्वनाम, जैसे कि स्वयं, स्वयं, स्वयं, और स्वयं, एक वाक्य या खंड के विषय को वापस संदर्भित करते हैं और व्यक्तिगत सर्वनाम या स्वामित्व वाले विशेषण में स्वयं या स्वयं को जोड़कर निर्मित होते हैं।
5. अनिश्चित सर्वनाम
हर कोई, या तो, कोई नहीं, और कुछ भी अनिश्चित सर्वनाम है जो किसी विशिष्ट व्यक्ति या चीज़ को संदर्भित नहीं करता है, बल्कि किसी अज्ञात या अपरिचित चीज़ को संदर्भित करता है।
सर्वनाम उदाहरण
सामान्य उपयोगों में से एक सर्वनाम का प्रयोग विशेष उपयोगों में भी किया जाता है, उनमें से कुछ का उल्लेख नीचे किया गया है:
लिंग गैर-विशिष्ट उपयोग, जिसमें किसी ऐसे व्यक्ति को संदर्भित करने के लिए सर्वनाम की आवश्यकता होती है जिसका लिंग अज्ञात है। अंग्रेजी में, सामान्य ‘वह’ और एकवचन ‘वे’ को कभी-कभी समाधान के रूप में नियोजित किया जाता है। एलजीबीटीक्यू+ संस्कृति में गैर-द्विआधारी या जेंडरक्यूअर के साथ-साथ लिंग-तटस्थ व्यक्ति के रूप में पहचान करने वाले लोगों को संदर्भित करने के तरीके के रूप में एकवचन ‘वे’ आम रहा है।
डमी सर्वनाम (एक्सप्लिटिव सर्वनाम) वे सर्वनाम होते हैं जो संज्ञा या सर्वनाम की व्याकरणिक आवश्यकता को पूरा करने के लिए नियोजित होते हैं लेकिन उनका कोई मूल्य नहीं होता है।
Nosism सर्वनाम ‘हम’ का प्रयोग स्वयं को संदर्भित करने के लिए किया जाता है।
पुनरुत्पादक सर्वनाम “आक्रामक” व्यक्तिगत सर्वनाम होते हैं जो सापेक्ष खंडों में पाए जा सकते हैं (उदाहरण के लिए) जहां एक अंतर (निशान) की उम्मीद है।
Pronoun Examples
Out of the general uses, a pronoun is also used in special uses, some of them are mentioned below:
- Gender non-specific uses, in which a pronoun is needed to refer to someone whose gender is unknown. In English, the generic ‘he’ and singular ‘they’ are sometimes employed as solutions. The singular ‘they’ has been common in LGBTQ+ culture as a method to refer to people who identify as non-binary or genderqueer, as well as a gender-neutral individual.
- Dummy pronouns (expletive pronouns) are pronouns that are employed to fulfil a grammatical need for a noun or pronoun but have no value.
- Nosism The pronoun ‘we’ is used to refer to oneself.
- Resumptive pronouns are “invasive” personal pronouns that can be found (for instance) in relative clauses where a gap (trace) is expected.
- The ‘royal we’ is used by a single person who is a king.








 Biomolecules and Practical Organic Chemi...
Biomolecules and Practical Organic Chemi...
 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids ...
 CBSE Class 11 Geography Syllabus 2025-26...
CBSE Class 11 Geography Syllabus 2025-26...












