Table of Contents
The Brahmaputra river system is one of the most important and largest river systems of India. The flow system of this river starts from the Himalayan mountain range. The journey of the Brahmaputra river system passes through a total of three countries. First, the Brahmaputra river originates from Tibet and enters India. Passing through the Indian state of Assam, the Brahmaputra river reaches Bangladesh and merges into the Bay of Bengal. From the point of view of UPSC exam, the topic of Brahmaputra river system is important for General Studies-1.
Brahmaputra River System
The Brahmaputra River, besides being the largest river in India, is a major river in Central and South Asia. It is an international river as it flows through three countries- China, India and Bangladesh. The total length of the Brahmaputra River is about 2,900 km. The Brahmaputra River crosses many important areas along its route and receives many tributaries. In India, the Brahmaputra River flows through Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, where it meets important tributaries like the Dihang, Lohit and Dibang rivers.
The average width of the Brahmaputra River is about 5.46 km. The catchment area of this river is about 580,000 square km, with an average annual discharge of 19,820 cubic metres per second (cumec). It has an average annual sediment load of 735 million metric tonnes and a specific flood discharge of 0.149 cumec per square kilometer.
Brahmaputra River Origin
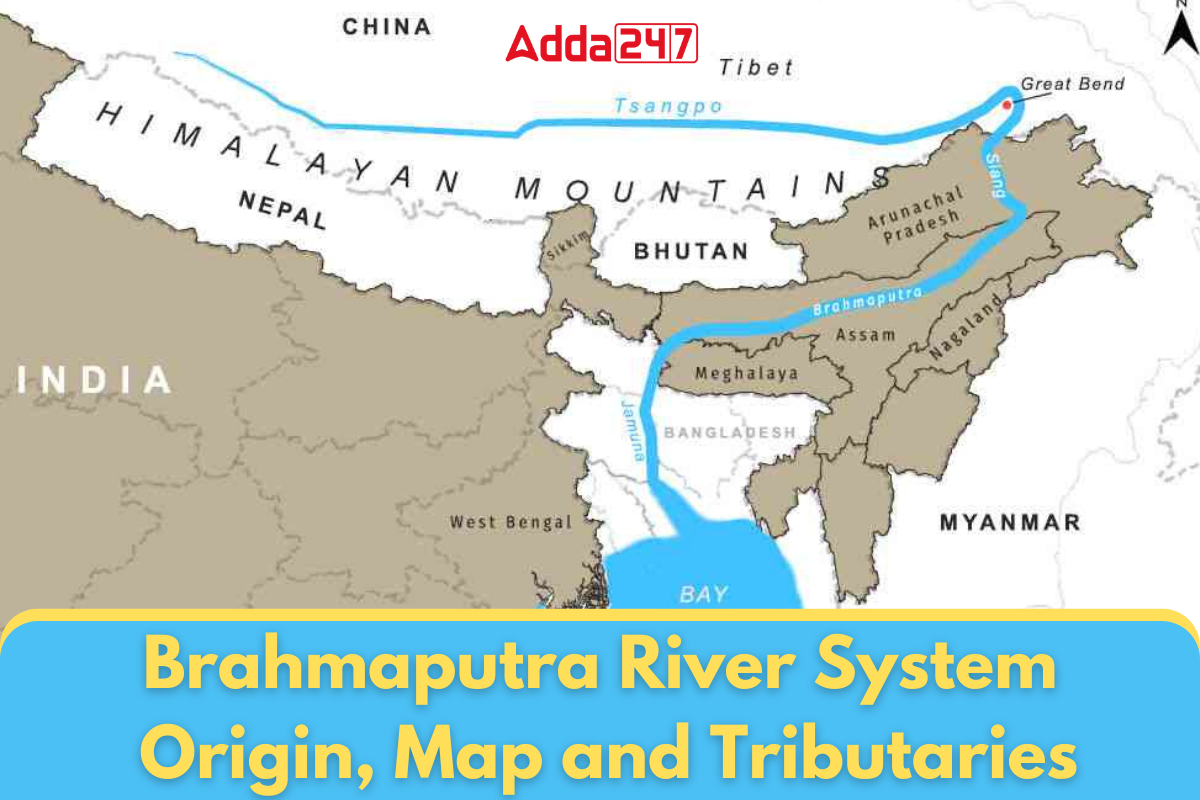
The Brahmaputra river’s origin in the Chemayungdung glacier of the Kailash range of the Himalayas (height 5,150 m) near the Mansarovar lake. The Brahmaputra River enters India through Arunachal Pradesh where it is called Dihang. The Brahmaputra has the largest catchment area in Tibet, covering a total of 2,93,000 square kilometers.
Brahmaputra River Maps
The Brahmaputra River one of the major rivers of the world, which flows through Three countries, further enhancing its significance. To understand, which countries the Brahmaputra River passes through can be challenging, but it becomes easier with the help of map provided below. Like other major rivers, the Brahmaputra is also fed by numerous tributaries.
Below we have attached the Brahmaputra river map reference for better and clear understanding about the flow of various rivers, their meeting points. This view helps us understand all the tributaries of the Brahmaputra and other important information with more ease and accuracy.
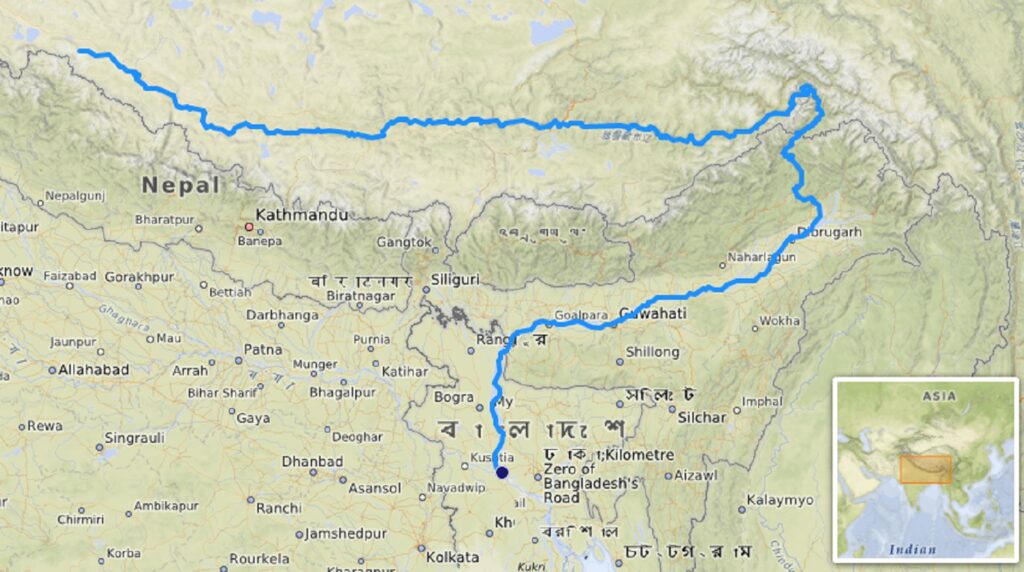
Brahmaputra River in INDIA
Brahmaputra River Length
The Brahmaputra River originates from the Chemayungdung Glacier of the Kailash Range near the Mansarovar Lake and ends in the Bay of Bengal after flowing through Tibet (China), India, and Bangladesh. The total length of this river is about 2900 km. Out of this, 1700 km flows in Tibet, while in India it is about 916 km long. Its length in Bangladesh is about 284 km.
| Country | Length (in kilometers) |
|---|---|
| Tibet (China) | 1700 |
| India | 916 |
| Bangladesh | 284 |
| Total | 2900 |
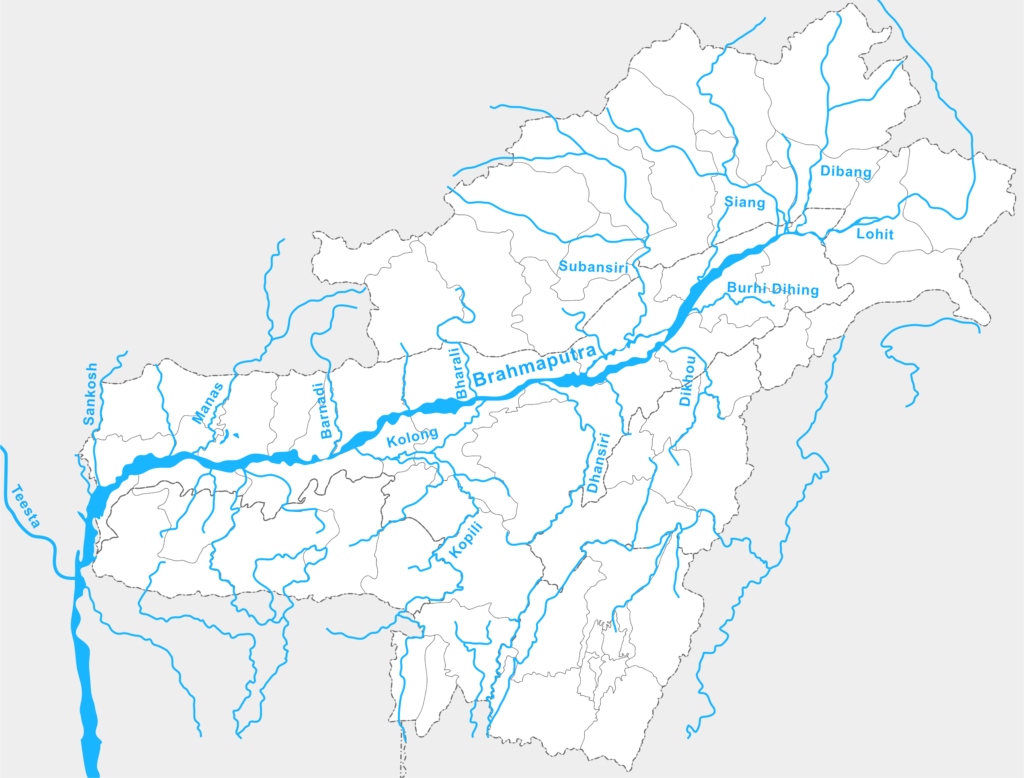
Brahmaputra River Tributaries
All the tributaries in the Himalayan region are glacier-fed and the water level of these rivers rises considerably during the monsoon. Heavy rainfall occurs here mainly from May to September due to the southwest monsoon, which causes flooding in these rivers. The tributaries of the Brahmaputra are divided into two parts: left bank northern bank tributaries and right bank southern bank tributaries. These rivers cause flooding in their catchment areas during the monsoon and affect the flow of the Brahmaputra.
North Bank Tributaries
The northern tributaries of the Brahmaputra River are several important water streams that enrich it. The major rivers include Subansiri, Rongnadi, Dikrong, Buroi, Borgong, Jiabharali, and Dhansiri (North). In addition, Siang, Puthimari, Manas, Beki, Ai, and Sonkosh are also important tributaries. These rivers originate from various mountainous regions and join the Brahmaputra, making its water flow more wide and powerful. These tributaries pass through various terrains and join the Brahmaputra, enriching the water flow of this great river.
South Bank Tributaries
The second group of major tributaries of the Brahmaputra River are the southern tributaries. These include Noadehing, Buridehing, Desang, Dikho, Bhogdoi, Dhansiri (South), Kopili, Kulsi, Krishnai, Dhadnoi, and Jinjiran. These rivers join the southern bank of the Brahmaputra River. The southern bank tributaries have different characteristics compared to the northern bank tributaries.
| Northern Bank Tributaries | Southern Bank Tributaries |
|---|---|
| Subansiri | Noadehing |
| Rongnadi | Buridehing |
| Dikrong | Desang |
| Buroi | Dikho |
| Borgong | Bhogdoi |
| Jiabharali | Dhansiri (South) |
| Dhansiri (North) | Kopili |
| Puthimari | Kulsi |
| Manas | Krishnai |
| Beki | Dhadnoi |
| Siang | Jinjiran |
| Sonkosh |
Brahmaputra River Major Tributaries
The Brahmaputra River has many tributaries, but some of the major tributaries important for UPSC exam are: Subansiri, Manas, Dhansiri (North), Raidak River, Beki, Siang, Dhansiri (South), Desang (Disang) and Kopili.
Subansiri River
The Subansiri River originates in Tibet and is considered an anticline river. It enters India near the town of Taksing in Arunachal Pradesh and flows east and southeast through the Miri Hills. Thereafter, it enters the Assam valley in a southerly direction through Dulangmukh in Dhemaji district and meets the Brahmaputra River at Jamurighat in Lakhimpur district.
Manas River
The river originates in Bhutan and flows through Assam and southern Bhutan, joining the Brahmaputra near Jogighopa. The total length of the Manas river is 376 km and it offers a unique view of hilly uplands and plains near its mouth.
Dhansiri River
This important tributary originates from the Patkai Mountain range in the Eastern Himalayas and has a length of 352 km passing through Tinsukia, Dibrugarh in Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
Sonkosh River
The Sankosh River, known as the Puna Tsang in Bhutan, originates in Bhutan and flows into the Indian state of Assam. The major tributaries of this river in Bhutan are the Mo Chhu and the Pho Chhu.
Siang River
The river originates from the glaciers of the Kailash range at an altitude of about 5300 metres and flows eastwards for about 1600 kilometres through the Tibetan plateau. After entering Arunachal Pradesh, the river flows in a south/south-east direction for about 230 kilometres to reach Pasighat. The Lohit and Dibang rivers join the Siang about 30 kilometres below Pasighat to form the mighty Brahmaputra River System.
Kopili River
The river originates from the Sapong Reserve Forest in the south-east of Meghalaya and has a total length of 256 km. Out of this, 78 km forms the shared border of Meghalaya and Assam, while the remaining 178 km flows in Assam. The river passes through the borders of Meghalaya, North Cachar Hills and Karbi Anglong and enters the plains of Assam. Ultimately, it meets the Brahmaputra River at Kopilimukh.
Key Feature of Brahmaputra River System
The Brahmaputra River System is one of the major river systems in South Asia, renowned for its vast drainage basin and key feature. Originating in Tibet and flowing through India and Bangladesh, it supports millions of lives along its course.
- The average width of the Brahmaputra is 5.46 km.
- Arunachal Pradesh has the largest drainage area of the Brahmaputra, which is up to 81,424 sq km.
- The Brahmaputra sub-basin covers an area of 580,000 sq km in Tibet (China), Bhutan, India and Bangladesh.
- The 9.15 km long Dhola-Sadiya Bridge, built on a tributary of the Lohit River, is India’s longest bridge over water.
- The name of the Brahmaputra is different in some places, such as the name of Brahmaputra is Sanpo in Tibet, Dihan in Arunachal and Brahmaputra in Assam.
- The world’s largest river island is Majuli Island, which is situated in the middle of this river.
- The Brahmaputra river system area collectively contributes significantly to India’s forest area, which is 55.48% of the country’s total forest area.
- The hydroelectric potential of the Brahmaputra river systems has been estimated at 66065 MW.
- The average discharge of the Brahmaputra river system is about 700,000 cubic feet per second.
- The region of the Brahmaputra river system, especially Assam, is one of the heaviest rainfall areas in the world, causing floods every year.
- During its course from Kobo to Dhubri in the Assam valley, the river has about 20 major tributaries on the northern bank and 13 tributaries on the southern bank.
Significance of Brahmaputra River System
- This river provides fertile soil for agriculture and facilitate connection with the remote villages.
- This river is also an important source for hydro electric power generation in India.
- India has 2 operational dams over Brahmaputra river in its territory which are Ranganadi Dam and Rangit dam the collective power generation of both the dams accounts for 465 MW.
- It provides inland water support between India and Bangladesh through NW 2 between Sadiya and Dhubri.
- Also the river serves as an important source of Fisheries in the region.
Brahmaputra River System for UPSC
Geography is an excellent topic for UPSC, especially rivers, which are frequently asked in the exam, be it Pre or Mains. The Brahmaputra River is one of the largest rivers in Asia and passes through four countries of Asia. This river is a refuge for diverse aquatic and terrestrial species and is the main source of food, water and livelihood for millions of people. There are many facts related to this river which can play an extremely important role in the UPSC exam. All such points are shared in this article.
| Related Articles | |
| Ganga River System | Yamuna River System |
| Rivers and their Tributaries | Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plains |


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





