Table of Contents
Dengue- Relevance for UPSC Exam
- GS Paper 2: Governance, Administration and Challenges- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health.
Dengue- Context
- According to a civic report, the Capital city of Delhi reported 1,171 cases of dengue and three deaths over the past week.
- While the fatality toll for the season has reached nine, the caseload stands at 2,708 — the highest since 2017.
Dengue- Key Points
- About Dengue Fever: Dengue is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus (Genus Flavivirus).
- Transmission: Dengue is transmitted by several species of mosquito within the genus Aedes, mainly by female Aedes aegypti.
- About Aedes aegypti: Aedes is a daytime feeder and can fly up to a limited distance of 400 meters. Dengue mosquitoes can’t breed once the temperature falls below 16 degrees.
- It is also responsible for the transmission of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika infection.
- Seasonal Pattern: Every year, from July to November, an upsurge in cases of dengue have been observed.
- The disease has a seasonal pattern, i.e., the peak comes after the monsoon and it is not uniformly distributed throughout the year.
Dengue- Tests are used to detect dengue
- ELISA Test: IgM and IgG test for dengue antibodies detected in an initial blood sample, meaning that it is likely that the person became infected with dengue virus within recent weeks.
- This test is normally done after 3-7 days of fever.
- IgM and IgG antibodies test and NS1 antigen test. Both are done through ELISA kits and hence are popularly known as Elisa test.
- NS1 Antigen test: It is a test for dengue, which allows rapid detection on the first day of fever before antibodies appear.
RTS,S or Mosquirix- World’s First Malaria Vaccine Approved by WHO
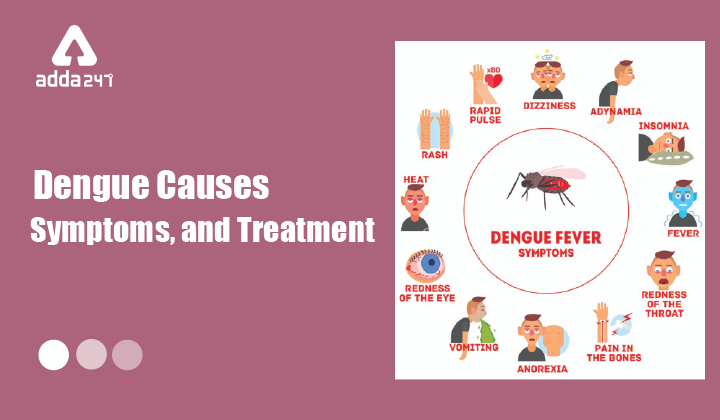
Dengue- Common Symptoms
- The onset of dengue fever is usually a sudden rise in temperature lasting 2-7 days and commonly associated with headache, flushing, retro-orbital pain and/or rash, myalgia, weakness, rash and itching.
- Severe Dengue: In extreme cases, the disease can develop into severe dengue (dengue hemorrhagic fever) that causes bleeding, low levels of blood platelets, and blood plasma leakage.
National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC)
Dengue- Treatment
- Mild dengue infection: It may be treated symptomatically. Fever and body aches are best treated with paracetamol.
- Salicylates and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided as these may predispose to mucosal bleeds.
- The patient should be encouraged to drink plenty of fluids.
- Severe Dengue Infection: Patient should be admitted to hospital in the care of specialists when following symptoms appear-
- Abdominal pain or persistent tenderness vomiting,
- Fluid accumulation in pleural cavity, abdomen, or subcutaneous tissues,
- Mucosal bleeds,
- Lethargy, restlessness or irritability,
- Liver enlargement >2 cm,
- Progressive increase in haematocrit with a concurrent decrease in platelet count.
- Home Remedy: Home remedies popularly used to treat dengue fever are papaya leaves, drinking adequate water, neem leaves, basil leaves tea (tulsi), coriander leaves, pomegranate juice, wheatgrass juice.




 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





