Table of Contents
What is Genome?
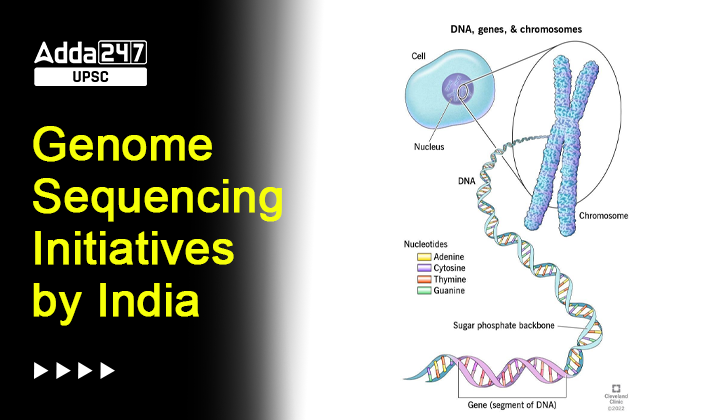
A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic instructions stored in the nucleus of every cell. It is made up of DNA, consisting of about 3 billion base pairs in humans. The genome encodes instructions for building proteins, which are essential for the body’s functions. Mutations can occur in the genome during DNA replication, leading to changes that can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. The study of genomes, known as genomics, has promising implications in medicine, biology, agriculture, and our understanding of evolution. Here are some of the important functions of the genome:
- Stores genetic information: The genome stores all of the genetic information that an organism needs to develop and function. This information is passed down from parents to offspring, ensuring that each individual has the same genetic makeup as their parents.
- Controls development: The genome controls the development of an organism by specifying the order in which genes are expressed. This process is called gene expression, and it determines the characteristics of an individual, such as its size, shape, and color.
- Maintains cellular functions: The genome also maintains the functions of cells by regulating the expression of genes that control metabolism, cell division, and other essential processes.
- Repairs damage: The genome can repair damage to its DNA, which is essential for maintaining the health of cells and preventing diseases.
- Evolves: The genome can change over time, which is how evolution occurs. These changes, called mutations, can be caused by environmental factors or by random errors during DNA replication. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
The genome is a complex and essential part of all living organisms. By understanding the genome, scientists can learn more about how organisms develop and function, and they can develop new ways to treat diseases and improve our understanding of evolution.
Genome Sequencing Meaning
Genome sequencing is the process of determining the order of the nucleotides (A, T, C, and G) that make up a genome. This can be done for a single organism, or for a group of organisms. Genome sequencing is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Medical research: Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic mutations that are associated with diseases. This information can be used to develop new diagnostic tests and treatments for diseases.
- Forensic science: Genome sequencing can be used to identify individuals from their DNA. This is useful in criminal investigations and paternity cases.
- Agriculture: Genome sequencing can be used to develop new crop varieties that are resistant to pests and diseases.
- Evolutionary biology: Genome sequencing can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
Genome sequencing is a complex and expensive process, but it is becoming increasingly affordable and accessible. As the cost of genome sequencing continues to decrease, it is likely that this technology will be used in more and more applications.
Genome Sequencing Definition
Genome sequencing refers to the process of determining the precise order of DNA nucleotides within an organism’s genome. It involves reading and decoding the genetic information encoded in the DNA. This technique allows scientists to identify and analyze specific genes, genetic variations, and even entire genomes. Genome sequencing plays a crucial role in various fields, including medical research, personalized medicine, evolutionary biology, and agriculture, enabling a deeper understanding of genetic traits, diseases, and the complexities of life itself. Here are some of the benefits of genome sequencing:
- Can help to diagnose diseases: By identifying genetic mutations that are associated with diseases, genome sequencing can help to diagnose diseases earlier and more accurately. This can lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes for patients.
- Can help to develop new treatments: By understanding the genetic basis of diseases, scientists can develop new treatments that target specific genes or pathways. This could lead to more effective and targeted treatments for diseases.
- Can help to prevent diseases: By identifying people who are at risk of developing certain diseases, genome sequencing can help to prevent those diseases from occurring. This could be done through early intervention, lifestyle changes, or gene therapy.
- Can help to personalize medicine: By understanding an individual’s genetic makeup, doctors can tailor treatments to their specific needs. This could lead to more effective and safer treatments for everyone.
Overall, genome sequencing is a powerful tool that has the potential to revolutionize medicine and biology. As the cost of genome sequencing continues to decrease, it is likely that this technology will be used in more and more applications in the years to come.
What is Genome Sequencing?
Genome sequencing is the process of determining the order of the nucleotides (A, T, C, and G) that make up a genome. A genome is the complete set of genetic instructions for an organism, stored in DNA. There are different types of genome sequencing, including:
- Whole genome sequencing (WGS): This is the most comprehensive type of genome sequencing. It determines the order of all of the nucleotides in an organism’s genome.
- Whole exome sequencing (WES): This type of genome sequencing only determines the order of the nucleotides in the exome, which is the part of the genome that codes for proteins.
- Targeted sequencing: This type of genome sequencing only determines the order of the nucleotides in specific genes or regions of the genome.
Genome sequencing is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Medical research: Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic mutations that are associated with diseases. This information can be used to develop new diagnostic tests and treatments for diseases.
- Forensic science: Genome sequencing can be used to identify individuals from their DNA. This is useful in criminal investigations and paternity cases.
- Agriculture: Genome sequencing can be used to develop new crop varieties that are resistant to pests and diseases.
- Evolutionary biology: Genome sequencing can be used to study the evolutionary relationships between different organisms.
Genome sequencing is a complex and expensive process, but it is becoming increasingly affordable and accessible. As the cost of genome sequencing continues to decrease, it is likely that this technology will be used in more and more applications in the years to come.
| Follow US | |
| UPSC Govt. Jobs UPSC Current Affairs UPSC Judiciary PCS Download Adda 247 App here to get the latest updates |


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





