Table of Contents
What is Green Hydrogen?
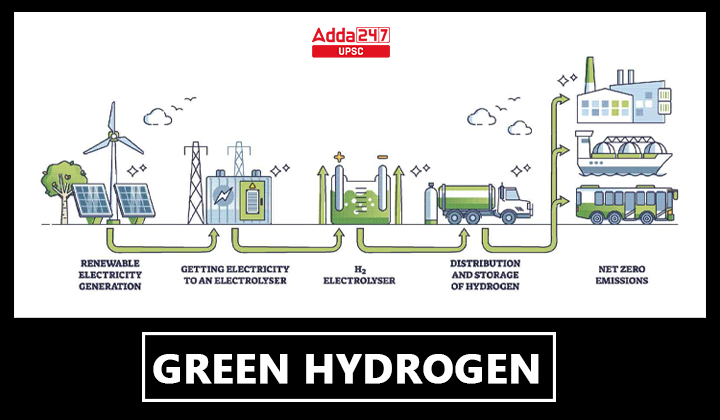
A green hydrogen is a form of hydrogen that is created by electrolyzing water with the use of renewable energy sources like solar or wind energy. Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen during the electrolysis process, and the hydrogen that is created can be used as a clean, sustainable fuel.
Green Hydrogen UPSC Relevancy
For Prelims: General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity, and Climate Change – that do not require subject specialization.
For Mains: GS Paper- III- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Green Hydrogen Why in News?
New Delhi welcomes the start of the three-day international conference on green hydrogen. A platform for developing partnerships to realize the goal of a clean and green planet. The government, in collaboration with businesses, will create cutting-edge technology for a sustainable hydrogen environment.
Types of Hydrogen Based on Extraction Methods
Depending on the nature of the method of its extraction, hydrogen is categorized into three categories, namely, Grey, Blue, and Green.
- Grey Hydrogen: It is produced via coal or lignite gasification (black or brown), or via a process called steam methane reformation (SMR) of natural gas or methane (grey). These tend to be mostly carbon-intensive processes.
- Blue Hydrogen: It is produced via natural gas or coal gasification combined with carbon capture storage (CCS) or carbon capture use (CCU) technologies to reduce carbon emissions.
- Green Hydrogen: It is produced using electrolysis of water with electricity generated by renewable energy. The carbon intensity ultimately depends on the carbon neutrality of the source of electricity (i.e., the more renewable energy there is in the electricity fuel mix, the “greener” the hydrogen produced).
Green Hydrogen Mission
India has set goals to achieve Net Zero by 2070 and energy independence by 2047. India’s Energy Transition is focused on maximizing the usage of renewable energy across all economic sectors in order to meet this goal. A potential substitute for facilitating this shift is green hydrogen. In addition to replacing fossil fuels in industry and providing clean transportation, hydrogen can also be used for decentralized power generation, aviation, and maritime transportation.
Green Hydrogen Mission Objectives
- Making India a leading producer and supplier of Green Hydrogen in the world
- Creation of export opportunities for Green Hydrogen and its derivatives
- Reduction in dependence on imported fossil fuels and feedstock
- Development of indigenous manufacturing capabilities
- Attracting investment and business opportunities for the industry
- Creating opportunities for employment and economic development
- Supporting R&D projects
The Mission Outcomes Projected by 2030 are
- Development of green hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 MMT (Million Metric Tonne) per annum with an associated renewable energy capacity addition of about 125 GW in the country
- Over Rs. Eight lakh crore in total investments
- Creation of over Six lakh jobs
- The cumulative reduction in fossil fuel imports is over Rs. One lakh crore
- Abatement of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions
Importance of Green Hydrogen
-
Emission Targets
Using green hydrogen energy can help India reach its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) targets and guarantee the security, accessibility, and availability of the country’s energy supply.
In accordance with the Paris Climate Agreement, India committed to reducing its economy’s carbon intensity by 33–55% from 2005 levels by 2030. India’s move to sustainable energy and fight against climate change can be fueled by green hydrogen.
-
Mobility and Energy Storage
Green hydrogen can serve as an energy storage option, which will be necessary to handle renewable energy’s erratic supply in the future.
In terms of transportation, green hydrogen can be utilized in trains, huge ships, buses, trucks, and other vehicles for long-distance mobilizations for either urban freight movement within cities and states or for people.
-
Reducing Dependence on Imports
This will lessen India’s reliance on fossil fuel imports. The localization of electrolyzer production and the growth of green hydrogen projects have the potential to generate thousands of employment in India as well as a new market for green technologies worth US$18–20 billion.
Green Hydrogen Mission Challenges
- High Production Costs: At the moment, it costs more to manufacture green hydrogen than hydrogen derived from fossil fuels.
This is due to the fact that electrolysis, the method used to create green hydrogen, uses a significant quantity of electricity, and in India, the price of renewable electricity is still quite expensive.
- Infrastructure: India does not currently have the necessary facilities for the generation, storage, and delivery of green hydrogen.
For example, there aren’t enough hydrogen refueling stations or pipelines to move hydrogen.
- Technological barriers: Despite the potential advantages of green hydrogen, this technology has just recently gained traction in India.
This is because there aren’t enough incentives for enterprises to use this technology and because the general public doesn’t know much about or understand green hydrogen.
- Economic Sustainability: One of the main obstacles to using hydrogen commercially is the extraction of green hydrogen.
Hydrogen must be cost-competitive with traditional fuels and technology for transportation fuel cells on a per-mile basis.
Green Hydrogen Mission Way Forward
- Increase the Capacity to Generate Renewable Electricity: India has to increase its capacity to produce renewable electricity in order to lower the price of producing green hydrogen.
Expanding sustainable energy sources like solar and wind power would help achieve this.
- Building Infrastructure for Hydrogen: In order to make this technology more widely available, it is necessary to build infrastructure for the production, storage, and distribution of green hydrogen. This entails constructing hydrogen fueling stations and pipelines for hydrogen transportation.
- Implement Regulatory Incentives: By implementing regulatory incentives, including as tax credits and subsidies, to promote the development and use of this technology, the government can play a significant role in boosting the adoption of green hydrogen.
- Increase Public Awareness and Understanding: It’s critical to inform people about the advantages of green hydrogen and how it may contribute to the effort to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
| Follow US | |
| UPSC Govt. Jobs UPSC Current Affairs UPSC Judiciary PCS Download Adda 247 App here to get the latest updates |


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





