Table of Contents
Gurjara Pratiharas: The Gurjara Pratiharas, also known as the Pratiharas or Gurjaras, were a prominent Indian dynasty that ruled from the 6th century to the 11th century CE. They were mainly concentrated in the northwestern regions of India, specifically in the area of modern-day Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh. The dynasty is known for their contributions to Indian culture, especially in the areas of literature, art, and architecture.
Gurjara Pratiharas: Origin
-
- The Gurjara Pratiharas were initially a tribe of Gurjars, an Indo-Aryan ethnic group.
- They rose to prominence during the 6th century CE under the leadership of Harichandra, who established the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty.
- Harichandra was succeeded by his son Nagabhata I, who expanded the Gurjara Pratihara kingdom and established it as a major power in North India.
- Under the rule of Nagabhata I, the Gurjara Pratiharas defeated the Arab invaders and successfully defended their territory.
- This victory marked the beginning of the Pratihara Golden Age, during which the dynasty flourished both politically and culturally.
- The Gurjara Pratiharas were known for their military prowess and efficient administration, and they established a vast network of roads and trade routes, which contributed to the growth of commerce and trade in the region.
Bhoja, one of the most well-known Gurjara Pratihara kings, ruled from 836 to 885 CE. Bhoja was a well-known literary contributor, particularly in the domains of play and poetry. He was also a patron of the arts. He gave the playwright commission for the well-known Sanskrit drama “Prabodha Chandrodaya,” which is being performed today. Bhoja was also an avid supporter of architecture, and he is credited with building a number of palaces and temples, notably the Dhar temple known as Bhojshala.

Gurjara Pratiharas: Architecture
The Gurjara Pratiharas were also known for their architecture, and their style is characterized by intricate carvings and sculptures. The Khajuraho temples, which are a UNESCO World Heritage site, are a fine example of Gurjara Pratihara architecture. The temples were built between the 10th and 12th centuries and are renowned for their intricate carvings and sculptures.

Gurjara Pratiharas: Founder
The Gurjara-Pratiharas were a medieval Indian dynasty that ruled much of Northern and Central India from the 6th to the 11th century CE. The founder of the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty is believed to be Harichandra, who ruled in the mid-6th century CE. However, the most prominent and influential ruler of the dynasty was Mihira Bhoja, who ruled from the late 8th century to the early 9th century CE. Mihira Bhoja is credited with transforming the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty into a major political and military power in Northern India.
Gurjara Pratiharas: Rulers
The Gurjara Pratiharas were a prominent dynasty that ruled parts of northern India from the 6th century CE to the 11th century CE. The dynasty was founded by Harichandra, who established his rule in the region of modern-day Rajasthan. The Gurjara Pratiharas went on to become a powerful empire, with their influence extending from modern-day Punjab to Central India. The dynasty was known for its military prowess, cultural achievements, and patronage of the arts.
The Gurjara Pratiharas had a long line of rulers who contributed significantly to the growth and development of the dynasty. Some of the most notable rulers of the dynasty are discussed below:
Nagabhata I (730 CE – 760 CE)
Nagabhata I was the first ruler of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty to establish a significant presence in northern India. He is known for his victories over the Arab invaders who had come to India during the early 8th century CE. Nagabhata I also defeated the Palas of Bengal and established his rule over a vast region of northern India.
Bhoja I (836 CE – 885 CE)
Bhoja I was one of the most famous rulers of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty. He is known for his military campaigns against the Rashtrakutas, the Palas, and the Cholas. Bhoja I was also a patron of the arts and is credited with commissioning several temples and sculptures in his capital city of Kannauj.
Mihira Bhoja (890 CE – 910 CE)
Mihira Bhoja was the son of Bhoja I and ruled the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty during a period of relative peace and stability. He was known for his patronage of learning and is credited with establishing a university in his capital city of Kannauj. Mihira Bhoja was also a prolific writer and wrote several works on grammar, poetics, and astronomy.
Mahendrapala I (915 CE – 950 CE)
Mahendrapala I was one of the most powerful rulers of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty. He defeated the Rashtrakutas and established his rule over a vast region of northern and central India. Mahendrapala I was also a patron of the arts and commissioned several temples and sculptures in his capital city of Kannauj.
Bhoja II (1018 CE – 1055 CE)
Bhoja II was the last ruler of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty. He ruled during a period of decline and was eventually defeated by the Chaulukyas of Gujarat. Bhoja II was known for his patronage of learning and is credited with commissioning several works of literature and poetry.
The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty made significant contributions to the cultural, political, and military history of northern India. Their rulers were known for their military prowess, patronage of the arts, and contributions to learning. The dynasty eventually declined due to internal strife and external invasions, but its legacy continues to live on in the art and architecture of northern India.
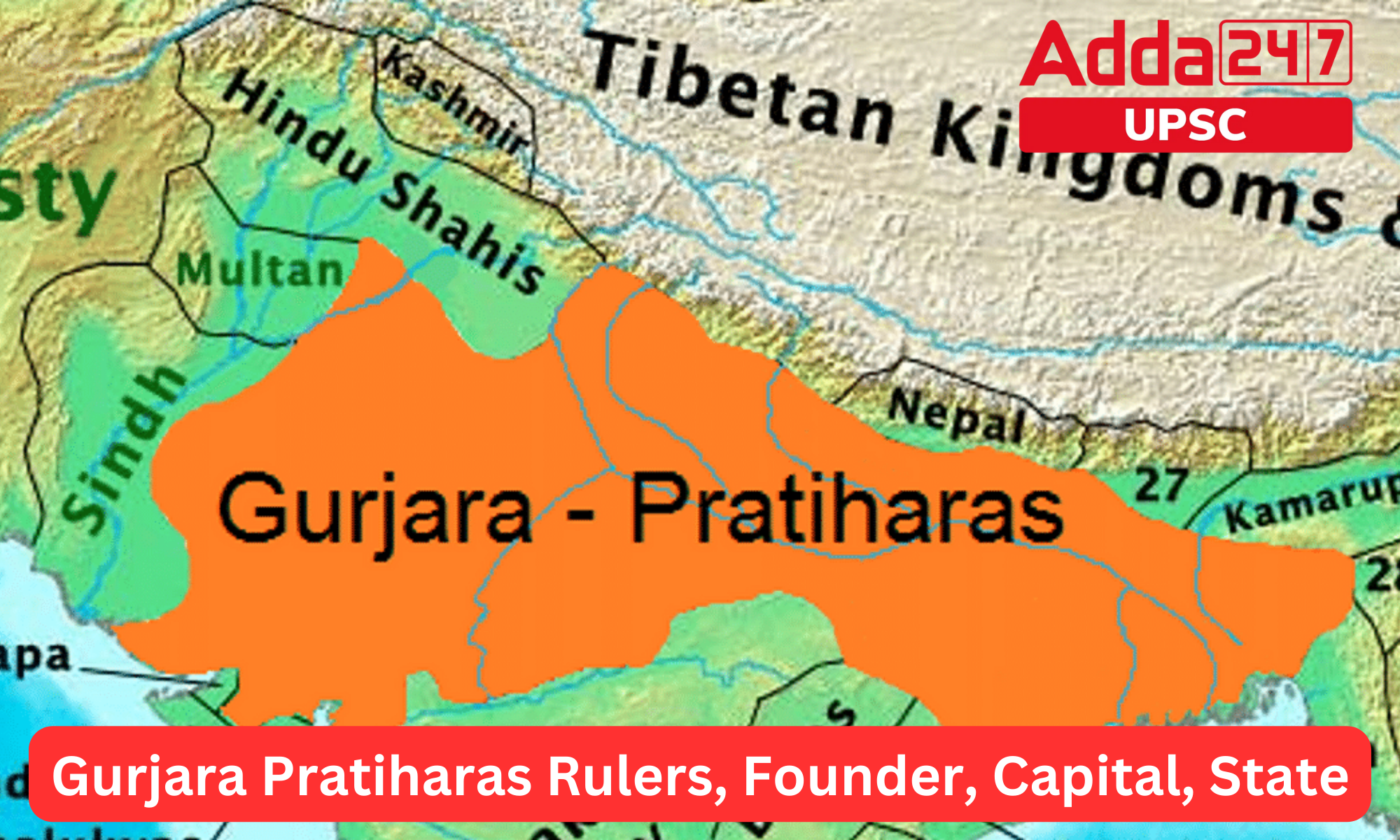
Gurjara Pratiharas: Capital
The capital of the Gurjara Pratihara dynasty, which ruled in northern India from the 8th to the 11th century, was Kannauj. The city of Kannauj, located in present-day Uttar Pradesh, was an important center of politics, culture, and commerce during the Gurjara Pratihara period. The dynasty was known for its military prowess, and its rulers were patrons of art, literature, and learning. They played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of medieval India.

Gurjara Pratiharas: State of Rule
Gurjara Pratiharas: Tripartite Struggle
- The Tripartite struggle was a period of intense conflict in northern India during the 8th-10th centuries CE, between three powerful dynasties – the Gurjara Pratiharas, the Rashtrakutas, and the Palas.
- The Gurjara Pratiharas were a powerful dynasty that ruled over much of northern India from the 6th to the 11th centuries CE.
- The dynasty was founded by Harichandra in the 6th century CE, but it was under the leadership of Nagabhata I (730-760 CE) that the Gurjara Pratiharas emerged as a major power in northern India.
- During the Tripartite struggle, the Gurjara Pratiharas were pitted against the Rashtrakutas and the Palas.
- The Rashtrakutas were a powerful dynasty that ruled over much of western India and the Deccan, while the Palas were a dynasty that ruled over much of eastern India, including present-day Bengal and Bihar.
- The conflict between the three dynasties was primarily over control of northern India, and it lasted for over two centuries.
- The Gurjara Pratiharas were initially successful in the conflict, and they were able to expand their territory and establish their dominance over much of northern India.
- However, they faced stiff resistance from the Rashtrakutas and the Palas, and the conflict eventually resulted in the weakening of all three dynasties.
The Tripartite struggle was a significant period in Indian history, as it led to the emergence of new regional powers and the decline of the major dynasties that had previously dominated northern India. Despite the conflict, the period also saw significant cultural and intellectual achievements, particularly in the fields of literature, architecture, and art.
Gurjara Pratiharas: Decline
Despite their many achievements, the Gurjara Pratiharas eventually declined in the 11th century CE due to internal conflicts and invasions from the Ghaznavids. However, their legacy lives on, and they are remembered for their contributions to Indian culture and civilization.
In conclusion, the Gurjara Pratiharas were a prominent Indian dynasty that ruled from the 6th to the 11th century CE. They were known for their military prowess, efficient administration, and contributions to Indian culture in the fields of literature, art, and architecture. Their legacy continues to inspire and influence Indian culture and civilization to this day.


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





