Table of Contents
Down To Earth Magazine is a fortnightly magazine focusing on politics of environment and development, published in New Delhi, India.
UPSC Previous years’ questions on Development, Environment, Health and Disaster Management give us a clear idea about the increased importance of Down To Earth Magazine.
Down To Earth Magazine is one of the most important and indispensable source for UPSC Civil Services Exam Preparation. Keeping this in mind, here, we come with ”Gist Of Down To Earth Magazine” which covers important environmental current affairs articles in smooth pointed form, keeping in mind the demand of UPSC aspirants.
Impact Of 1.5 o C Temperature Rise On India: Introduction
- Since the middle of the twentieth century, India has witnessed a rise in extreme temperature and rainfall events, droughts, and sea levels; and an increase in the intensity of severe cyclones, alongside other changes in the monsoon system, according to an assessment by the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences in June 2020.
- If this is India’s situation when the Earth is 1.1o C hotter than in the pre-industrial period, then we can imagine the scenario when the global temperature rises by 1.5 o C.
- According to the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) Assessment Report 6 of Working Group I, the world is on track to breach this temperature guardrail in the next 18 years.
Impact Of 1.5 o C Temperature Rise On India: How will Temperature Rise Impact India?
- The repercussions of a 1.5oC global temperature rise would be catastrophic for India.
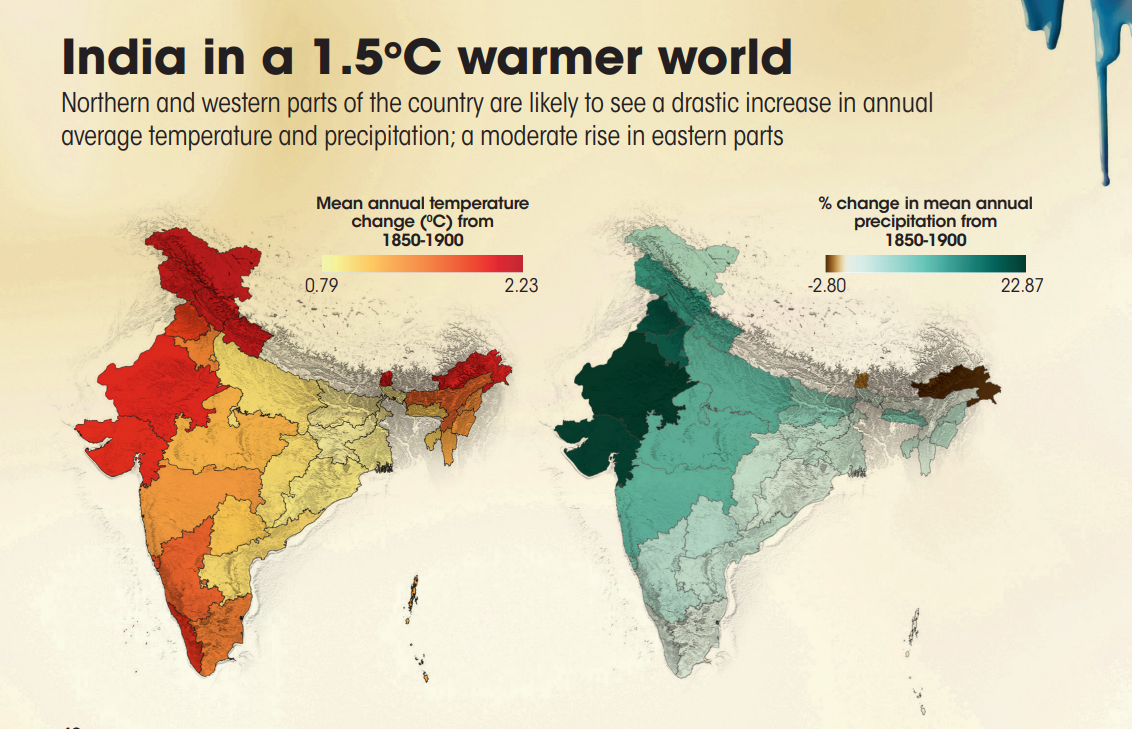
- India could become 1.2o C warmer and receive almost 10 per cent more rainfall every year.
- Ladakh is likely to be the worst hit at 2.23o C warmer than pre-industrial levels.
- Annual mean temperatures may rise in five other Himalayan states—Jammu and Kashmir (1.76o C), Himachal Pradesh (1.73o C), Uttarakhand (1.62o C), Sikkim (1.55o C) and Arunachal Pradesh (1.47o C). The temperature rise is most likely to trigger the rapid melting of glaciers and pre-cipitation change.
- Rajasthan could receive 23 per cent more rainfall.
Impact Of 1.5 o C Temperature Rise On India: More Days Of Heatwaves
- The warmer temperatures may translate into an increase in the number of days of heatwaves.
- Rajasthan could record 13 additional days with temperatures beyond 40o C, followed by Delhi, Gujarat (12 additional days each), Telangana (10 additional days) and Andhra Pradesh (8 additional days).
- The India Meteorological Department considers a non-hilly region for the declaration of a heatwave when the temperature crosses 40o.
Impact Of 1.5 o C Temperature Rise On India: Low Jet Streams Moving Northward!
- The low-level jet stream winds, responsible for the monsoon rains, have been moving northwards over the past three decades. This is the reason rainfall levels in Kerala have decreased over time.
- The northward or poleward shift of the low-level jet stream has been identified as major impacts (sic) of global warming on large-scale atmospheric dynamics.
- Consistent movement in the jet stream has led to a drying trend in the southern part of the Western coast of India.
- It has also led to a wetter monsoon season in the upper parts of the Western coast in the last three decades.



 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





