Table of Contents
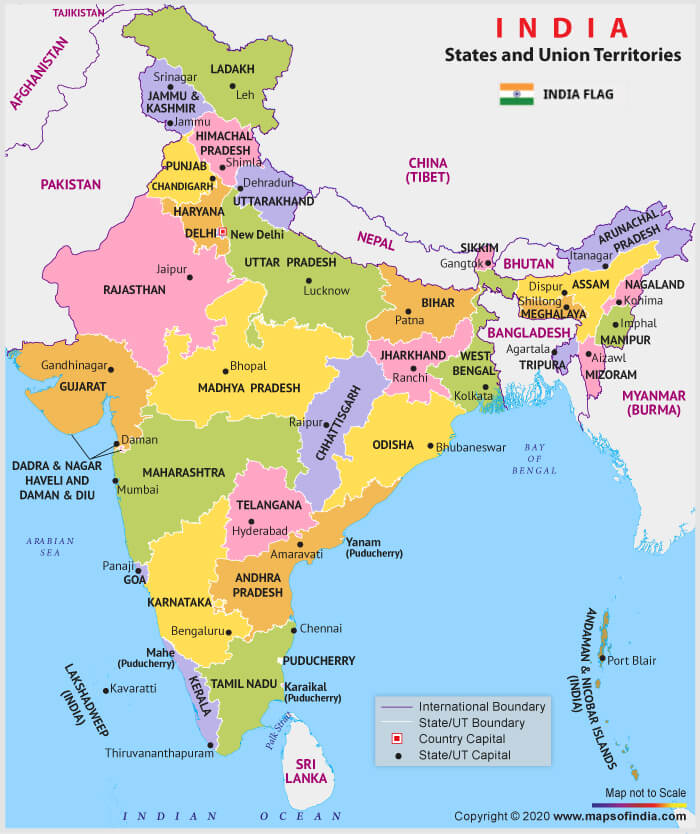
New Political Map of India
India’s map has changed because the big state of Jammu and Kashmir is now two smaller parts called Union Territories: J&K and Ladakh.
Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019:
- Introduced in the Rajya Sabha on August 5, 2019, the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Bill, 2019 aimed to divide the state into two Union Territories – the UT of Jammu and Kashmir and the UT of Ladakh.
- The bill received approval from both houses of parliament, resulting in a significant alteration in the administrative divisions of India.
- Consequently, India’s state count now stands at 28, while the number of Union Territories has reached 8. This change occurred due to the amalgamation of Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu, which officially took effect on January 26, 2020.
What are the differences since the State of Jammu & Kashmir was split into two Union Territories?
- The districts of Kargil and Leh will form the Union Territory of Ladakh, while the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir will encompass the remaining territories of the former state.
- Similar to Puducherry, the UT of Jammu and Kashmir will have its own legislature, while Ladakh, akin to Chandigarh, will function as a Union Territory without a legislature.
- The governance structure mandates two distinct lieutenant governors (LG) to oversee the administration of each UT in accordance with the Act.
- The central government will exercise direct authority over the police and law enforcement in Jammu and Kashmir. However, the elected government will retain control over the land.
- In contrast, the central government will have direct administrative control over the UT of Ladakh, with the region being governed by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central authority.
Union Territory of Ladakh
Ladakh, designated as a Union Territory on October 31, 2019, is celebrated for its picturesque mountain landscapes and unique cultural identity. The governance of the Union Territory of Ladakh will be overseen by the President through the appointment of a Lieutenant Governor.
| Ladakh Union Territory – Without Legislature | |
| Capital | Leh and Kargil |
| Area | 59,146 km sq. km |
| Districts | 2 districts namely Leh and Kargil. |
| Languages | Hindi, English, Ladakhi, Purgi, Brokskat, and Balti. |
| Population | 274289 (2011- Census) |
Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir
The unallocated regions from the former state of Jammu and Kashmir will form the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The President will govern this Union Territory through a designated administrator known as the Lieutenant Governor.
| Jammu & Kashmir Union Territory – With Legislature | |
| Capital | Jammu(winter), Srinagar(summer) |
| Area | 222, 236 sq. km |
| Districts | 20 |
| Languages | Kashmiri, Dogri, Urdu, Hindi, and English |
| Literacy | 67.16% |
How Many States are in India?
The list of States and Union Territories in India are mentioned below:
| States | Union Territories |
|
|
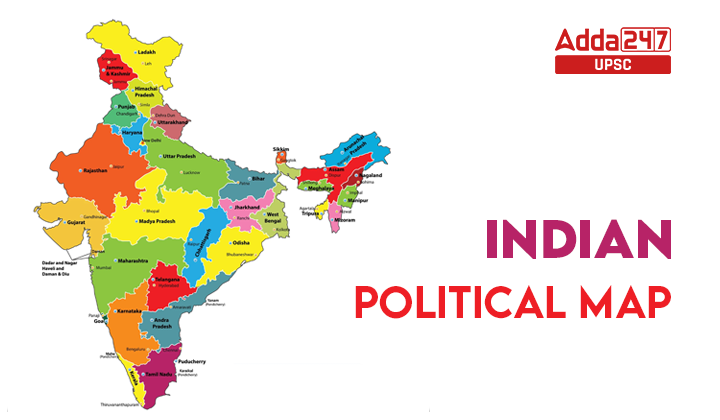
Types of Indian Political Maps
A political map illustrates artificial boundaries or divisions created by humans in a particular region. It provides insight into human interactions within that area, displaying cities’ locations in relation to each other. Unlike topographic maps, political maps do not include terrain details. Essentially, a political map focuses on showcasing the political features and characteristics specific to a given area.
- Country & State’s border.
- Public transportation, railways, etc.
- Water bodies.
- Roads & highways.
- Cities and towns.
- Religious & historical sites, etc.
Major Divisions in India Political Map
India is a vast nation with a federal structure comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, as indicated on a political map. The organization and governance of India’s political divisions are structured in the following manner:
- The reorganization of states and Union Territories in India is driven by considerations of language and ethnicity.
- The Union Government, with its capital and legislature (Parliament) in New Delhi, formulates national rules and regulations.
- India is divided into states, each having its own capital, legislature, and key officials like the Governor, Chief Minister, and Ministers.
- Union Territories are under the direct control of the Central Government.
- Notably, certain Indian Union Territories, such as Delhi, Pondicherry, and Jammu and Kashmir, have elected legislatures, providing them with a distinctive political structure.
Uses of Political Map of India
The purpose of a political map is to convey political information to the viewer. Various government sectors in India utilize political maps to comprehend the country’s political boundaries and their relevance in decision-making processes.
- A political map delineates the political features of an area, including country or state borders, major highways, waterways, and other regionally relevant information.
- It aids in identifying district boundaries, population distribution, and workplace concentrations.
- The map serves to highlight diverse communities for effective municipal service planning.
- India’s political map plays a crucial role in understanding regional socio-political conventions that shape collective behavior and government outcomes.
- It visually represents the geographic divisions, restricted areas in the northern and southern zones, and ethnic characteristics across India from east to west.
- Additionally, the map portrays various modes of transportation, such as railways, highways, and network passages, facilitating a cultural network that connects different parts of the country.


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...






