Table of Contents
The Indus River system, one of the major river systems of India, combines several major rivers to form a huge water body. The Indus River system flows mainly through North India and across Pakistan and finally merges into the Arabian Sea. The Indus River system notes are useful for UPSC GS 1 and GS 2, so let’s discuss them in detail.
Indus River System
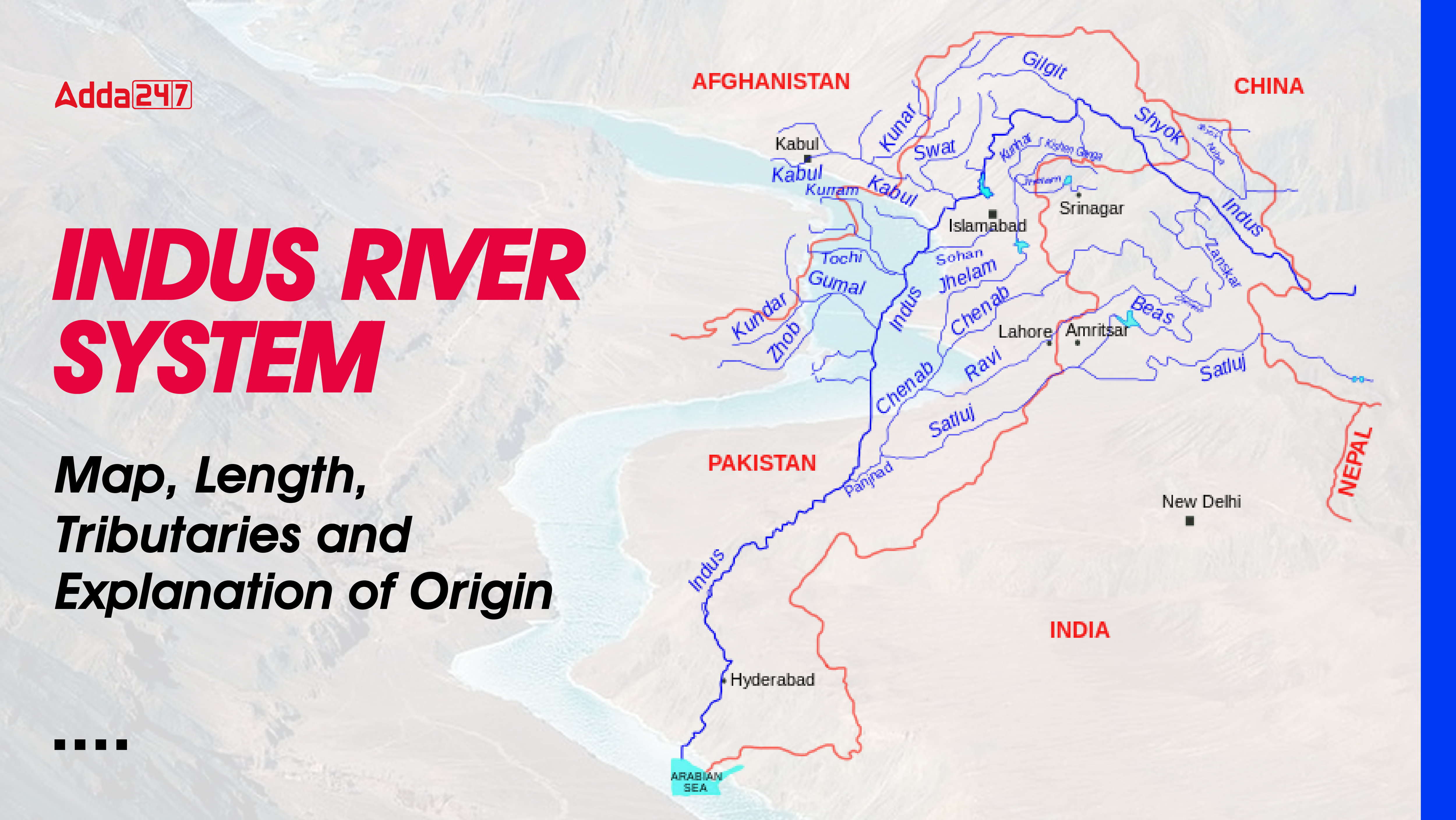
The Indus River system is one of the largest river systems in India and Pakistan. It originates from Lake Mansarovar in Tibet. A part of the Indus River enters India through Ladakh and enters Pakistan covering the Jammu and Kashmir region. After India, the Indus River enters Pakistan at Chillar near the Dardistan region. The total length of the Indus River in India is 1114 kilometers, and the river stretches for approximately 2,880 kilometers. many tibutaries of idus river system amonog them Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Satluj and many more. The Indus River is also known as the Sindhu River.
Origin of the Indus River System
The Indus River originates from the Kailash Range near Lake Mansarovar in Tibet, China. This system is known as the Indus River System because the Indus River is its main river of the system. The Indus River is the largest river in Punjab, and five of its major tributaries – the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej – flow through the state. This is why the region is called Punjab, meaning ‘land of five rivers’.
Indus River System Map
Indus River is one of the major rivers of Asia and the world. Indus river has many tributaries like Shyok, Hounza, Gilgit, Suru, Zanskar, The Jhelam, The Chenabh, The Ravi, The Beas and many more. It can be quite challenging to understand the regions through which the Indus River and its tributaries flow. However, the map given below proves to be helpful in understanding it. Through this map, candidates get to understand the overall information about the route of the Indus River and all its tributaries with ease and accuracy.
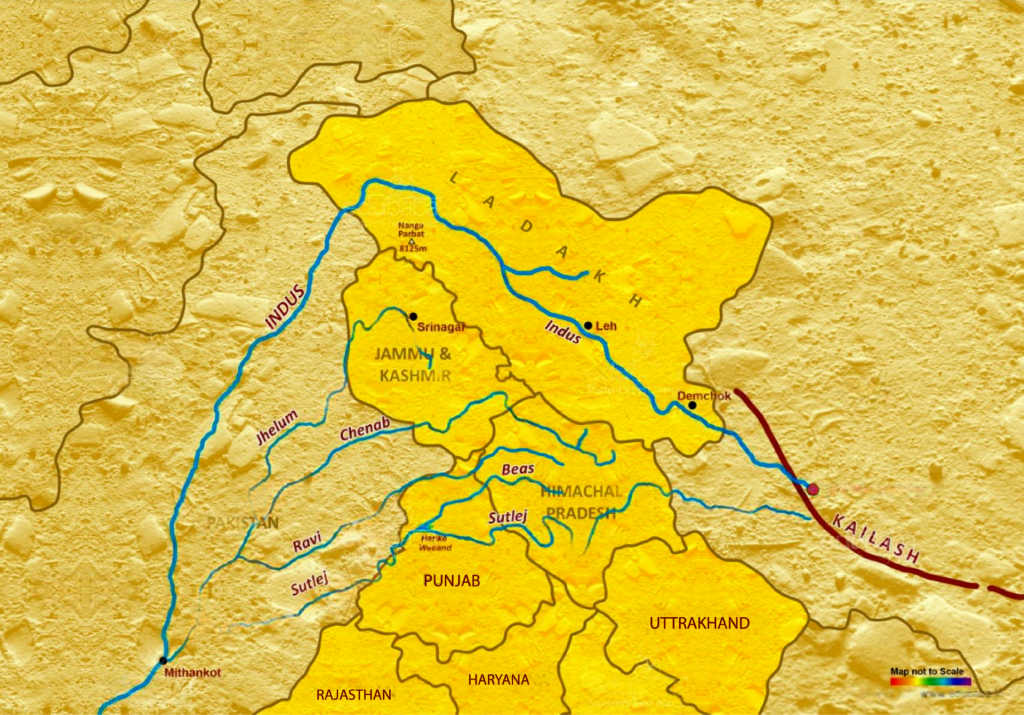
Length of the Indus River System
The Indus River, also known as Sindhu, is one of the largest river basins in the world, with an area of 11,65,000 square kilometers. Its area in India is 321,289 square kilometers and its total length is 2,880 kilometers, of which 1114 kilometers flow in India. The Indus is the westernmost river among the Himalayan rivers.
Tributaries of Indus River
The Indus river system is one of the largest river system of north India as well as Pakistan. This river has many major tributaries which originate from North India and the Himalayas. It has many tributaries like the Indus River receives many tributaries from the Himalayas such as Shyok, Gilgit, Jaskar, Hunza, Nubra, Shigar, Ghasting and Drass. It finally originates from the hills near Attock where it meets the Kabul River on its right bank and has five major tributaries – Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej. Let us discuss all these major rivers in detail.
| River | Origin | Length (km) | Major Tributaries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Satluj | Mansarovar-Rakas Lake, Tibet | 1,450 | Right Bank: Spiti, Beas, Chenab |
| Left Bank: Baspa | |||
| Jhelum | Verinag, Pir Panjal Range | 813 | Right Bank: Arpath, Lidder, Neelam, Sindh, Kunhar |
| Left Bank: Poonch, Sukhnag | |||
| Chenab | Bara Lacha Pass, Zaskar Range | 1,180 | Right Bank: Jhelum, Marusudar |
| Left Bank: Ravi, Tawi | |||
| Ravi | Kullu Hills, Rohtang Pass | 725 | Right Bank: Budhil, Tundahan Beljedi, Saho, Siul |
| Left Bank: Chirchind Nala | |||
| Beas | Rohtang Pass, Beas Kund | 460 | Right Bank: Uhel |
| Left Bank: Parvati, Sainj, Larji |
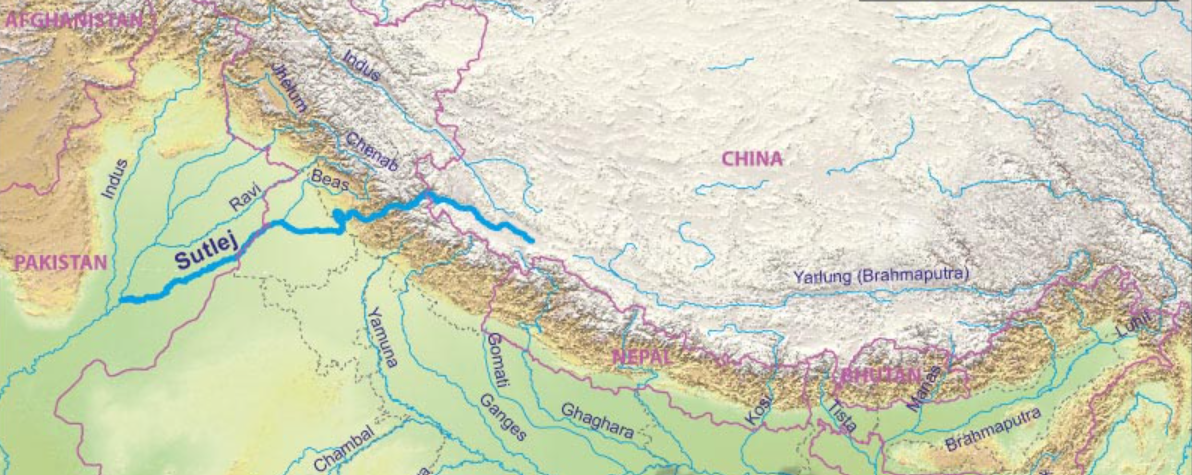
Satluj
The Satluj River originates from the Mansarovar-Rakas Lake near the Darma Pass in Tibet, with a total length of 1,450 km, of which 1,050 km flows in India. The river passes through the Kapurthala district of Punjab and eventually joins the Chenab River. Together, they form the Panjnad, which drains into the Indus River. The right bank tributaries of the Sutlej include the Spiti, Beas, and Chenab rivers, while its left bank tributary is the Baspa River. A major dam in India on the Sutlej River is the Bhakra-Nangal Dam.
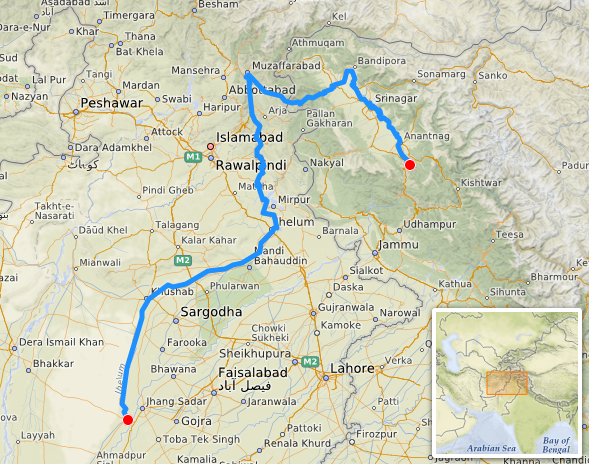
Jhelum
The Jhelum River originates from Verinag in the foothills of the Pir Panjal range. Its right bank tributaries include the Arpath, Lidder, Neelam (Kishanganga), Sindh and Kunhar rivers, while the left bank tributaries include the Poonch and Sukhnag rivers. The Jhelum River flows for a total length of 813 km and merges with the Chenab River.
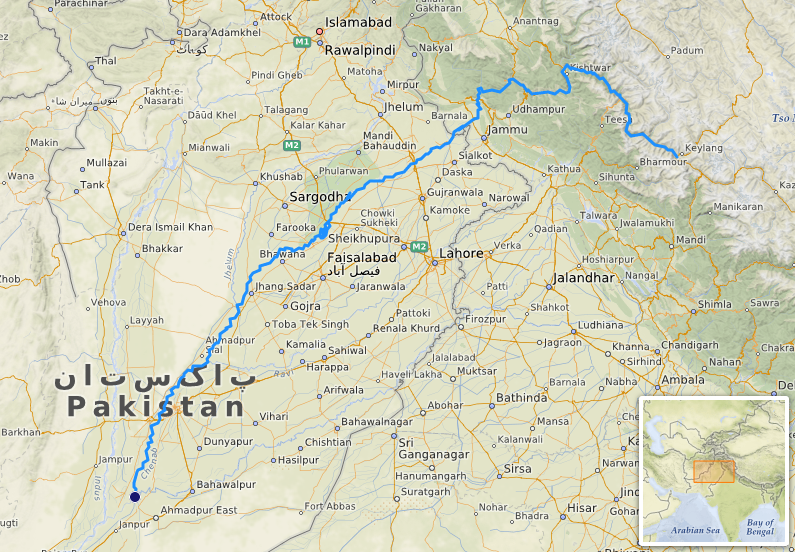
Chenab
The Chenab River originates from the Bara Lacha Pass in the Lahaul-Spiti part of the Zaskar Range and stretches for a length of 1,180 kilometers. It flows through significant areas including the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir and the Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh. The right bank tributaries of the Chenab include the Jhelum and Marusudar rivers, while its left bank tributaries are the Ravi and Tawi rivers. The Baghliar Dam is a major dam built on the Chenab River. The river eventually joins the Sutlej, and together they form the Panjnad, which drains into the Indus River.
Ravi
The river Ravi originates from the Kullu Hills near the Rohtang Pass in Himachal Pradesh. It flows through major areas like Dalhousie in Kangra district and Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh. The important right bank tributaries of the Ravi include the Budhil, Tundahan Beljedi, Saho and Siul rivers, while the left bank tributary is the Chirchind Nala. One of the major dams built on the Ravi River is the Ranjit Sagar Dam, also known as the Thein Dam. The river traverses a length of 725 km and finally merges with the Chenab River.
Beas
The Beas River originates from the Rohtang Pass near Beas Kund in Himachal Pradesh. It passes through important cities like Manali in Himachal Pradesh and Amritsar and Kapurthala in Punjab. The Beas River travels a distance of 460 km and finally falls into the Sutlej River. Its right bank tributary is Uhel, while left bank tributaries include Parvati, Sainj and Larji rivers.
Key Points of Indus River System for UPSC GS 1 and GS 2
- The Indus River system is one of the largest river systems in India and Pakistan, originating from Lake Mansarovar in Tibet.
- The total length of the Indus River in India is 1114 kilometers, and the river stretches for approximately 2,880 kilometers.
- Indus River is one of the major rivers of Asia and the world.
- Indus River is one of the largest river basins in the world, with an area of 11,65,000 square kilometers.
- Its area in India is 321,289 square kilometers and its total length is 2,880 kilometers.
- The region of Punjab, meaning ‘land of five rivers,’ is named after the five major tributaries of the Indus River: Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej.
- Important dams on these rivers include Bhakra-Nangal Dam on Sutlej, Baghliar Dam on Chenab, and Ranjit Sagar Dam on Ravi.
Indus River System UPSC
The Indus River system, one of the major river systems of India and Pakistan, originates from the Mansarovar Lake in Tibet and flows through the Jammu and Kashmir region of India before entering Pakistan and finally merging into the Arabian Sea.
This extensive river system, with a total length of about 2,880 km, includes 1,114 km of stream flowing through India. It includes several important tributaries, including the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas and Sutlej, as well as smaller rivers such as the Shyok, Gilgit, Zanskar, Hunza, Nubra, Shigar, Ghashing and Drass.
Each of these tributaries has different origins and characteristics. For example, the Sutlej River, originating from the Mansarovar-Rakas Lake in Tibet, flows for 1,450 km and hosts the Bhakra-Nangal Dam. The Jhelum river originating from Verinag in the Pir Panjal range merges with the Chenab river after flowing for 813 km. The Chenab river originates from the Bara Lacha pass and stretches for 1,180 km to merge with the Sutlej river, with the Baghliar Dam being an important structure along its route. There are many such tributaries which are important from the point of view of UPSC GS1.
These multifaceted aspects underline the importance of the Indus river system, making it an important topic for UPSC GS1 and GS2.


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





