Table of Contents
The Israel-Palestine conflict was the first matter presented to the United Nations and still has not been resolved which shows how complex this conflict is, this conflict has impacted the world throughout the period from 1946 to present days and will impact until resolved so to be a citizen who is well equipped with the world affairs it becomes important to understand this conflict.
This article with dwell in depth of the Israel-Palestine conflict and will be talking about how the issue started, worlds reaction to the issue, impact on India , present situation and way forward for the peace.
This topic is important for UPSC GS2 and PSIR optional paper
Israel Geography
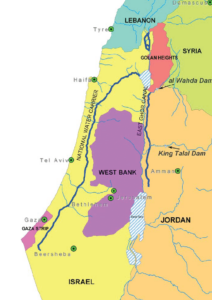
- Israel is a small country and lies in the Asian continent.
- Israel is the only Jewish nation in the world.
- Neighboring countries of Israel include Lebanon and Syria to the north, the West Bank and Jordan to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the west, and Gaza Strip, Egypt, and Red sea to the Sout sh.
- Israel claims Jerusalem as its capital. (Not recognized by India, we will discuss further)
Now that we have clarity on the geography of Israel we should study further about what was here before Israel existed it will help us understand about the Israel-Palestine conflict more clearly.
Before Israel
- Israel came into existence in 1948.
- The land today known as Israel was under control of Britain between 1918-1948
- Before World war 1 this land came under the rule of Ottoman Empire
- When Ottoman empire was defeated in the World War 1 Britain took control of this land.
- In 1890 World Zionist Organization was formed to demand a country for Jews
World Zionist Organization
- Formed in 1890
- Played key role in establishing Israel.
- Formulated the Aliyah Policy.
- Aliyah is a Hebrew word for immigration, of Jewish diaspora to the historic land.(Note: Israel-Palestine Conflict is a complex topic and requires understanding of every fact as every thing goes interconnected, we will explain the term historic land further in the article)
Aliyah Policy
- For historical conflicts many Jewish were forced to leave the Israeli land.
- In the late 19th century only 2-3% of the the Jews lived in the Jerusalem, while 97% Jewish population lived in other countries.
- World Zionist Organization in the initial phase gave reference to the Jews to come back to the historic land, this was particularly on the religious lines.
- First Aliyah (1882-1902) – approximately 35000 Jews came back and immigrated to ottoman palestine.
- Under the Aliyah Policy Jews were offered land for agriculture the revenue of which was shared among them equally.
- First Aliyah was followed by Second Aliyah(1904-1914), Third Aliyah(1919-1923), Fourth Aliyah(1924-1929) and Fifth Aliyah(1929-1939)
- But as we discussed earlier after the defeat of Ottoman Empire in world war 1 ths land was under British control and because of the Aliyah Policy the British feared a rebel from the Muslim population.
- Most of the Aliyah immigrants used the waterways for the travel
- British who feared the rebel from the muslim community started to limit the immigration to the palestine.
Now that we have an idea of the modern history of the land of Israel-Palestine conflict, to understand the reference for the term historic land we will have to dwell in the ancient history for this land, it will help you understand the sentiments of the population and the reason why this was selected as the Jewish state Israel.
Ancient History of Israel Palestine Conflict
- In the sixth century BCE, Jerusalem was conquered by the Babylonians, who took control of Judah.
- The First Temple was destroyed and the Jews were expelled to Babylon.
- In 538 BCE, the Babylonians were conquered by the Achaemenid Empire
- Cyrus, Emperor of Achaemenid Empire allowed the Jews to go back to Judah, where they rebuilt Solomon’s Temple (Second Temple).
- In 70 CE, Solomon’s Temple was destroyed by the Romans.
- Roman Emperor Hadrian expelled all Jews from Jerusalem
- Hadrian renamed Judah to Palaestina with the aim to destroy the presence of Jewish.
- The Solomon’s Temple was a sacred to the Jews.
- When the Romans destroyed the temple in 70 CE, the support wall survived, today it is known as The Western Wall.
You should now be aware of the rationale behind Jewish settlement in the area, which is why this area was designated as historic land for Jews. Moving forward, we will go deeper into the details of World War II and the Israel-Palestine conflict.
World War-II and Israel
- Jewish people during the world war II were brought to the Palestine illegally because of the immigration limit we discussed above.
- This illegal immigration was mainly carried out by the World Zionist Organization and other Jewish communities to rescue the Jews from the Europe Holocaust and other areas of world.
- As this matter got the escalated the matter was handed hover to the newly formed United Nation as we discussed in the beginning.
Formation of Israel
- In 1948, Israel was declared independent by the United Nations.
- David Ben Gurion became the first Prime Minister of Israel.
- UN presented a plan for the partition of Palestine to form Israel.
- The image below shows the Israel map as per the UN plan and today

- Though both Jewish and the Palestine people were not happy with the partition plan.
- The part given to Israel was mostly the desert of Negev Desert, with no permanent settlement.
- With this map the Gaza Strip and West Bank came into the existence, West Bank lies west to the Jordan river that’s why the name comes to be west bank.
- With formation of Israel, war broke out with five Arab states, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan and Egypt invading Israel the very next morning of the formation of Israel.
Now that we have covered the formation of Israel, we will examine Israel’s wars and its foreign relations with other countries. This will help us understand Israel’s expansion and its broader geopolitical context. Additionally, we will study India’s stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict to gain insight into its position and actions regarding the issue.
Isarel-Arab War
- With the formation of Israel, war broke out with five Arab states, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan and Egypt invading Israel the very next morning of the formation of Israel.
- Israeli call this the war of independence
- Palestinian call it as Naqba, when many Palestinians were displaced by the creation of the new state of Israel.
- Many of the Jews had fought in the second world war because of which they had the training and Golda Meir, one of the prominent leader who also became 2nd Prime Minister of Israel, had arranged the the support for Israel after 2nd world war and along with other leaders the weapons for future wars.
- With the above mentioned preparation the newly formed state was able to sustain the attack from 5 states, not only sustained but also defeated them.
- Took control of the portion of Gaza Strip and Golan Heights by defeating Egypt in Gaza Strip and Syria in Golan Heights and Cease Fire was established.
Note – Till 1967 Palestine is not established as a country, because during this war the areas of Gaza Strip came under Egypt Control and West Bank was under Jordan’s control
After the Israel- Arab War the next major event in the Israel and Palestine conflict came up in 1968 with another war, popularly known as the 6 day war.
1968, The Six Day War
- Was primarily fought between Israel and the arab coalition of Egypt, Syria and Jrodan from June 5 to June 10.
- During the Suez Crisis of 1956, Israel invaded Egypt
- Both Egypt and Jordan agreed for the cease fire on 8th June and Syria on 9th June and was signed with the Israel on 11th June.
- With the cessation Israel had seized Syria’s Golan Heights, the Jordanian annexed west bank and Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula.
- Israel established military occupancy in the annexed areas and established settlements in the west bank area, providing tax benefits to settlers.
1973, Yom Kippur War
- This is also known as the Ramadan war or the October War
- The fourth Arab – Israeli war.
- Yom Kippur was being celebrated on 7 October 1973 when the coalition of Egypt, Jordan and Syria attacked the Israel.
- Egypt’s objective was to seize the hold for the Suez canal.
- Majorly the war was fought in the Senai Peninsula and Golan Heights.
- By October 24th with the counter attacks Israel gained a good position and was near both Cairo and Damascus.
- At the 1978 Camp David Accords that followed the war, Israel returned the entire Sinai Peninsula to Egypt
- This devlopment led to the 1979 Israel – Egypt Peace Treaty.
- This was a major turning point in the Israel-Palestine conflict as it was for the first time when an Arab country accepted Israel as a legitimate state.
Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO)
- PLO was formed in 1964.
- After repeated failures from the Arab coalition to establish the Palestine, the locals became active and one of them was the prominent leader of PLO, Yasir Arafat.
- PLO with the frustration for the arab nations carried out operations in the Jordan too.
- PLO had major support from the Lebanon.
- PLO shifted the headquaters to Tunasia in 1982.
OSLO ACCORDS 1993
- With the mediation Oslo I Acoord were signed between Israel and PLO in Washington DC.
- Oslo process began with secret mediation in Oslo and recognition of Isarel by PLO and recognition of PLO as representative of Palestine by Israel.

- Yasir Arafat, Clinton and Yitzhak Rabin in the Washington DC.
- Most notable outcome of the Oslo I Accord was that Palestinian National Authority was created.
- Palestinian National Authority was tasked to establish self governance in areas of west bank and Gaza Strip.
- These accords established PLO as official partner for the Israel-Palestine conflict.
- Oslo I Accord was followed by the Oslo II Accord in Taba, Egypt.
HAMAS, 1987
- HAMAS is acronym for Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiya
- Founded by Palestinian activist Ahmed Yasin in 1987.
- Hamas initially after the Oslo accords was engaged only in terror activities as it was not pleased with the PLO’s decision to recognize Israel.
- In 2006 Hamas won the majority seats in the Plaestinian Legislative elections.
- Hamas took control of the Gaza Strip from the rival faction Fatah.
- Today, Fatah majorly operates in the west bank.
- and Hamas in the West Bank, though the top leadership does not reside in Gaza.
- After Hamas took over Gaza, Israel has intensified the blockades and action at Gaza border.
- This has lead to several wars between Israel and Hamas in 2008-09, 2012, 2014, 2021 and 2023.
- Hamas has often claimed that Israel had attempts attrocities in the Jerusalem region and offers inhuman behavior on the religious lines with muslims visiting to Al Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem.
Now we have had a basic history of the Israel-Palestine conflict and before heading towards understanding about the recent devlopments we should also take account of Israel-India relations and India-Palestine relations.
Israel-India Relations
- In 1947 India voted against the partition plan of Palestine.
- Gandhi and Nehru when asked for the support of Israel, had sympothy for what had happened with Jews in the holocaust but were not in the favor of what Jews were demanding.
- India recognized Israeli soverignty in 1950
- Israel was allowed to open a consulate in Mumbai in 1953.
- India formally established relations with Israel when it opened an embassy in Tel Aviv in January 1992.
- India recognize Tel Aviv as Israel’s capital, not Jerusalem.
- Israel-India Co-operations:
- Israel Supplied India with weapons in the 1971 India-Pakistan war.
- Israel helped India with the logistics in the 1999 Kargil war.
- Both India and Israel are members of I2U2 group.
- Israelicompanies also announced desalination plant for lakshdweep.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi was 1st Indian Prime Minister to visit Israel in 2014.
- As of 2024, India in among Israel’s top 10 trading partner.
India-Palestine Relations
- In 1974, India became the first Non-Arab State to recognize Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole and legitimate representative of the Palestinian people.
- It is said that Yasir Arafat had good relations with India and Indra.
- PLO was allowed to operate a consulate in India
- The major development assistance projects executed successfully by India include:
- Palestine-India Techno-Park
- Construction of Jawaharlal Nehru Library at the Al Azhar University in Gaza city
- The Mahatma Gandhi Library-cum-Student Activity Centre at the Palestine Technical College at Deir Al Balah in the Gaza Strip.
Recent devlopments of Israel-Palestine Conflict
Recently the Israel-Palestine conflict has gained escalations after the attacks of 7th October 2023 and its been about 10 months of the conflict further we will discuss about the recent devlopments in the Israel-Palestine conflict which will include the 7th October attacks, Hostage by Hamas, Israel’s invasion into Gaza, Israel facing resistance from Hezbollah and Houthis, bombing of the Iranian Consulate in Damascus and all the devlopments that have been made so far.
Israel-Hamas war, 2023
- War began when Israel was attacked by the Hamas with thousands of rockets which took lives of many and many were taken as hostage by the Hamas intruders from the Gaza.
- Hamas used the hostages as human shields for evading the Israeli attacks.
- these attacks were commanded and guided by Yahya Sinwar, currently most important leader of Hamas in Gaza.
- Soon Israel invaded the Gaza Strip to eradicate Hamas.
- Hamas attack was condemned at world stage.
- But soon the Israeli invasion to Gaza Strip was also condemned because of civilian killings by Israeli air raids.
- Israel successfully took control of the Gaza and reached the Rafah Border (border of Egypt and Gaza)
- Isarel also Destroyed the bunkers and underground tunnels in Gaza city.
- Philadelphi corridor was also taken over by the Israeli forces in the war, from here only Hamas had launched the rocket attack on Israel.
Major Devlopments of Israel-Hamas War
Below are major events of Israel-Hamas war 2023, it is being seen as a major point in Israel-Palestine conflict.
- Israel as invaded Gaza and made civilian casualities faced a missile attack from Houthi’s in Yemen.
- Houthi also started targeting the Israeli ships in the red sea.
- From the north Israel faced Hezbollah.
- The war has killings of over 113 journalist, most in any war in the world.
- In April 2024, Israel conducted an airstrike in the Damascus and bombarded a building of Iran’s consulate (it had a poster of former IRGC chief Qasim Soleimani) claiming presence Hamas leadership in the building.
- Unfortunately 2 top level commanders of Iran Revolutionary Guards Corp died in this air strike.
- This marked direct entry of Iran into the escalations.
- On the evening of 13 April 2024, Iran launched a drone and missile attack on Israel, most of the missiles and rockets were intercepted and destroyed.
- On 27th July 2024 , a rocket was hit at a football field and 12 Druze children lost their lives while playing in the Majdal Shams, Golan Heights.
- Israel eliminated Mohamed Daif, top Hezbollah leader with airstrikes in Lebanon.
- On 31st July 2024 after the swearing in ceremony of Iran’s president, Ismail Haniyeh, Chief of political wing of Hamas and perhaps the most important leader of Hamas was assassinated in a bomb attack in Iran.
- Israel has not claimed the assassination, but Iran has alleged that Israel was involved in the assassination and Iran has vowed to take the revenge for Ismail Haniyeh.
- Following this most of the countries have stopped the flights towards Israel.
| ALSO READ | |
| The UNSC and Israel-Hamas Conflict | Arab-Israeli War of 1948 |
| India-Israel Relations | India- Israel BIA |



 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





