Table of Contents
The Magadha Empire, which spanned the northern and eastern regions of India, was one of the most significant empires of ancient India. The empire was known for its military might, political astuteness, and cultural richness. This article delves into the history of the Magadha Empire, its rise, family tree, kings, founder, and reasons for its success. We will also take a closer look at the Haryanaka, Sisunaga, and Nanda dynasties, and the last ruler of the Magadha Empire.
Magadha Empire
- The Magadha Empire was an ancient Indian kingdom that existed from the 6th century BCE to the 4th century BCE.
- The empire was known for its military strength and innovation, particularly in the use of elephants in battle.
- The Magadha Empire was ruled by powerful kings like Bimbisara, Ajatashatru, and Mahapadma Nanda.
- The empire expanded its territory and influence by conquering neighboring states.
- The Magadha Empire was an important center of intellectual and spiritual activity, with notable figures like Gautama Buddha and Mahavira.
- The empire’s capital was located at various locations over time, including Rajagriha, Pataliputra, and Magadhapura.
Also Read:- Anglo-Maratha War
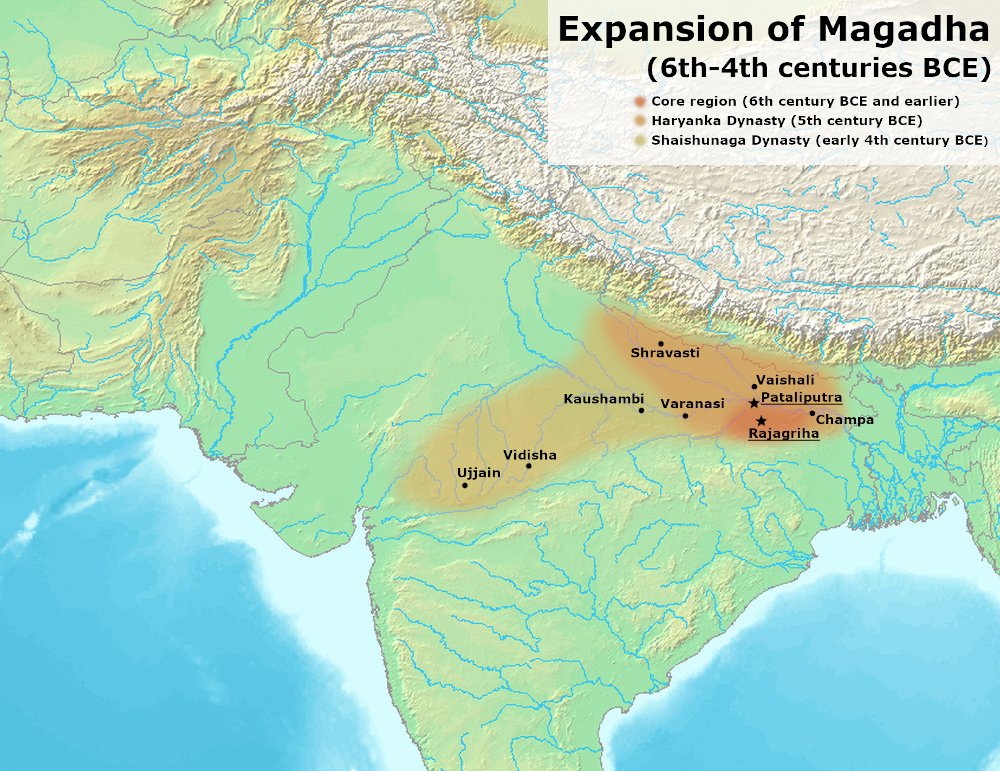
Magadha Empire- Haryanaka Dynasty
The Haryanka Dynasty was an early ruling dynasty of the Magadha Empire, which existed from around 600 BCE to 413 BCE. Here are some key points about the Haryanka Dynasty, along with the names of its rulers:
Bimbisara (558 BC – 491 BC)
Bimbisara was a king of the Magadha Empire who ruled from around 558 BC to 491 BC. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Bimbisara was the founder of the Haryanka Dynasty, an early ruling dynasty of the Magadha Empire.
- Bimbisara is known for his military conquests and strategic alliances, which helped him expand the kingdom and establish Magadha as one of the most powerful states of ancient India.
- He is said to have defeated the neighboring kingdom of Anga and married its princess Chellana as a diplomatic alliance.
- Bimbisara was also a patron of the Buddha, and it is said that he became a follower of Buddhism after meeting the young prince Siddhartha Gautama, who would later become the Buddha.
- He was imprisoned by his son Ajatashatru and died in prison, according to some accounts, though the circumstances of his death are unclear.
- Bimbisara is remembered as one of the most successful and accomplished kings of the Magadha Empire, who laid the foundation for its later greatness.
Read this:- Mauryan Empire
Ajatasatru (492 BC – 460 BC)
Ajatasatru was a king of the Magadha Empire who ruled from around 492 BC to 460 BC. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Ajatasatru was the son of King Bimbisara.
- He is known for his military conquests and his role in expanding the Magadha Empire.
- Ajatasatru defeated his powerful neighbor, the kingdom of Kosala, in a series of wars and established control over a large part of northern India.
- Ajatasatru was a controversial figure, and he is said to have imprisoned and killed his own father in order to gain the throne.
- Despite this, he was known for his patronage of the Buddha and his support for the growth of Buddhism in India.
- Ajatasatru’s reign marked a significant period of expansion and consolidation for the Magadha Empire, and he is remembered as one of its most important kings.
Read Also:- Ashoka Biography
Udayabhadra/Udayin (460 BCE – 444 BCE)
Udayin, also known as Udayabhadra, was a king of the Magadha Empire who ruled from around 460 BCE to 444 BCE. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Udayin was the son of King Ajatasatru and the grandson of King Bimbisara.
- He is known for his role in establishing the city of Pataliputra as the new capital of the Magadha Empire, replacing the previous capital of Rajagriha.
- Udayin is also credited with expanding the kingdom through a combination of military conquests and strategic alliances, including a marriage alliance with the powerful kingdom of Kosala.
- He is said to have commissioned the construction of many public works, including reservoirs and canals, which helped to improve the agriculture and economy of the kingdom.
- Udayin was a patron of the arts and is said to have encouraged the development of literature, music, and dance in his court.
- Despite his many accomplishments, Udayin’s reign was also marked by some controversy, including a rebellion by one of his own ministers, which he was able to suppress.
- Udayin is remembered as an important king of the Magadha Empire, who played a key role in its growth and development during the early years of its existence.
Magadha Empire – Sisunaga Dynasty
The Sisunaga Dynasty was a ruling dynasty of the Magadha Empire that existed from around 413 BCE to 345 BCE. Here are some key points about the dynasty and its rulers:
Sisunaga
Sisunaga was a king who founded the Sisunaga Dynasty and ruled over the Magadha Empire from around 413 BCE to 395 BCE. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Sisunaga is said to have overthrown the previous ruling dynasty of the Magadha Empire, the Haryanka Dynasty, and established himself as the new king.
- According to some accounts, Sisunaga was a minister or adviser to the previous king before he seized power.
- Sisunaga’s reign marked a period of consolidation and expansion for the Magadha Empire, with the king reportedly conquering many neighboring kingdoms and expanding the empire’s territory.
- He is said to have built a new capital city for the Magadha Empire, called Sisunaga, which is now identified with the city of Vaishali in modern-day Bihar, India.
- Sisunaga was succeeded by his son, Kakavarna, who continued his father’s policies of conquest and expansion.
- Despite his significant role in the history of the Magadha Empire, relatively little is known about Sisunaga’s life and reign, and many details about him are based on legend and folklore.
Kalasoka
Kalasoka was a king who ruled over the Magadha Empire. Here are some key points about his life and reign.
- Kalasoka’s reign was marked by conflicts with neighboring kingdoms, including the kingdom of Avanti to the west.
- He is also remembered for his patronage of the arts, particularly the performing arts, and is said to have been a great lover of music and dance.
- According to some accounts, Kalasoka was a cruel and despotic ruler who was unpopular with his subjects, and he was eventually overthrown in a rebellion led by his own ministers.
Magadha Empire – Nanda Dynasty
The Nanda Dynasty was a ruling dynasty of the Magadha Empire that existed from around 345 BCE to 321 BCE. Here are some key points about the dynasty and its rulers:
Mahapadma Nanda
Mahapadma Nanda was the founder and first ruler of the Nanda Dynasty, which ruled over the Magadha Empire from around 345 BCE to 321 BCE. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- He was born to a Sudra woman and the last Sisunaga king. However, certain Jain texts and the Greek writer Curtius suggest that he was the offspring of a courtesan and a barber.
- He is credited with laying the foundations for the highly centralized and bureaucratic administration that would later be developed further by the Mauryan Dynasty.
- Mahapadma Nanda’s reign marked a period of consolidation and centralization for the Magadha Empire, with the king reportedly establishing a highly centralized and powerful administration.
- Under Mahapadma Nanda, the Magadha Empire reportedly became one of the wealthiest in the world, thanks in part to his successful military campaigns and conquests.
- However, Mahapadma Nanda’s reign was also marked by his alleged cruelty and tyranny, with some accounts describing him as a ruthless and despotic ruler.
- Despite his controversial legacy, Mahapadma Nanda played an important role in the history of the Magadha Empire, paving the way for the Nanda Dynasty and the later Mauryan Dynasty that would follow.
Dhana Nanda
Dhana Nanda was an important ruler of the Nanda Dynasty, which ruled over the Magadha Empire in ancient India from around 345 BCE to 321 BCE. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Dhana Nanda was the last Nanda ruler.
- Dhana Nanda refferred to Agrammers or Xandrames in Greek texts.
- During the Dhana Nanda rule, Alexander invaded North-Western India. But Alexander could not proceed towards the Gangetic plains.
Rise of the Magadha Empire
The Magadha Empire rose to prominence in ancient India through a combination of military might, political astuteness, and cultural significance. Here are some key points about the rise of the Magadha Empire:
- The region of Magadha had been inhabited for thousands of years before the rise of the empire, with the earliest known civilization dating back to the 8th century BCE.
- Magadha was ruled by various kingdoms and republics before the rise of the empire, including the Haryanka dynasty and the Shishunaga dynasty.
- The empire was founded by King Bimbisara in the 6th century BCE, who expanded his kingdom through military conquest and strategic alliances.
- Bimbisara was succeeded by his son Ajatashatru, who further expanded the empire’s territory and consolidated its power.
- The empire reached its peak under the rule of King Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, who united most of India under a single political entity.
- The Magadha Empire was known for its innovation in warfare, including the use of elephants and chariots.
- The empire was also an important center of intellectual and spiritual activity, with the emergence of religions like Buddhism and Jainism.
- The fall of the Magadha Empire was marked by invasions from foreign powers like Alexander the Great and the Maurya dynasty, as well as internal conflicts and political instability.
Founder of the Magadha Empire
The founder of the Magadha Empire was Bimbisara, who ruled from 543 BCE to 491 BCE. Here are some key points about his life and reign:
- Bimbisara was a king of the Haryanka Dynasty, which ruled over the Magadha region of ancient India.
- He is said to have been a patron of the Buddha, and there are many stories about his interactions with the famous philosopher.
- Bimbisara was also a skilled military strategist and is said to have expanded the borders of his kingdom through a combination of diplomacy and warfare.
- He established the city of Rajgir as his capital and is credited with building many of its important structures, including the famous Ajatashatru Fort.
- Bimbisara was eventually imprisoned and killed by his own son, Ajatashatru, who is said to have been motivated by a desire for power and a belief that his father had not treated him fairly.
- Despite his untimely death, Bimbisara is remembered as one of the most important figures in the early history of the Magadha Empire, and his legacy continues to be celebrated in India today.
Magadha Empire Family Tree
Here is a family tree of the rulers of the Magadha Empire.
Magadha Empire Kings
Here is a table showing the kings of the Magadha Empire:
| Dynasty | Ruler |
|---|---|
| Haryanka | Bimbisara |
| Haryanka | Ajatashatru |
| Haryanka | Udayin |
| Haryanka | Anuruddha |
| Haryanka | Munda |
| Haryanka | Nagadasaka |
| Shishunaga | Shishunaga |
| Shishunaga | Kalasoka |
| Nanda | Mahapadma Nanda |
| Nanda | Dhana Nanda |
Reasons for Magadha’s Success
The Magadha Empire was one of the most powerful and successful empires in ancient India. There were several reasons for its success, which are outlined below:
- Geographical Advantage: Magadha was located in a strategic position in the Ganges River valley, with access to fertile agricultural land, abundant natural resources, and a strong network of rivers and trade routes.
- Military Strength: The Magadhan army was one of the strongest and most disciplined in ancient India. The empire’s rulers maintained a large and well-trained standing army, which was augmented by a powerful cavalry and an effective system of fortifications.
- Political Stability: The Magadhan rulers were able to maintain a stable and centralized government, which was supported by an efficient bureaucracy and a system of law and order. The rulers also had a keen sense of diplomacy, which helped them to maintain good relations with neighboring kingdoms and empires.
- Economic Prosperity: The Magadhan Empire was known for its economic prosperity and wealth, which was based on a strong agricultural economy, a thriving trade network, and the presence of valuable resources such as gold, silver, and precious stones.
- Religious and Cultural Diversity: The Magadhan Empire was a melting pot of different religious and cultural traditions, which gave it a unique identity and helped it to forge strong ties with neighboring kingdoms and empires.
- Patronage of the Arts and Literature: Magadhan rulers were known for their patronage of the arts and literature, which helped to create a rich cultural legacy for the empire. This patronage also helped to attract talented artists, writers, and scholars to the court of Magadha.
- Innovation and Adaptability: The Magadhan rulers were known for their innovative and adaptable approach to governance, which allowed them to respond quickly to changing circumstances and maintain their position as a dominant power in ancient India.
Magadha Empire Economic
The Magadha Empire was one of the wealthiest and most powerful empires in ancient India, and its economic prosperity played a significant role in its rise and expansion. Here are some key points related to the empire’s economic development:
- The fertile plains of the Ganges River provided the Magadha Empire with abundant agricultural resources, including wheat, rice, and sugarcane, which were grown using advanced irrigation techniques.
- The empire also had rich mineral resources, including iron and copper, which were used to produce weapons and other goods.
- The Magadhan rulers encouraged trade and commerce, and the empire was strategically located on important trade routes that connected it with other regions of India, as well as with Central Asia and China.
- The empire had a well-developed system of roads and canals that facilitated the movement of goods and people, and a sophisticated system of taxation that generated significant revenue for the state.
- The empire also had a vibrant manufacturing sector, with skilled artisans producing goods such as textiles, pottery, and jewelry.
- The use of coins as a medium of exchange was widespread during the Magadhan period, with the empire producing its own coins in gold, silver, and copper.
- The Magadha Empire’s economic prosperity contributed to its military and political dominance, allowing it to finance its armies and maintain its status as a regional power.
Magadha Empire UPSC
The Magadha Empire is an important topic for the UPSC exam as it played a significant role in the history of ancient India. UPSC aspirants should have a good understanding of the empire’s rise, expansion, and decline, as well as the key rulers, their contributions, and the social, economic, and cultural factors that influenced the empire’s growth and development.
- The Magadha Empire was one of the most powerful empires in ancient India, with its capital located in modern-day Bihar.
- The empire is said to have been founded by King Bimbisara, who ruled from around 543 BCE to 491 BCE.
- Bimbisara was succeeded by his son Ajatashatru, who expanded the empire’s territory through conquest and alliances with neighboring kingdoms.
- The Sisunaga dynasty followed Ajatashatru’s rule, and their most notable ruler was King Mahapadma Nanda, who established the Nanda dynasty.
- Under the Nanda dynasty, the Magadhan Empire reached its zenith, with a vast and powerful army, a strong economy, and a well-developed administrative system.
- The empire declined after the death of King Dhana Nanda, due in part to the rise of the Mauryan Empire under the leadership of Chandragupta Maurya.
- The Magadhan Empire was known for its cultural and intellectual achievements, including the spread of Buddhism under the rule of King Ashoka.
- The empire also had a significant impact on the wider political and social context of ancient India, including its relations with neighboring kingdoms and empires.
Check: All UPSC History Notes


 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





