Table of Contents
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory of Motivation- Relevance ESIC Deputy Director Exam
- PART-B of Recruitment Test (RT): Public Administration and Development Issues.
Public Administration- Definition
- Defining Public Administration:
- Public administration is formed by two different terms, public and administration.
- Public: means government which is mainly focus on government activities and actions
- Administration: is derived from the Latin word “Administer” which means to serve, too direct, to control, to care for, or to look after people. The term “administration” means management of public or private affairs.
- Hence, simply public administration is known as the management of public affairs.
- Public Administration is nothing but ‘government in action’. Public Administration is the implementation arm of the executive.
- Public Administration is responsible for the implementation of government policies.
Public Administration- Motivation Theories
Public Administration- Motivation Theories
- Motivation is a state-of-mind, filled with energy and enthusiasm, which drives a person to work in a certain way to achieve desired goals.
- Motivation is a force that persuades a person to work with enhanced commitment and focus even if things are against that person.
- Sustained Motivation often translates into a certain kind of human behaviour.
Importance of Public Administration
Motivation Theories- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory of Motivation
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory is a content-based motivation theory in public administration as it focuses on ‘what’ motivated people in the organization.
- “A Theory of Human Motivation” article was published by Maslow in 1943 through which he introduced his five hierarchy of needs motivation theory.
- According to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory, the individual strives to seek a higher need when lower needs are fulfilled. Once a lower-level need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a source of motivation.
- Maslow believes that needs are motivators only when they are unsatisfied.
Theories of Public Administration- Broad View Perspective
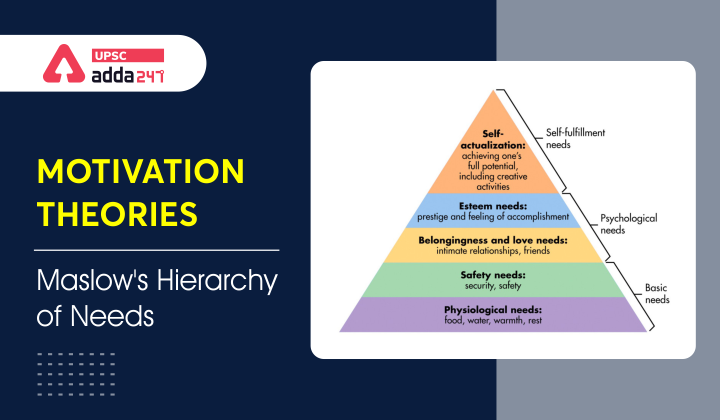
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs- Five Hierarchy of Needs in Ascending Order
- Physiological needs: It includes the most basic needs of humans which are necessary for human survival, such as air, water, and food.
- Safety needs: Safety needs arise only after the Physiological needs of an individual are fulfilled. It includes personal security, health, well-being and safety against accidents, etc.
- Social Needs/ Belonging Needs: It exists at the third level and arises after the first two needs have been fulfilled. This is where people need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance.
- It is about relationships, families and friends. Organizations fulfill this need for people.
- Self-esteem needs: Self-esteem needs comes after the first three needs in the hierarchy if fulfilled. This is where people look to be respected and to have self-respect.
- Self-actualization needs: It exists at the top level. This level of need pertains to doing something that person loves to do irrespective of its economic output or societal approval. Fulfillment of this need gives true happiness to the concerned person.



 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...






