Table of Contents
Relevance of Nuclear Fusion and the Future of Clean Energy for UPSC
Nuclear Fusion and the Future of Clean Energy: Climate change is the biggest problem of today’s world and every successful step towards Nuclear Fusion Energy has a great significance. So, the success of US Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in California is a major milestone and an important progress that every UPSC aspirant need to be aware about it. The Title ”Nuclear Fusion and the Future of Clean Energy” covers GS 3: Environmental Pollution & Degradation, Climate Change, International Treaties & Agreements
Why ”Nuclear Fusion” is in the News?
- A major breakthrough has been announced by US scientists in the race to recreate nuclear fusion.
- The experiment took place at the National Ignition Facility at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in California.
- The amount of energy they’ve generated in this experiment is tiny – just enough to boil a few kettles. But what it represents is huge.

How does the experiment happen?
- The scientists put a tiny amount of hydrogen into a capsule the size of a peppercorn.
- Then a powerful 192-beam laser is used to heat and compress the hydrogen fuel.
- The laser is so strong it can heat the capsule to 100 million degrees Celsius – hotter than the centre of the Sun, and compress it to more than 100 billion times that of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Under these forces the capsule begins to implode on itself, forcing the hydrogen atoms to fuse and release energy.
Also Read:
Analysis Of Down To Earth Magazine: Nuclear Fusion Energy Code
What is nuclear fusion?

- Nuclear fusion is the process which gives the Sun its energy.
- Scientists from more than 50 countries have been trying to recreate it on Earth since the 1960s.
- They hope it could eventually provide huge quantities of clean energy for the world.
- In nuclear fusion, pairs of tiny particles called atoms are heated and forced together to make one heavier one.
- It is the opposite of nuclear fission, in which heavy atoms are split apart. Nuclear power stations currently use nuclear fission to generate electricity.
Also Read:
Homi Jehangir Bhabha: Father of Nuclear Program in India
Why is nuclear fusion is called “holy grail” of energy production ?
- Nuclear fission produces a lot of radioactive waste, which can be dangerous and must be stored safely – potentially for hundreds of years.
- The waste produced by nuclear fusion is less radioactive and decays much more quickly.
- Nuclear fusion doesn’t need fossil fuels like oil or gas. It also doesn’t generate greenhouse gases, which trap the Sun’s heat and are responsible for climate change.
- Most fusion experiments use hydrogen, which can be extracted cheaply from seawater and lithium, meaning fuel supplies could last for millions of years.
- It has been described as the “holy grail” of energy production.
How does nuclear fusion works?
- When two atoms of a light element such as hydrogen are heated and combine to form a single heavier element such as helium, the chemical reaction produces massive amounts of energy which can be captured.
- But getting two identical elements to combine is actually very hard.
- Because they have the same charge – like the positive ends of two batteries – they naturally repel each other.
- A lot of energy is needed to overcome this resistance.
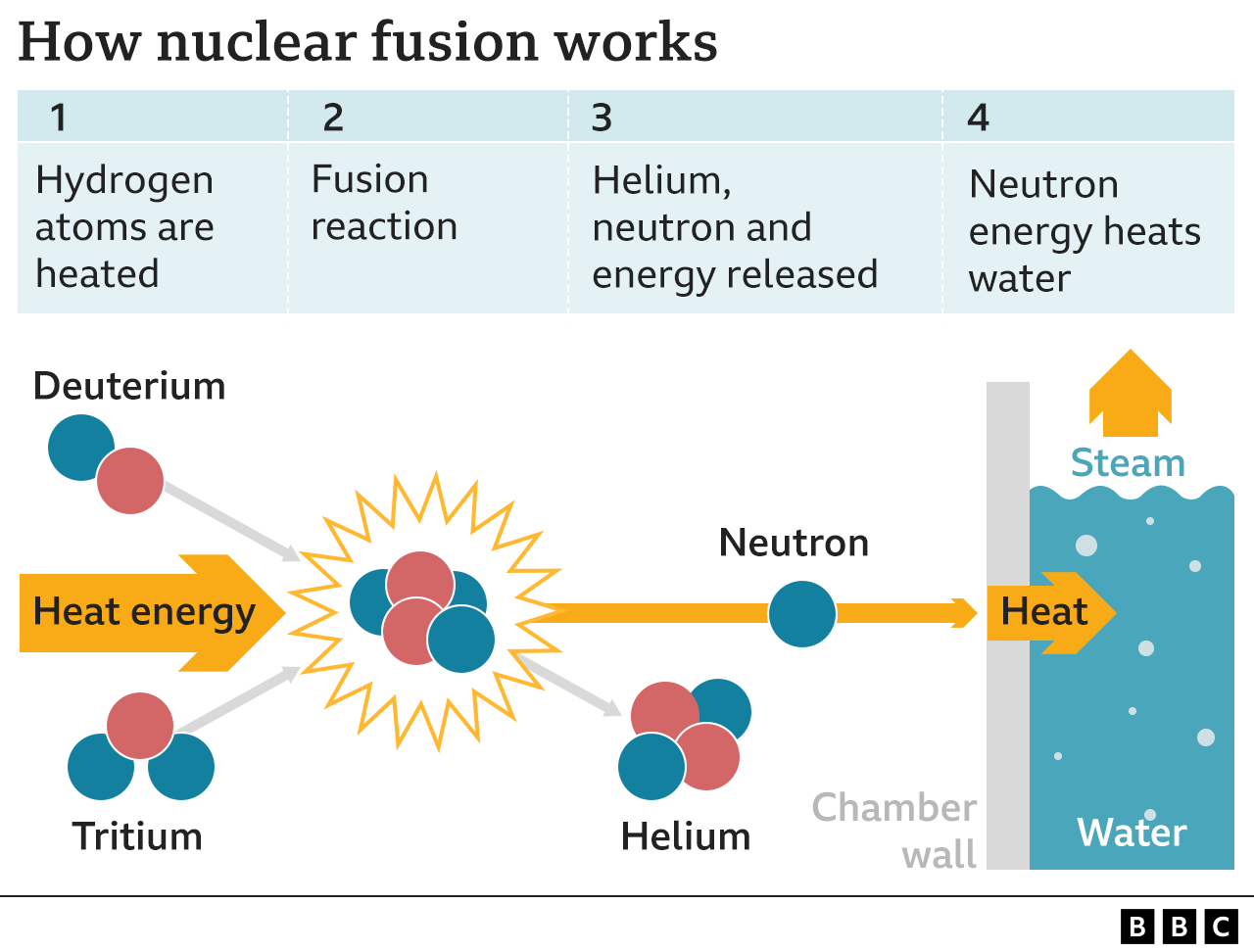
- In the Sun, this happen thanks to extremely high temperatures of around ten million degrees Celsius, and significant pressure – more than 100 billion times that of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- On Earth, scientists have used various different techniques to attempt to recreate these conditions.
- But it has proved very difficult to maintain the high temperature and pressure needed for long enough.
- The US’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) has announced it successfully used a 192-beam laser to turn a tiny amount of hydrogen into enough energy to power about 15 – 20 kettles.
- This means that – for the first time – scientists were able to generate more power than the lasers put in to the experiment.
Also Read:
Analysis of Down to Earth Magazine: Are nuclear power, natural gas green?
Should we consider nuclear fusion a lone weapon to fight Global Warming?
- Nuclear fusion does not rely on fossil fuels like oil or gas, and produces none of the greenhouse gases which drive global warming.
- Unlike solar or wind energy it is not dependent on beneficial weather conditions.
- It uses two relatively abundant materials found on Earth: lithium and hydrogen.
- Widescale use of nuclear fusion could help countries meet their targets to produce “net zero” emissions by 2050.
- However, it will be many years before recent experimental successes can be meaningfully scaled up.
Environment and Ecology current affairs:




 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





