Table of Contents
What is a tax haven country?
- Tax haven meaning: A tax haven— an offshore financial center—is any country or jurisdiction that offers minimal tax liability to foreign individuals and businesses.
- Tax havens do not require businesses to operate out of their country or the individuals to reside in their country to receive tax benefits.
Criteria for tax havens
- In 1998, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) gave a number of factors to identify tax havens.
- Some of the most common factors are given below:
- No, or nominal, tax on relevant income
- Lack of effective exchange of information
- Lack of transparency
- No substantial activities
How governments earn money from tax havens?
- Tax havens are not completely tax-free: These countries charge a lower tax rate than other countries. Low tax jurisdictions generally charge high customs or import duties to cover the losses in tax revenues.
- Fee for new registration: Tax havens may charge a fee for new registration of companies and renewal charges to be paid every year. Additional fees may also be charged such as license fees. Such fees and charges would add up to a recurring fixed income for the tax havens.
- More tax revenues: By attracting foreign individuals or businesses, the country may earn substantially more in tax revenues than it would otherwise.
- Also, the country may benefit from corporate investments in business operations that offer jobs to the country’s residents.
Benefits of a tax haven
- Tax Haven Countries benefit by way of attracting capital to their banks and financial institutions, which can then be used to build a thriving financial sector.
- Individuals or Businesses benefit by saving tax, which in tax haven countries may range from zero to low single digits compared to high taxes in their country of citizenship or domicile.
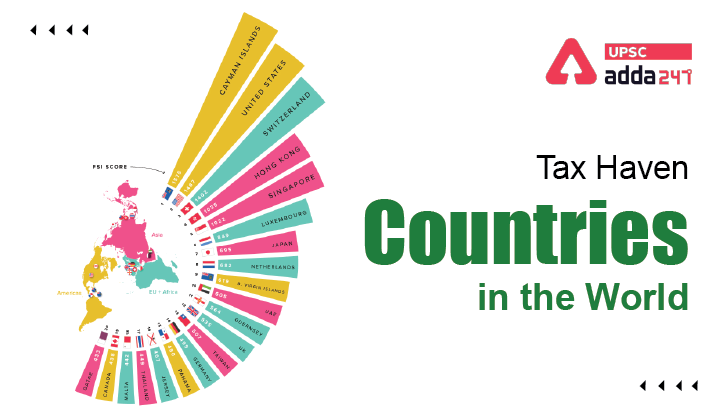
List of tax havens countries in the world
- Bermuda, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Cayman Islands, Singapore, The Channel Islands, Isle of Man, Mauritius, Switzerland, Ireland.
Tax haven countries in the world: Issues
- Escape tax obligations: Secret bank accounts and offshore trusts in tax havens provide wealthy elites and companies with the mean to escape their tax obligations.
- Unfair competitive advantage: Multinationals’ ability to substantially lower their tax burden by routing capital flows through mailbox companies in tax havens provides them with unfair competitive advantages vis-à-vis their – often smaller – competitors in developing countries.
- Money laundering: Banking secrecy and offshore trusts offered by financial institutions in tax havens make it possible to launder the proceeds of political corruption, illicit arms deals, and other crimes.
- Financial crisis: Tax havens have contributed to the rising incidence of financial crisis that can destroy livelihoods in poor countries.
Read current affairs for UPSC




 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...






