Table of Contents
Banda Singh Bahadur
In News
National Monuments Authority(NMA) released ‘Banda Singh Bahadur Martyrdom Monument Poster’, ahead of his 306th Martyrdom Day on 9th June in New Delhi.
About Baba Banda Singh Bahadur
- He was a great warrior to defend India and defeat the Mughals.
- His original name was Baba Madhav Das and he was a Bairagi Sadhu.
- Baba Banda Singh Bahadur aimed at the National awakening and Liberation of the country from the oppressive rule of the Mughals.
- Though Independence came to India much later, it was Baba Banda Singh Bahadur who first taught the Indians to fight, conquer and establish their independent rule.
- Baba Banda Singh Bahadur and his son Ajai Singh were martyred on 9 June, 1716 A.D. along with his other 18 companions near a gate en-route the tomb of so-called Sufi saint Qutub-ud-din Bakhtiar kaki at Mehrauli.
- The butchers first killed his son Ajai Singh in his lap. But Banda Bahadur remained unmoved and sat in a composed state. After that Baba Banda Singh Bahadur’s cruelly martyred.
- His glorious martyrdom validates Bhagat Kabir’s rendition in Guru Granth Sahib.
eSanjeevani
In News
‘eSanjeevani’, Govt. of India’s free Telemedicine service integrated with NHA’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
About eSanjeevani
- The National Health Authority (NHA) announces the successful integration of eSanjeevani with its flagship scheme – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- This integration allows the existing users of eSanjeevani, the telemedicine service of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) to easily create their Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) and use it to link and manage their existing health records like prescriptions, lab reports, etc.
- The users would also be able to share their health records with doctors on eSanjeevani which will help in better clinical decision making and ensuring the continuum of care.
- ABDM aims to build digital highways to bridge the gaps in existing digital health solutions and stakeholders in India. The integration of eSanjeevani with ABDM is one such example where the 22 crore ABHA holders can link and store their health records created via eSanjeevani directly in the health lockers of their choice.
- The users can also share their previously linked health records with the doctors on eSanjeevani making the entire consultation process paper-less.
- Two Variants:
- eSanjeevani service is available in two variants. The first one is eSanjeevani Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centre (AB-HWC) – the Doctor-to-Doctor telemedicine service through which the beneficiaries visiting a HWC can virtually connect to doctors/ specialists in the Hub that could be at tertiary healthcare facility/hospital/medical college. This enables the government to provide general and specialised health services in rural areas and isolated communities.
- The second variant, eSanjeevani OPD is serving patients across the country, connecting them directly to doctors from the comforts of their homes. Both versions – eSanjeevani AB-HWC and eSanjeevani OPD have been integrated with ABDM platform.
Vision India @2047
In News
Dr Jitendra Singh said that emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), blockchain, drones, Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, 3D printing and virtual reality (VR) are going to have a huge impact on all aspects of life including governance.
About Vision India @ 2047
- India@2047 is a vision plan for a ‘future-ready India’ that befits the 100th year of Indian Independence.
- An exercise to envision India@2047 is being undertaken by the Government of India under the rubric of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav to meet the following aspirations:
- Attaining new heights of prosperity of the country
- Making best facilities available both in the villages and the cities
- Eliminating unnecessary interference by the Government in the lives of citizens
- Building world’s most modern infrastructure.
- In this regard, the many themes have been identified for rural development sectors in which action need to be taken.
- 25 Year Target: The Centre also wants to start right away on the 25-year targets.
- The key areas: Identified so far include agriculture, commerce & industry, infrastructure and urban landscape, security & defence, technology and governance.
- The first set of suggestions on the table is: Freeing up India’s defence acquisitions from foreign reliance and a road map for ‘India’s place in the world in 2047’.
- On the industry side, restructuring and merger of public sector banks and creation of 3 or 4 big banks is being looked at.
- Similarly, developing 3 or 4 global champions in each sector, including oil and gas sector by merger or restructuring of companies, developing semi-conductor complexes and making India a hub and leader in green technology and skilling are ideas under discussion.
National Monuments Authority
About NMA
- National Monuments Authority (NMA) under the Ministry of Culture, Govt. of India has been setup as per provisions of The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains AMASR (Amendment and Validation) Act, 2010 which was enacted in March, 2010.
- Several functions have been assigned to the NMA for the protection and preservation of monuments and sites through management of the prohibited and regulated area around the centrally protected monuments.
- One amongst these responsibilities of NMA is also to consider grant of permissions to applicants for construction related activity in the prohibited and regulated area.
- With increase of urbanization, development, growth and increasing population pressure, there is growing pressure on land including the land around centrally protected monuments.
- As this often affects the monument/site adversely it is important that such growth around the centrally protected monuments is properly regulated, balancing the needs of individuals and growth and development on the one hand and the requirements of preservation and protection of these monuments on the other.
- These provisions underwent a change in 2010 following the Amendment to the AMASR Act. The NMA and the Competent Authorities (CA) were setup and now all applications for construction related work in the prohibited and regulated area are to be submitted to the CA and then to NMA for consideration of the application.
Alarming Global Food Crisis
Introduction
- Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine on February 24, the number of countries imposing export restrictions on food has risen from three to 17.
- Current trade restrictions due to the war affect nearly 36 per cent of wheat exports, 55 per cent of palm oil, 17.2 per cent of corn, 78.2 per cent of sunflower oil exports, and 5.8 per cent of soybean oil.
- On May 5, the government of India also stopped wheat purchase from Punjab, procuring only 56 per cent of its target of 44 million tonnes. When the wheat stock dwindled, the government replaced 5.5 million tonnes of wheat with rice for its pandemic relief programme, the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana.
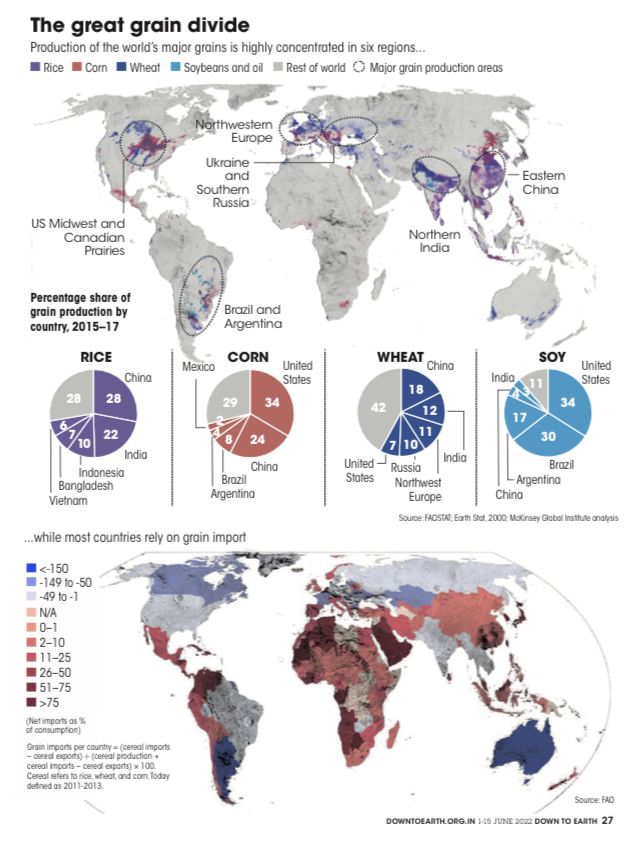
Importance Of Black Sea Region For Global Food Chain
- The Black Sea region, which includes Russia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan, is one of the world’s six food baskets.
- Russia is the world’s largest wheat exporter while Ukraine is sixth on the list.
- Together, the two warring countries produce 12 per cent of all food calories traded globally; control 29 per cent of global wheat exports, 19 per cent of maize exports, and 78 per cent of sunflower oil exports.
- Russia is also the world’s top exporter of nitrogen fertilisers, the second leading supplier of potassium fertilisers and the third largest exporter of phosphorus fertilisers.
- Some 50 countries depend on Russia-Ukraine for their food supply, particularly for wheat, maize and sunflower oils.
- The majority of these are poor and import-dependent countries in Asia and Africa. Of the 53 countries or ter- ritories that faced food crisis last year, 36 depended on Ukrainian and Russian exports for more t han 10 per cent of their total wheat imports, as per an analysis by Washington DC-based International Food Policy Research Institute (ifpri).
- In terms of food supply, in 2019 wheat and wheat products represented 408 kilocalories per capita per day in the countries facing food crisis.
- In east Africa, where wheat and wheat products account for a third of the average cereal consumption, 90 per cent of the wheat imports come from Russia and Ukraine, as per UN’s World Food Programme (wfp).
Three Dimensional Crisis
- A preliminary assessment by the UN Task Team for the Global Crisis Response Group says the war has led to a “three-dimensional” crisis—rising food prices, rising energy prices and tightening finance.
- Some 1.7 billion people in 107 countries (41 in Africa, 38 in Asia and the Pacific and 28 in Latin America and the Caribbean) are exposed to at least one of the dimension.
- Some 69 economies with 1.2 billion of the world’s people are “severely or significantly” exposed to the three-dimensional crisis.
- Consequently, thousands of kilometres from the war zone, some 70 per cent of Africa’s economies are at risk of collapsing, putting millions on the verge of food scarcity.
- Egypt, for instance, depends on Ukraine and Russia for 60 per cent of its food imports. Its food inflation rose to 26 per cent in April.
- Angola—a country that does not produce wheat traditionally but consumes 0.65 million tonnes of it annually—meets 30 per cent of its demands from Russia-Ukraine. With the war curbing supply, wheat price at the consumer level has increased by 40 per cent.
- Lebanon, a country that has not registered growth in the last four years, sources up to 25 per cent of its average calorie consumption from wheat and sunflower oil imported from Russia-Ukraine.
Uncertainties in Near Future
- In the immediate future, the overall global availability of foodgrains will be further reduced.
- The rise in prices of energy and fertilisers is likely to reduce yield, as per ifpri’s report.
- The fertiliser shortfall comes at the start of planting seasons in many countries, including India.
- As countries substitute the commodities that are in short supply with others, the prices of the substitutes will go up. For example, rice is being used to fill the gap in cereal imports, and its price has increased by 12 per cent globally since the beginning of the year.
- As countries start sourcing food, fuel and fertilisers from countries other than Russia and Ukraine, it will add to the overall costs, ultimately adding to the cost of the produce.
Conclusion
The current crisis has shown us the true character of a “globalised world” with countries already resorting to hoarding staple foods that till recently exported for profits.
eSanjeevani Integrated with ABDM
Relevance
- GS 2: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
eSanjeevani telemedicine: Context
- Recently, National Health Authority (NHA) announces the successful integration of eSanjeevani with its flagship scheme – Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
eSanjeevani and ABDM mission: Key points
- This integration allows the existing users of eSanjeevani to easily create their Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) and use it to link and manage their existing health records like prescriptions, lab reports, etc.
- The users would also be able to share their health records with doctors on eSanjeevani which will help in better clinical decision making and ensuring the continuum of care.
What is eSanjeevani?
- eSanjeevani is a telemedicine service of the telemedicine service of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- eSanjeevani service is available in two variants:
- eSanjeevani Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centre (AB-HWC): It is a Doctor-to-Doctor telemedicine service under Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centres scheme of the Government of India, to provide general and specialised health services in rural areas and isolated communities.
- eSanjeevaniOPD: This is a patient-to-doctor telemedicine service to enable people to get outpatient services in the confines of their homes. ‘eSanjeevaniOPD’ has also been speedily and widely adopted by citizens in all parts of the country. It is available as a mobile app for both Android and iOS based smart phones, and these apps have seen over 3 million downloads.
- eSanjeevaniOPD now enables creation of Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA), which will facilitate access and shareability of health data with consent of the beneficiary, with participating healthcare providers and beneficiaries as per Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
eSanjeevani significance
- eSanjevani was initially launched amid the COVID 19 pandemic to enable patient to doctor tele-consultation.
- Offered at no cost, eSanjeevani app has made it convenient for the people to avail of the health services without having to travel to any hospital.
- The telemedicine includes many specialty OPDs such as Psychiatry, Gynecology, Non-Communicable Disease (NCD), Pediatrics, Oncology etc.
- This is very useful for the people in the rural areas who don’t have easy access to medical specialists located in cites.
What is Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission?
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aims to create a seamless online platform through the provision of a wide-range of data, information and infrastructure services, duly leveraging open, interoperable, standards-based digital systems while ensuring the security, confidentiality and privacy of health-related personal information.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission aims to connect the digital health solutions of hospitals across the country with each other.
- Under this program, every citizen will now get a digital health ID and their health record will be digitally protected.
- The mission was first implemented on a pilot basis in six Union Territories—Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, and Puducherry.
- After the successful demonstration of technology platform developed by the NHA, the cabinet has rolled out its nationwide implementation.
- The initiative is designed to benefit the poor and middle class, specifically in finding the right doctor and a hospital.
SHRESHTA scheme
Relevance
- GS 2: Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes.
SHRESHTA Scheme: Context
- Recently, Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment has launched a new scheme SHRESHTA for residential education for students in High school in Targeted Areas.
SHRESHTA Scheme: Key points
- SHRESHTA full form: Scheme for Residential Education for Students in Targeted Areas
- The Scheme will be beneficial for SC students those who could not reach for higher quality education.
- SHRESHTA has been formulated with the objective to provide quality education and opportunities for even the poorest Scheduled Caste students.
- The SHRESHTA scheme has been launched to provide quality education in top class private Residential Schools to the meritorious SC students who cannot afford the fee of such schools.
About SHRESHTA scheme
- SHRESHTA provides for high quality education for meritorious but poor SC students in CBSE-affiliated reputed residential schools across the country.
- Approximately 3,000 seats are provided each year for admission in class 9th and 11th and the entire cost of the school fee and residential charges are borne by the Department.
- The students, belonging to Scheduled Castes, studying in class 8th and 10th in the current academic year are eligible for availing the benefits of scheme are selected through a transparent mechanism through a National Entrance Test for SHRESHTA (NETS), which is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for admission in class 9th and 11th.
- Students belonging to marginalized income group within the SC community, whose parental annual income is up to Rs.2.5 Lakh are eligible.
- Successful candidates, after following the e-counselling process, are given admission in the school of their choice anywhere in the Country for their academic persuasion.
- The Department shall bear the total cost of the school fee and hostel charges till completion of their academic up to class 12th. There after the students of the scheme may avail benefits of other schemes of the Department for their higher education.



 TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Question Paper 2024, Downl...
 TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
TSPSC Group 1 Answer key 2024 Out, Downl...
 UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...
UPSC Prelims 2024 Question Paper, Downlo...





